HashSet 源码浅析
Java HashSet
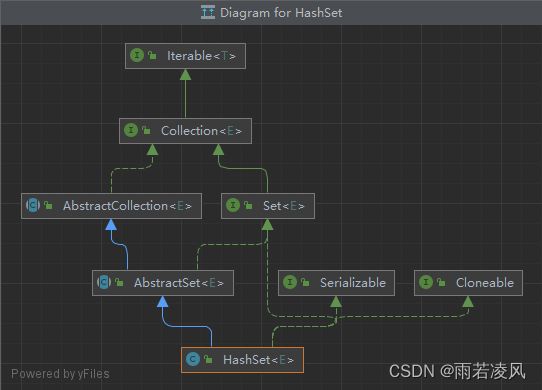
HashSet 基于 HashMap 来实现的,是一个不允许有重复元素的集合。
HashSet 允许有 null 值。
HashSet 是无序的,即不会记录插入的顺序。
HashSet 不是线程安全的, 如果多个线程尝试同时修改 HashSet,则最终结果是不确定的。 您必须在多线程访问时显式同步对 HashSet 的并发访问。
HashSet 实现了 Set 接口。
HashSet 中的元素实际上是对象,一些常见的基本类型可以使用它的包装类。
基本类型对应的包装类表如下:
| 基本类型 | 引用类型 |
|---|---|
| boolean | Boolean |
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| char | Character |
HashSet 类位于 java.util 包中,使用前需要引入它,语法格式如下:
import java.util.HashSet; // 引入 HashSet 类
以下实例我们创建一个 HashSet 对象 sites,用于保存字符串元素:
HashSet<String> sites = new HashSet<String>();
添加元素
HashSet 类提供了很多有用的方法,添加元素可以使用 add() 方法:
// 引入 HashSet 类
import java.util.HashSet;
public class BingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> sites = new HashSet<String>();
sites.add("Google");
sites.add("Bing");
sites.add("Taobao");
sites.add("Zhihu");
sites.add("Bing"); // 重复的元素不会被添加
System.out.println(sites);
}
}
执行以上代码,输出结果如下:
[Google, Bing, Zhihu, Taobao]
在上面的实例中,Bing 被添加了两次,它在集合中也只会出现一次,因为集合中的每个元素都必须是唯一的。
判断元素是否存在
我们可以使用 contains() 方法来判断元素是否存在于集合当中:
// 引入 HashSet 类
import java.util.HashSet;
public class BingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> sites = new HashSet<String>();
sites.add("Google");
sites.add("Bing");
sites.add("Taobao");
sites.add("Zhihu");
sites.add("Bing"); // 重复的元素不会被添加
System.out.println(sites.contains("Taobao"));
}
}
执行以上代码,输出结果如下:
true
删除元素
我们可以使用 remove() 方法来删除集合中的元素:
// 引入 HashSet 类
import java.util.HashSet;
public class BingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> sites = new HashSet<String>();
sites.add("Google");
sites.add("Bing");
sites.add("Taobao");
sites.add("Zhihu");
sites.add("Bing"); // 重复的元素不会被添加
sites.remove("Taobao"); // 删除元素,删除成功返回 true,否则为 false
System.out.println(sites);
}
}
执行以上代码,输出结果如下:
[Google, Bing, Zhihu]
删除集合中所有元素可以使用 clear 方法:
// 引入 HashSet 类
import java.util.HashSet;
public class BingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> sites = new HashSet<String>();
sites.add("Google");
sites.add("Bing");
sites.add("Taobao");
sites.add("Zhihu");
sites.add("Bing"); // 重复的元素不会被添加
sites.clear();
System.out.println(sites);
}
}
执行以上代码,输出结果如下:
[]
计算大小
如果要计算 HashSet 中的元素数量可以使用 size() 方法:
// 引入 HashSet 类
import java.util.HashSet;
public class BingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> sites = new HashSet<String>();
sites.add("Google");
sites.add("Bing");
sites.add("Taobao");
sites.add("Zhihu");
sites.add("Bing"); // 重复的元素不会被添加
System.out.println(sites.size());
}
}
执行以上代码,输出结果如下:
4
迭代 HashSet
可以使用 for-each 来迭代 HashSet 中的元素。
// 引入 HashSet 类
import java.util.HashSet;
public class BingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet<String> sites = new HashSet<String>();
sites.add("Google");
sites.add("Bing");
sites.add("Taobao");
sites.add("Zhihu");
sites.add("Bing"); // 重复的元素不会被添加
for (String i : sites) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
执行以上代码,输出结果如下:
Google
Bing
Zhihu
Taobao
源码
HashSet是对HashMap的一个简单包装,所以对于HashSet来说,调用它的函数都会转成对应的HashMap的方法。
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
/**
* Constructs a new, empty set; the backing HashMap instance has
* default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
/**
* Returns true if this set contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns true if and only if this set
* contains an element e such that
* (o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e)).
*
* @param o element whose presence in this set is to be tested
* @return true if this set contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return map.containsKey(o);
}
/**
* Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present.
* More formally, adds the specified element e to this set if
* this set contains no element e2 such that
* (e==null ? e2==null : e.equals(e2)).
* If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set
* unchanged and returns false.
*
* @param e element to be added to this set
* @return true if this set did not already contain the specified
* element
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
/**
* Removes the specified element from this set if it is present.
* More formally, removes an element e such that
* (o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e)),
* if this set contains such an element. Returns true if
* this set contained the element (or equivalently, if this set
* changed as a result of the call). (This set will not contain the
* element once the call returns.)
*
* @param o object to be removed from this set, if present
* @return true if the set contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}