深度学习之 python pandas
在数据科学领域,pandas是非常有用的工具,在数据科学细分领域大数据(通常和深度学习有关)这部分,本篇博客从pandas重要函数开始,到数据变换以及数据分析。pandas提供了数据变换、数据清理、数据可视化以及数据提取等主要数据处理功能。本篇使用的博客python版本是:
#!/usr/local/bin/python3
# Copyright 2022 shichaog
import platform
print(platform.python_version())
输入:
3.8.7
pandas基础
python中使用pandas需要import该模块,使用import pandas as pd,dataframe是pandas中最常用的一种数据格式,股票数据、超市百货商店交易数据等很多都可以用dataframe表示。dataframe的创建如下:
#!/usr/local/bin/python3
# Copyright 2022 shichaog
import pandas as pd
Speeds={'Animal': ['Falcon', 'Falcon',
'Parrot', 'Parrot'],
'MaxSpeed': [380., 370., 24., 23.0]}
df = pd.DataFrame(Speeds)
print(df)
其输出是一张表,如下:
Animal MaxSpeed
0 Falcon 380.0
1 Falcon 370.0
2 Parrot 24.0
3 Parrot 23.0
上述代码中Speeds是一个字典,Animal 和MaxSpeed是key值,其后list是对应的value值,0,1,2,3是索引值,用于dataframe的索引,可以用于检索、查询、修改、删除等操作。
如果想获取一列值,则只需要dataframe名其后加中括号,中括号中写入列名就行,如下所示:
#!/usr/local/bin/python3
# Copyright 2022 shichaog
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'Animal': ['Falcon', 'Falcon',
'Parrot', 'Parrot'],
'MaxSpeed': [380., 370., 24., 23.0]})
#下一行的等价写法是:print(df.MaxSpeed)
print(df['MaxSpeed'])
输出为:
0 380.0
1 370.0
2 24.0
3 23.0
pandas还可以增加列,筛选等操作:
#接上df
#增加一列
df['Size'] = [16., 60., 25., 40.]
print(df)
输出为:
Animal MaxSpeed Size
0 Falcon 380.0 16.0
1 Falcon 370.0 60.0
2 Parrot 24.0 25.0
3 Parrot 23.0 40.0
#筛选过滤
print(df[df['Size'] >= 40.0])
输出为:
Animal MaxSpeed Size
1 Falcon 370.0 60.0
3 Parrot 23.0 40.0
除了自己构建dataframe之外,还可以读入已有的一些文件格式,比如csv、xsl等,iris.csv是常用于深度学习的kaggle开源数据集iris数据集地址,使用pd.read_csv方法即可。pandas dataframe的基本用法如下:
#!/usr/local/bin/python3
# Copyright 2022 shichaog
import pandas as pd
iris = pd.read_csv('iris.csv')
#数据样本信息
print(iris.shape)
输出:
(150, 5)
#样本实例
print(iris.head(5))
print(iris.tail(5))
输出:
sepallength sepalwidth petallength petalwidth class
0 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
2 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 Iris-setosa
3 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 Iris-setosa
4 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
sepallength sepalwidth petallength petalwidth class
145 6.7 3.0 5.2 2.3 Iris-virginica
146 6.3 2.5 5.0 1.9 Iris-virginica
147 6.5 3.0 5.2 2.0 Iris-virginica
148 6.2 3.4 5.4 2.3 Iris-virginica
149 5.9 3.0 5.1 1.8 Iris-virginica
#数据类型
print(iris.dtypes)
输出:
sepallength float64
sepalwidth float64
petallength float64
petalwidth float64
class object
dtype: object
#数据取子集,选择3,,4,,5三个行,行索引从0开始
print(iris.loc[3:5])
输出:
sepallength sepalwidth petallength petalwidth class
3 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 Iris-setosa
