movi命令(do_movi函数的源码分析)
以下内容源于网络资源的学习与整理,如有侵权请告知删除。
一、do_movi函数分析
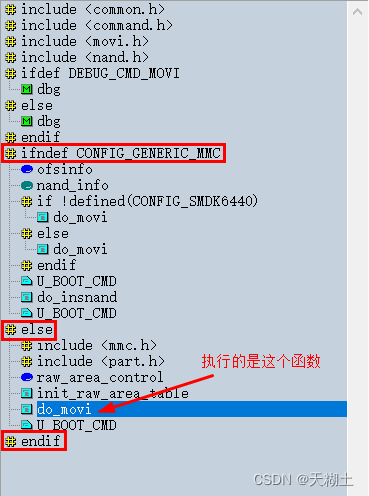
当执行movi相关命令时,实际执行的是do_movi函数。
x210 # help movi
movi init - Initialize moviNAND and show card info
movi read {u-boot | kernel} {addr} - Read data from sd/mmc
movi write {fwbl1 | u-boot | kernel} {addr} - Write data to sd/mmc
movi read rootfs {addr} [bytes(hex)] - Read rootfs data from sd/mmc by size
movi write rootfs {addr} [bytes(hex)] - Write rootfs data to sd/mmc by size
movi read {sector#} {bytes(hex)} {addr} - instead of this, you can use "mmc read"
movi write {sector#} {bytes(hex)} {addr} - instead of this, you can use "mmc write"
x210 # movi read kernel 30008000
reading kernel.. 1073, 8192
MMC read: dev # 0, block # 1073, count 8192 ...8192 blocks read: OK
completed
x210 # 该函数位于/common/cmd_movi.c文件中,根据是否定义了CONFIG_GENERIC_MMC这个宏来选择不同的内容。因为在/include/configs/X210_sd.h文件定义了这个宏,所以这里的do_movi函数是底下的那个。
删除条件编译语句后,该函数的内容与分析(以“movi read kernel 30008000”为例进)如下:
/*
执行命令“ movi read kernel 30008000 ”时,
argc=4,argv[0]="movi",argv[1]="read",argv[2]="kenel",argv[3]="30008000"
*/
int do_movi(cmd_tbl_t * cmdtp, int flag, int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *cmd;
ulong addr, start_blk, blkcnt;
uint rfs_size;
char run_cmd[100];
uint rw = 0, attribute = 0;
int i;
member_t *image;
struct mmc *mmc;
int dev_num = 0;
#if defined(CONFIG_VOGUES)//不满足
int boot_dev;
#endif
cmd = argv[1];// cmd="read"
switch (cmd[0]) {
case 'i'://i即init
raw_area_control.magic_number = 0;
run_command("mmcinfo", 0);
return 1;
case 'r': //r即read,选择这个
rw = 0; /* read case */
break;
case 'w'://w即write
rw = 1; /* write case */
break;
default:
goto usage;
}
cmd = argv[2];//cmd="kernel"
switch (cmd[0]) {
case 'f'://f即fwbl1
if (argc != 4)
goto usage;
attribute = 0x0;
addr = simple_strtoul(argv[3], NULL, 16);
break;
case 'u'://u即u-boot
if (argc != 4)
goto usage;
attribute = 0x2;
addr = simple_strtoul(argv[3], NULL, 16);
break;
case 'k'://k即kernel,选择这个
if (argc != 4)
goto usage;
attribute = 0x4;
addr = simple_strtoul(argv[3], NULL, 16);//把字符串形式的数字转为数字,此时addr=30008000
break;
case 'r'://r即rootfs
if (argc != 5)
goto usage;
attribute = 0x8;
addr = simple_strtoul(argv[3], NULL, 16);
break;
default:
goto usage;
}
#if defined(CONFIG_VOGUES)//不满足
boot_dev = movi_boot_src();
if (boot_dev) {
/* boot device is NOR */
/* read kernel from eMMC */
mmc = find_mmc_device(0);
printf("MMC #0 is boot device\r\n");
} else {
/* boot device is SD card */
/* read kernel from SD card */
mmc = find_mmc_device(1);
printf("MMC #1 is boot device\r\n");
}
#else//执行这个
mmc = find_mmc_device(dev_num);//这里的dev_num在开头就赋值为0,表示inand。
#endif
mmc_init(mmc);//初始化
/* firmware BL1 r/w */
if (attribute == 0x0) {//不满足,因为attribute = 0x4
/* on write case we should write BL1 1st. */
