JAVA调用R
JAVA很适合开发应用系统,但是数学建模和计算能力非其所长,如果该系统需要进行大量的统计或者优化的计算,调用R是一种很好的方式。JAVA负责系统的构建,R用来做运算引擎,从而实现应用型和分析性相结合的系统。
Rserve方式
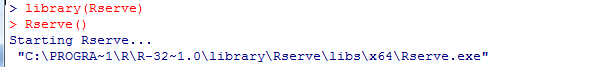
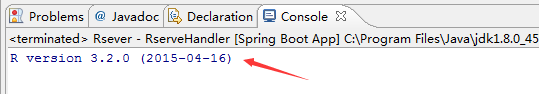
Rserve作为一个package发布在CRAN上,可以直接使用install.packages("Rserve")进行安装。需要使用时在R控制台下加载该包,然后输入命令Rserve(),开启服务器,就可以供客户端调用。
客户端,下载REngine.jar和RserveEngine.jar两个文件。
启动"Rserve"
import org.rosuda.REngine.REXP;
import org.rosuda.REngine.Rserve.RConnection;
public class RserveHandler {
/**
* Application entry point.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
RConnection conn = new RConnection();
REXP ex = conn.eval("R.version.string");
System.out.println(ex.asString());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
JRI方式
Java/R Interface,通过调用R的动态链接库从而利用R中的函数。通过install.packages("rJava")安装rJava就行,在安装文件夹中,可以看到一个jri的子文件夹,里面有自带的例子可以用来测试。
配置环境变量:
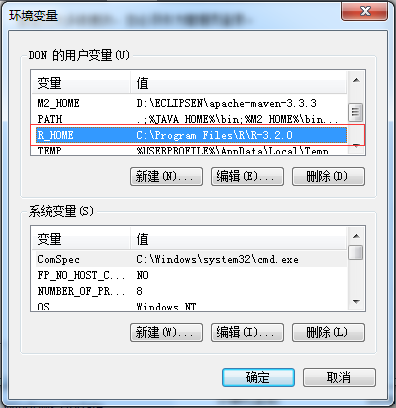
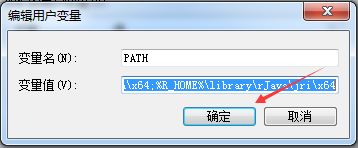 PATH .;%JAVA_HOME%\bin;%M2_HOME%\bin;%R_HOME%\bin\x64;%R_HOME%\library\rJava\jri\x64
PATH .;%JAVA_HOME%\bin;%M2_HOME%\bin;%R_HOME%\bin\x64;%R_HOME%\library\rJava\jri\x64
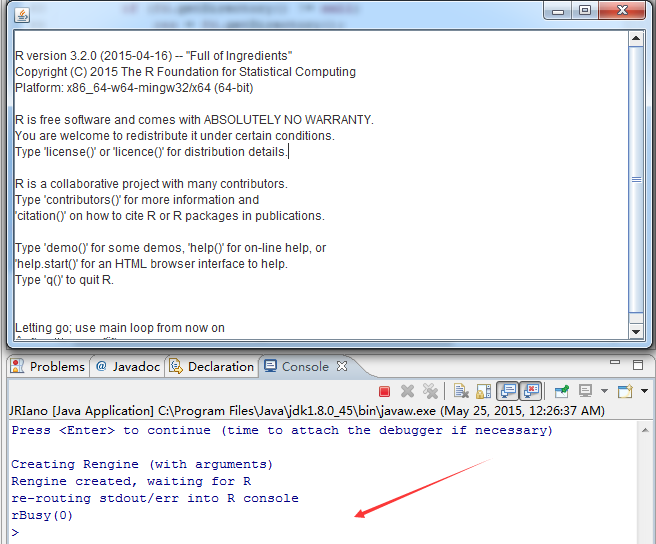
package com.nsecn.rns; import java.awt.FileDialog; import java.awt.Frame; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.Enumeration; import org.rosuda.JRI.REXP; import org.rosuda.JRI.RList; import org.rosuda.JRI.RMainLoopCallbacks; import org.rosuda.JRI.RVector; import org.rosuda.JRI.Rengine; class TextConsole implements RMainLoopCallbacks { public void rWriteConsole(Rengine re, String text, int oType) { System.out.print(text); } public void rBusy(Rengine re, int which) { System.out.println("rBusy(" + which + ")"); } public String rReadConsole(Rengine re, String prompt, int addToHistory) { System.out.print(prompt); try { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader( System.in)); String s = br.readLine(); return (s == null || s.length() == 0) ? s : s + "\n"; } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("jriReadConsole exception: " + e.getMessage()); } return null; } public void rShowMessage(Rengine re, String message) { System.out.println("rShowMessage \"" + message + "\""); } @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") public String rChooseFile(Rengine re, int newFile) { FileDialog fd = new FileDialog(new Frame(), (newFile == 0) ? "Select a file" : "Select a new file", (newFile == 0) ? FileDialog.LOAD : FileDialog.SAVE); fd.show(); String res = null; if (fd.getDirectory() != null) res = fd.getDirectory(); if (fd.getFile() != null) res = (res == null) ? fd.getFile() : (res + fd.getFile()); return res; } public void rFlushConsole(Rengine re) { } public void rLoadHistory(Rengine re, String filename) { } public void rSaveHistory(Rengine re, String filename) { } } public class JIRunit { /** * Application entry point. */ public static void main(String[] args) { // just making sure we have the right version of everything if (!Rengine.versionCheck()) { System.err.println("** Version mismatch - Java files don't match library version."); System.exit(1); } System.out.println("Creating Rengine (with arguments)"); // 1) we pass the arguments from the command line // 2) we won't use the main loop at first, we'll start it later // (that's the "false" as second argument) // 3) the callbacks are implemented by the TextConsole class above Rengine re = new Rengine(args, false, new TextConsole()); System.out.println("Rengine created, waiting for R"); // the engine creates R is a new thread, so we should wait until it's // ready if (!re.waitForR()) { System.out.println("Cannot load R"); return; } /* * High-level API - do not use RNI methods unless there is no other way * to accomplish what you want */ try { REXP x; re.eval("data(iris)", false); System.out.println(x = re.eval("iris")); // generic vectors are RVector to accomodate names RVector v = x.asVector(); if (v.getNames() != null) { System.out.println("has names:"); for (Enumeration<?