4 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
5 5.4 3.9 1.7 0.4 Iris-setosa
#相比上面,增加了列,信息,列可以是列名,也可以是列所以,如果是是列索引值,则需要使用iloc
#下面两个作用等同,都是选取3行0列所在位置的值
print(iris.loc[3, 'sepallength'])
print(iris.iloc[3,0])
输出:
4.6
4.6
#数据导出为csv
iris.to_csv('iris-out.csv', index=False)
此外pandas还有对异常数据的一些处理方法,这放到后续小节。
pandas数据计算
数据类型转换
这里以nasa的行星数据为例,
#!/usr/local/bin/python3
# Copyright 2022 shichaog
import pandas as pd
planets = pd.read_csv('planets.csv')
print(planets.head(3))
输出
method number orbital_period mass distance year
0 Radial Velocity 1 269.300 7.10 77.40 2006
1 Radial Velocity 1 874.774 2.21 56.95 2008
2 Radial Velocity 1 763.000 2.60 19.84 2011
print(planets.dtypes)
输出
method object
number int64
orbital_period float64
mass float64
distance float64
year int64
dtype: object
#获取均值,所有结果都是浮点数
print(planets.mean())
输出
number 1.785507
orbital_period 2002.917596
mass 2.638161
distance 264.069282
year 2009.070531
dtype: float64
#整数除以浮点数,结果是浮点数
print(planets['number'][0]/planets['mass'][0])
输出
0.14084507042253522
#使用astype强制类型转换,将整数类型转换为浮点数类型
print(planets['number'][0].astype(float))
输出
1.0
#强制类型转换,将浮点数转换为整数
print(planets['mass'][0].astype(int))
输出
7
planets['year'][0].astype(str)
输出
‘2006’
planets['year_dt'] = pd.to_datetime(planets['year'], format='%Y')
print(planets['year_dt'])
输出
0 2006-01-01
1 2008-01-01
2 2011-01-01
3 2007-01-01
4 2009-01-01
...
1030 2006-01-01
1031 2007-01-01
1032 2007-01-01
1033 2008-01-01
1034 2008-01-01
Name: year_dt, Length: 1035, dtype: datetime64[ns]
字符串类型
在pandas中,.str是字符串的存取器,其提供了大量的字符串操作方法。
#!/usr/local/bin/python3
# Copyright 2022 shichaog
import pandas as pd
names = pd.Series([' github; Shichaog','csdn; Shichaog'])
#字符串替换,将;替换成/
names = names.str.replace(';','/')
print(names)
#字符串长度获取
print(names.str.len())
#删除字符串前的前导空格
names = names.str.strip()
print(names)
print(names.str.len())
#字符串大小写转换,.lower是大写转小写
names = names.str.upper()
print(names)
#按;分割series为list
names = names.str.split('; ')
print(names)
#::-1是list索引方法
names = pd.Series([i[::-1] for i in names])
print(names)
#jion方法连接单词
names = [' '.join(i) for i in names]
print(names)
日期数据处理
#!/usr/local/bin/python3
# Copyright 2022 shichaog
import pandas as pd
#构建日期period_range生成日期series,第一个参数是起始日期,第二个参数生成频率
daterange = pd.period_range('1/1/2020', freq='30d', periods=4)
date_df = pd.DataFrame(data=daterange,columns=['sample date'])
print(date_df)
输出:
sample date
0 2020-01-01
1 2020-01-31
2 2020-03-01
3 2020-03-31
#日期差异,使用diff,period是比较周期,在股票趋势派交易中常会比较均线和股价的上下穿关系,也常用到diff
date_df['date difference'] = date_df['sample date'].diff(periods=1)
print(date_df)
输出:
sample date date difference
0 2020-01-01 NaT
1 2020-01-31 <30 * Days>
2 2020-03-01 <30 * Days>
3 2020-03-31 <30 * Days>
#查询该月第一天
date_df['first of month'] = date_df['sample date'].values.astype('datetime64[M]')
print(date_df)
输出:
sample date date difference first of month
0 2020-01-01 NaT 2020-01-01
1 2020-01-31 <30 * Days> 2020-01-01
2 2020-03-01 <30 * Days> 2020-03-01
3 2020-03-31 <30 * Days> 2020-03-01
#数据类型
print(date_df.dtypes)
输出:
sample date period[30D]
date difference object
first of month datetime64[ns]
dtype: object
date_df['sample date'] = date_df['sample date'].dt.to_timestamp()
print(date_df.dtypes)
输出:
sample date datetime64[ns]
date difference object
first of month datetime64[ns]
dtype: object
#数据相减
date_df['sample date'] - date_df['first of month']
date_df['sample date'] - date_df['date difference']
date_df['sample date'] - pd.Timedelta('30 d')
#使用dt获取更多属性
date_df['sample date'].dt.day_name()
错误数据处理
未经过清理的数据会有错误、缺失等,据统计,通常在数据清理在整个项目中通常需要花费80%-90%时间,pandas和python提供了一些数据清理方法,可以大大节省数据清理所需的时间
数值错误
对于数值类的数据,如成交量之类,有数值丢失、数值错误以及数据重复三种类型错误可能发生。
pandas.isnull可用于判别数据缺失的情况,如下的array使用nan初始化时是一个缺失的值,这时可以使用该方法判断。
#!/usr/local/bin/python3
# Copyright 2022 shichaog
>>>array = np.array([[1, np.nan, 3], [4, 5, np.nan]])
>>>array
array([[ 1., nan, 3.],
[ 4., 5., nan]])
>>>pd.isna(array)
array([[False, True, False],
[False, False, True]])
>>>index = pd.DatetimeIndex(["2017-07-05", "2017-07-06", None,
"2017-07-08"])
>>>index
DatetimeIndex(['2017-07-05', '2017-07-06', 'NaT', '2017-07-08'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq=None)
>>>pd.isna(index)
array([False, False, True, False])
>>>df = pd.DataFrame([['ant', 'bee', 'cat'], ['dog', None, 'fly']])
>>>df
0 1 2
0 ant bee cat
1 dog None fly
>>>pd.isna(df)
0 1 2
0 False False False
1 False True False
此外也可以使用dropna()等方法去掉非数值的行/列,或者fillna()方法设置为某个值。
异常值
这种类型的值是超出了正常范围,比如cpu的使用率、汽车速度、人类的身高、体重等数据都是有一个合理范围的,这比较符合统计学里的正太分布。
#!/usr/local/bin/python3
# Copyright 2022 shichaog
import pandas as pd
#这里的1000和1.0是两个异常值
df = pd.DataFrame({'Animal': ['Falcon', 'Falcon','Falcon', 'Falcon', 'Falcon',
'Parrot', 'Parrot', 'Parrot', 'Parrot', 'Parrot'],
'MaxSpeed': [380., 370., 330., 1000, 320, 24., 26., 23.0, 1.0, 25.0]})
#查看数据统计信息
print(df.groupby('Animal').describe())
输出:
MaxSpeed
count mean std min 25% 50% 75% max
Animal
Falcon 5.0 480.0 291.804729 320.0 330.0 370.0 380.0 1000.0
Parrot 5.0 19.8 10.568822 1.0 23.0 24.0 25.0 26.0
#统计样本数
print(df['Animal'].value_counts())
输出
Falcon 5
Parrot 5
#见下图所绘制
pd.pivot(df, columns='Animal').plot(subplots=True)
#通过以下句子筛选错误值
print(df.query('Animal=="Falcon" & ( MaxSpeed > 400.)'))