> e = v.getNames().elements(); e .hasMoreElements();) { System.out.println(e.nextElement()); } } // for compatibility with Rserve we allow casting of vectors to // lists RList vl = x.asList(); String[] k = vl.keys(); if (k != null) { System.out.println("and once again from the list:"); int i = 0; while (i < k.length) System.out.println(k[i++]); } // get boolean array System.out.println(x = re.eval("iris[[1]]>mean(iris[[1]])")); // R knows about TRUE/FALSE/NA, so we cannot use boolean[] this way // instead, we use int[] which is more convenient (and what R uses // internally anyway) int[] bi = x.asIntArray(); { int i = 0; while (i < bi.length) { System.out.print(bi[i] == 0 ? "F " : (bi[i] == 1 ? "T " : "NA ")); i++; } System.out.println(""); } // push a boolean array boolean by[] = { true, false, false }; re.assign("bool", by); System.out.println(x = re.eval("bool")); // asBool returns the first element of the array as RBool // (mostly useful for boolean arrays of the length 1). is should // return true System.out.println("isTRUE? " + x.asBool().isTRUE()); // now for a real dotted-pair list: System.out.println(x = re.eval("pairlist(a=1,b='foo',c=1:5)")); RList l = x.asList(); if (l != null) { int i = 0; String[] a = l.keys(); System.out.println("Keys:"); while (i < a.length) { System.out.println(a[i++]); } System.out.println("Contents:"); i = 0; while (i < a.length) { System.out.println(l.at(i++)); } } System.out.println(re.eval("sqrt(36)")); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("EX:" + e); e.printStackTrace(); } // Part 2 - low-level API - for illustration purposes only! // System.exit(0); // simple assignment like a<-"hello" (env=0 means use R_GlobalEnv) long xp1 = re.rniPutString("hello"); re.rniAssign("a", xp1, 0); // Example: how to create a named list or data.frame double da[] = { 1.2, 2.3, 4.5 }; double db[] = { 1.4, 2.6, 4.2 }; long xp3 = re.rniPutDoubleArray(da); long xp4 = re.rniPutDoubleArray(db); // now build a list (generic vector is how that's called in R) long la[] = { xp3, xp4 }; long xp5 = re.rniPutVector(la); // now let's add names String sa[] = { "a", "b" }; long xp2 = re.rniPutStringArray(sa); re.rniSetAttr(xp5, "names", xp2); // ok, we have a proper list now // we could use assign and then eval "b<-data.frame(b)", but for now // let's build it by hand: String rn[] = { "1", "2", "3" }; long xp7 = re.rniPutStringArray(rn); re.rniSetAttr(xp5, "row.names", xp7); long xp6 = re.rniPutString("data.frame"); re.rniSetAttr(xp5, "class", xp6); // assign the whole thing to the "b" variable re.rniAssign("b", xp5, 0); { System.out.println("Parsing"); long e = re.rniParse("data(iris)", 1); System.out.println("Result = " + e + ", running eval"); long r = re.rniEval(e, 0); System.out.println("Result = " + r + ", building REXP"); REXP x = new REXP(re, r); System.out.println("REXP result = " + x); } { System.out.println("Parsing"); long e = re.rniParse("iris", 1); System.out.println("Result = " + e + ", running eval"); long r = re.rniEval(e, 0); System.out.println("Result = " + r + ", building REXP"); REXP x = new REXP(re, r); System.out.println("REXP result = " + x); } { System.out.println("Parsing"); long e = re.rniParse("names(iris)", 1); System.out.println("Result = " + e + ", running eval"); long r = re.rniEval(e, 0); System.out.println("Result = " + r + ", building REXP"); REXP x = new REXP(re, r); System.out.println("REXP result = " + x); String s[] = x.asStringArray(); if (s != null) { int i = 0; while (i < s.length) { System.out.println("[" + i + "] \"" + s[i] + "\""); i++; } } } { System.out.println("Parsing"); long e = re.rniParse("rnorm(10)", 1); System.out.println("Result = " + e + ", running eval"); long r = re.rniEval(e, 0); System.out.println("Result = " + r + ", building REXP"); REXP x = new REXP(re, r); System.out.println("REXP result = " + x); double d[] = x.asDoubleArray(); if (d != null) { int i = 0; while (i < d.length) { System.out.print(((i == 0) ? "" : ", ") + d[i]); i++; } System.out.println(""); } System.out.println(""); } { REXP x = re.eval("1:10"); System.out.println("REXP result = " + x); int d[] = x.asIntArray(); if (d != null) { int i = 0; while (i < d.length) { System.out.print(((i == 0) ? "" : ", ") + d[i]); i++; } System.out.println(""); } } re.eval("print(1:10/3)"); boolean flag = true; if (flag) { // so far we used R as a computational slave without REPL // now we start the loop, so the user can use the console System.out.println("Now the console is yours ... have fun"); re.startMainLoop(); } else { re.end(); System.out.println("end"); } } }
package com.nsecn.rns; import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.FileDialog; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.PrintStream; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JScrollPane; import javax.swing.JTextArea; import org.rosuda.JRI.RConsoleOutputStream; import org.rosuda.JRI.RMainLoopCallbacks; import org.rosuda.JRI.Rengine; class TextConsole2 implements RMainLoopCallbacks { JFrame frame; public JTextArea textarea = new JTextArea(); @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") public TextConsole2() { frame = new JFrame(); frame.getContentPane().add(new JScrollPane(textarea)); frame.setSize(new Dimension(800, 600)); frame.show(); } public void rWriteConsole(Rengine re, String text, int oType) { textarea.append(text); } public void rBusy(Rengine re, int which) { System.out.println("rBusy(" + which + ")"); } public String rReadConsole(Rengine re, String prompt, int addToHistory) { System.out.print(prompt); try { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader( System.in)); String s = br.readLine(); return (s == null || s.length() == 0) ? s : s + "\n"; } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("jriReadConsole exception: " + e.getMessage()); } return null; } public void rShowMessage(Rengine re, String message) { System.out.println("rShowMessage \"" + message + "\""); } @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") public String rChooseFile(Rengine re, int newFile) { FileDialog fd = new FileDialog(frame, (newFile == 0) ? "Select a file" : "Select a new file", (newFile == 0) ? FileDialog.LOAD : FileDialog.SAVE); fd.show(); String res = null; if (fd.getDirectory() != null) res = fd.getDirectory(); if (fd.getFile() != null) res = (res == null) ? fd.getFile() : (res + fd.getFile()); return res; } public void rFlushConsole(Rengine re) { } public void rLoadHistory(Rengine re, String filename) { } public void rSaveHistory(Rengine re, String filename) { } } public class JRIano { /** * Application entry point. */ public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Press <Enter> to continue (time to attach the debugger if necessary)"); try { System.in.read(); } catch (Exception e) { } System.out.println("Creating Rengine (with arguments)"); Rengine re = new Rengine(args, true, new TextConsole2()); System.out.println("Rengine created, waiting for R"); if (!re.waitForR()) { System.out.println("Cannot load R"); return; } System.out.println("re-routing stdout/err into R console"); System.setOut(new PrintStream(new RConsoleOutputStream(re, 0))); System.setErr(new PrintStream(new RConsoleOutputStream(re, 1))); System.out.println("Letting go; use main loop from now on"); } }