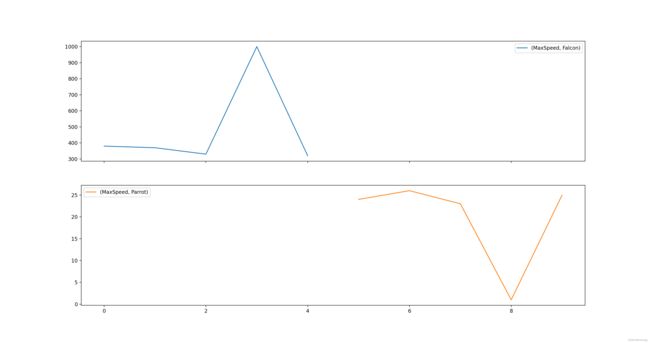 从上图可以看到明显有两个值远远超出了平均值,这种值往往需要预先处理掉再训练模型。
从上图可以看到明显有两个值远远超出了平均值,这种值往往需要预先处理掉再训练模型。
apply & map
pandas dataframe值修改时可以通过apply以及map等函数提供的方法,这类的方法的好处是不再需要使用其它语言类似for/loop之类的语句。
#!/usr/local/bin/python3
# Copyright 2022 shichaog
import pandas as pd
#read in apple stock info
apple_df = pd.read_csv('../AAPL Historical Data.csv')
该df的输出如下,其是一个股票的daily交易信息,包括日期、收盘价、开盘价以及成交量和换手率等。
Date Price Open High Low Vol. Change %
0 Jul 19, 2022 151.00 147.98 151.20 146.92 82.15M 2.67%
1 Jul 18, 2022 147.07 150.84 151.54 146.74 77.54M -2.06%
2 Jul 15, 2022 150.17 149.78 150.86 148.20 76.26M 1.15%
3 Jul 14, 2022 148.47 144.08 148.95 143.25 78.14M 2.05%
4 Jul 13, 2022 145.49 142.99 146.45 142.12 71.19M -0.25%
5 Jul 12, 2022 145.86 145.76 148.45 145.05 77.59M 0.68%
6 Jul 11, 2022 144.87 145.67 146.64 143.78 63.31M -1.48%
7 Jul 08, 2022 147.04 145.26 147.55 145.00 64.30M 0.47%
8 Jul 07, 2022 146.35 143.29 146.55 143.28 65.73M 2.40%
9 Jul 06, 2022 142.92 141.35 144.12 141.08 73.55M 0.96%
10 Jul 05, 2022 141.56 137.77 141.61 136.93 70.95M 1.89%
11 Jul 01, 2022 138.93 136.04 139.04 135.66 71.05M 1.62%
12 Jun 30, 2022 136.72 137.25 138.37 133.77 98.63M -1.80%
13 Jun 29, 2022 139.23 137.46 140.67 136.67 65.98M 1.30%
14 Jun 28, 2022 137.44 142.13 143.42 137.32 66.75M -2.98%
15 Jun 27, 2022 141.66 142.70 143.49 140.96 70.21M 0.00%
16 Jun 24, 2022 141.66 139.90 141.91 139.77 88.44M 2.45%
17 Jun 23, 2022 138.27 136.82 138.59 135.63 72.11M 2.16%
18 Jun 22, 2022 135.35 134.79 137.76 133.91 73.12M -0.38%
19 Jun 21, 2022 135.87 133.42 137.06 133.32 80.68M 3.28%
#drop uncessary
apple_df=apple_df.drop(columns=['Open', 'High', 'Low', 'Vol.', 'Change %'])
#reverse and calculate Moving Average
apple_df = apple_df.iloc[::-1]
apple_df['SMA3'] = apple_df['Price'].rolling(3).mean()
Date Price SMA3
19 Jun 21, 2022 135.87 NaN
18 Jun 22, 2022 135.35 NaN
17 Jun 23, 2022 138.27 136.496667
16 Jun 24, 2022 141.66 138.426667
15 Jun 27, 2022 141.66 140.530000
14 Jun 28, 2022 137.44 140.253333
13 Jun 29, 2022 139.23 139.443333
12 Jun 30, 2022 136.72 137.796667
11 Jul 01, 2022 138.93 138.293333
10 Jul 05, 2022 141.56 139.070000
9 Jul 06, 2022 142.92 141.136667
8 Jul 07, 2022 146.35 143.610000
7 Jul 08, 2022 147.04 145.436667
6 Jul 11, 2022 144.87 146.086667
5 Jul 12, 2022 145.86 145.923333
4 Jul 13, 2022 145.49 145.406667
3 Jul 14, 2022 148.47 146.606667
2 Jul 15, 2022 150.17 148.043333
1 Jul 18, 2022 147.07 148.570000
0 Jul 19, 2022 151.00 149.413333
#drop na moving average
apple_df = apple_df.dropna()
#apply method to alter values along an axis
apple_df['Cross_direction'] = apple_df.apply(lambda x: 'upper' if x['Price']>x['SMA3'] else 'lower',axis=1)
Date Price SMA3 Cross_direction
17 Jun 23, 2022 138.27 136.496667 upper
16 Jun 24, 2022 141.66 138.426667 upper
15 Jun 27, 2022 141.66 140.530000 upper
14 Jun 28, 2022 137.44 140.253333 lower
13 Jun 29, 2022 139.23 139.443333 lower
12 Jun 30, 2022 136.72 137.796667 lower
11 Jul 01, 2022 138.93 138.293333 upper
10 Jul 05, 2022 141.56 139.070000 upper
9 Jul 06, 2022 142.92 141.136667 upper
8 Jul 07, 2022 146.35 143.610000 upper
7 Jul 08, 2022 147.04 145.436667 upper
6 Jul 11, 2022 144.87 146.086667 lower
5 Jul 12, 2022 145.86 145.923333 lower
4 Jul 13, 2022 145.49 145.406667 upper
3 Jul 14, 2022 148.47 146.606667 upper
2 Jul 15, 2022 150.17 148.043333 upper
1 Jul 18, 2022 147.07 148.570000 lower
0 Jul 19, 2022 151.00 149.413333 upper
#map method to substitute each value in a series
cross_map = {"upper":"Red","lower":"Blue"}
apple_df['Cross Color'] = apple_df['Cross_direction'].map(cross_map)
Date Price SMA3 Cross_direction Cross Color
17 Jun 23, 2022 138.27 136.496667 upper Red
16 Jun 24, 2022 141.66 138.426667 upper Red
15 Jun 27, 2022 141.66 140.530000 upper Red
14 Jun 28, 2022 137.44 140.253333 lower Blue
13 Jun 29, 2022 139.23 139.443333 lower Blue
12 Jun 30, 2022 136.72 137.796667 lower Blue
11 Jul 01, 2022 138.93 138.293333 upper Red
10 Jul 05, 2022 141.56 139.070000 upper Red
9 Jul 06, 2022 142.92 141.136667 upper Red
8 Jul 07, 2022 146.35 143.610000 upper Red
7 Jul 08, 2022 147.04 145.436667 upper Red
6 Jul 11, 2022 144.87 146.086667 lower Blue
5 Jul 12, 2022 145.86 145.923333 lower Blue
4 Jul 13, 2022 145.49 145.406667 upper Red
3 Jul 14, 2022 148.47 146.606667 upper Red
2 Jul 15, 2022 150.17 148.043333 upper Red
1 Jul 18, 2022 147.07 148.570000 lower Blue
0 Jul 19, 2022 151.00 149.413333 upper Red
applymap_df=apple_df.applymap(lambda x: len(str(x)))
Date Price SMA3 Cross_direction Cross Color
17 12 6 18 5 3
16 12 6 18 5 3
15 12 6 6 5 3
14 12 6 18 5 4
13 12 6 18 5 4
12 12 6 18 5 4
11 12 6 18 5 3
10 12 6 6 5 3
9 12 6 18 5 3
8 12 6 18 5 3
7 12 6 18 5 3
6 12 6 18 5 4
5 12 6 18 5 4
4 12 6 18 5 3
3 12 6 18 5 3
2 12 6 18 5 3
1 12 6 18 5 4
0 12 5 18 5 3
print(apple_df)
Dataframe 变换
分组和聚合
可通过groupby和agg方法实现。
#!/usr/local/bin/python3
# Copyright 2022 shichaog
import pandas as pd
iris = pd.read_csv('iris.csv')
print(iris.head(5))
sepallength sepalwidth petallength petalwidth class
0 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
2 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 Iris-setosa
3 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 Iris-setosa
4 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
#根据花类别分组,然后使用max方法聚合
print(iris.groupby(['class']).max())
sepallength sepalwidth petallength petalwidth
class
Iris-setosa 5.8 4.4 1.9 0.6
Iris-versicolor 7.0 3.4 5.1 1.8
Iris-virginica 7.9 3.8 6.9 2.5
#通过.agg传递多个聚合参数,参数是字典形式的
df = iris.groupby(['class']).agg({'petallength':['mean','min','max'],'petalwidth':'count'})
print(df)
petallength petalwidth
mean min max count
class
Iris-setosa 1.464 1.0 1.9 50
Iris-versicolor 4.260 3.0 5.1 50
Iris-virginica 5.552 4.5 6.9 50
#聚合之后,可以用下面方法修改列名
df.columns = ['_'.join(col).strip() for col in df.columns.values]
df.reset_index()
print(df)
petallength_mean ... petalwidth_count
class ...
Iris-setosa 1.464 ... 50
Iris-versicolor 4.260 ... 50
Iris-virginica 5.552 ... 50
groupings = iris.groupby(['class'])
groupings.get_group('Iris-setosa').head()
print(groupings.max())
sepallength sepalwidth petallength petalwidth
class
Iris-setosa 5.8 4.4 1.9 0.6
Iris-versicolor 7.0 3.4 5.1 1.8
Iris-virginica 7.9 3.8 6.9 2.5
#可以使用lamda方法,这里同groupings.max()作用是一样的
groupings.apply(lambda x: x.max())
sepallength sepalwidth ... petalwidth class
class ...
Iris-setosa 5.8 4.4 ... 0.6 Iris-setosa
Iris-versicolor 7.0 3.4 ... 1.8 Iris-versicolor
Iris-virginica 7.9 3.8 ... 2.5 Iris-virginica
#这是使用lamda方法过滤出最大值小于5的信息。
groupings.filter(lambda x: x['petalwidth'].max() <5)
sepallength sepalwidth petallength petalwidth class
0 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
2 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 Iris-setosa
3 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 Iris-setosa
4 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 Iris-setosa
.. ... ... ... ... ...
reshape
有时需要对原始的pandas dataframe 变换之后再使用,pandas中用于实现该功能的四个比较常用的方法是stack()、unstack()、pivot()以及melt()四个。
pivot
pivot用于生成一个新的dataframe,通过给定的索引(index)、列(column)以及给定的值(Values)重新生一个DataFrame对象。此函数不支持数据聚合,多个值将导致列中的多索引。
pivot(index=None,columns=None,values=None) -> DataFrame
index:指定一列做为生成DataFrame对象的索引,如果为空则默认为原来的索引。
columns:指定一列的值作为列名,必须传值。
values:指定一列作为生成DataFrame对象的值。可以为空。
#!/usr/local/bin/python3
# Copyright 2022 shichaog
import pandas as pd
data = {'水果':['苹果','梨','草莓','苹果','梨','草莓'],
'商店':["C1","C1","C1", "C2","C2","C2"],
'价格':[10,9,8,8,6,8]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)
输出:
水果 商店 价格
0 苹果 C1 10
1 梨 C1 9
2 草莓 C1 8
3 苹果 C2 8
4 梨 C2 6
5 草莓 C2 8
df_pivot = df.pivot(index='水果',columns='商店',values='价格')
print(df_pivot)
输出:
商店 C1 C2
水果
梨 9 6
苹果 10 8
草莓 8 8
stack和unstack
stack 提供和pivot相反的功能,将列转为行。
df2 = df.set_index(['水果','商店'])
print(df2)
stacked_df = pd.DataFrame(df2.stack())
print(stacked_df)
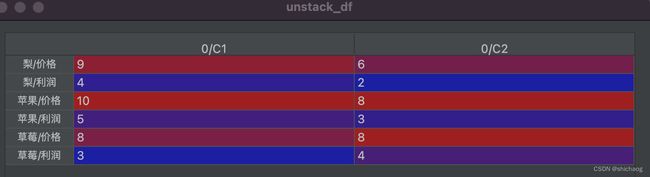
unstack_df = stacked_df.unstack('商店')
则上述df2和stacked_df分别如下:
df2

stacked_df

使用unstack
melt
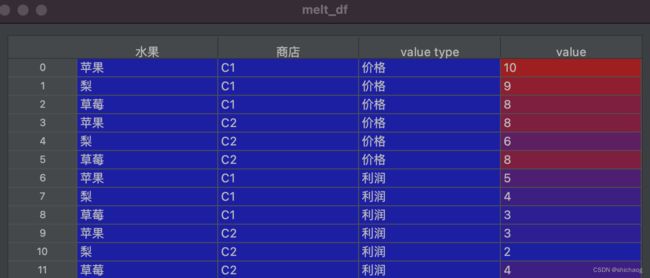
melt_df = df.melt(id_vars=['水果','商店'], var_name='value type')
print(melt_df)
pivot_table
pivot_table: 通过指定的索引和列对数据进行重塑,可以聚合。
pivot_table_df = df.pivot_table(index='水果',columns='商店',values='价格')
print(pivot_table_df)
拼接和合并
merge
merge 方法用于将两个dataframe、series合并成一个dataframe,其关键字how指明了合并的方式,on指示了按哪个字段合并。
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'Char': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'],
'number': [1, 2, 3, 4]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'Char': ['C', 'D', 'E', 'F'],
'number': [3, 4, 5, 6]})
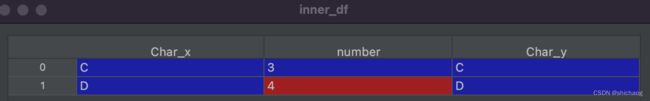
merge_df = df1.merge(df2,how='left',on='number')
inner_df = df1.merge(df2,how='inner',left_on='number',right_on='number')
m2_df = df1.merge(df2,how='right',on='number',suffixes=('','_right'))
concat和join
#可以用drop_duplicates去掉重复的内容
df3 = pd.concat([df1,df2]).drop_duplicates().reset_index(drop=True)
#水平方向拼接
df4 = pd.concat([df1,df2],axis=1)
#在dataframe尾部增加
new_row = pd.Series(['Z',26],index=df3.columns)
df3.append(new_row,ignore_index=True)
#根据索引拼接
join_df = pd.DataFrame({'Char': ['F','G', 'H', 'I'],
'number': [6, 7, 8, 9]})
df2.join(join_df, rsuffix='_right')
画图
pandas 提供了多种画图工具,可以绘制线性图、柱状图以及关系矩阵图等等。
df.plot();
df.plot.area(stacked=True);
df.hist();
from pandas.plotting import scatter_matrix
scatter_matrix(df,figsize=(4, 6),);
此外,在一个细分的行业或者领域里,还还有一些专用的绘图包,如seanborn绘制热力图,mplfinance绘制股票等金融数据图等。
统计信息
#均值
df.mean()
#中位数
df.median()
.mode()
.std()
#数据概览快速方法
.describe()
#数据本身相关方法
.corr()