for (i=0, image = raw_area_control.image; i<15; i++) {
if (image[i].attribute == attribute)
break;
}
start_blk = image[i].start_blk;
blkcnt = image[i].used_blk;
printf("%s FWBL1 .. %ld, %ld ", rw ? "writing":"reading",
start_blk, blkcnt);
sprintf(run_cmd,"mmc %s 0 0x%lx 0x%lx 0x%lx",
rw ? "write":"read",
addr, start_blk, blkcnt);
run_command(run_cmd, 0);
printf("completed\n");
return 1;
}
/* u-boot r/w */
if (attribute == 0x2) {//不满足,因为attribute = 0x4
/* on write case we should write BL2 1st. */
#if defined(CONFIG_FUSED)
for (i=0, image = raw_area_control.image; i<15; i++) {
if (image[i].attribute == 0x1)
break;
}
start_blk = image[i].start_blk;
blkcnt = image[i].used_blk;
printf("%s BL1.. %ld, %ld ", rw ? "writing":"reading",
start_blk, blkcnt);
sprintf(run_cmd,"mmc %s 0 0x%lx 0x%lx 0x%lx",
rw ? "write":"read",
addr, start_blk, blkcnt);
run_command(run_cmd, 0);
printf("completed\n");
#else
if (rw) {
start_blk = raw_area_control.image[1].start_blk;
blkcnt = raw_area_control.image[1].used_blk;
printf("Writing BL1 to sector %ld (%ld sectors).. ",
start_blk, blkcnt);
movi_write_bl1(addr);
}
#endif
for (i=0, image = raw_area_control.image; i<15; i++) {
if (image[i].attribute == attribute)
break;
}
start_blk = image[i].start_blk;
blkcnt = image[i].used_blk;
printf("%s bootloader.. %ld, %ld ", rw ? "writing":"reading",
start_blk, blkcnt);
#if defined(CONFIG_SECURE_BOOT)
#define BL2_SIZE 8192
sprintf(run_cmd,"mmc %s 0 0x%lx 0x%lx 0x%lx",
rw ? "write":"read",
addr + BL2_SIZE, start_blk, blkcnt);
#else
sprintf(run_cmd,"mmc %s 0 0x%lx 0x%lx 0x%lx",
rw ? "write":"read",
addr, start_blk, blkcnt);
#endif
run_command(run_cmd, 0);
printf("completed\n");
return 1;
}
/* kernel r/w */
if (attribute == 0x4) {//满足,因为attribute = 0x4
for (i=0, image = raw_area_control.image; i<15; i++) {
if (image[i].attribute == attribute)//根据attribute来匹配到底是哪个image[](即raw分区表中的哪个分区)
break;
}
start_blk = image[i].start_blk;//计算这个分区的信息(起始扇区号、)
blkcnt = image[i].used_blk;
printf("%s kernel.. %ld, %ld ", rw ? "writing" : "reading",
start_blk, blkcnt);
#if defined(CONFIG_VOGUES)//不满足
if (boot_dev)
sprintf(run_cmd, "mmc %s 0 0x%lx 0x%lx 0x%lx",
rw ? "write" : "read", addr, start_blk, blkcnt);
else
sprintf(run_cmd, "mmc %s 1 0x%lx 0x%lx 0x%lx",
rw ? "write" : "read", addr, start_blk, blkcnt);
#else//执行这个
sprintf(run_cmd, "mmc %s 0 0x%lx 0x%lx 0x%lx",
rw ? "write" : "read", addr, start_blk, blkcnt);//rw=0,所以是read
#endif
run_command(run_cmd, 0);//最终调用run_command函数来运行命令
printf("completed\n");
return 1;
}
/* root file system r/w */
if (attribute == 0x8) {//不满足,因为attribute = 0x4
rfs_size = simple_strtoul(argv[4], NULL, 16);
for (i=0, image = raw_area_control.image; i<15; i++) {
if (image[i].attribute == attribute)
break;
}
start_blk = image[i].start_blk;
blkcnt = rfs_size/MOVI_BLKSIZE +
((rfs_size&(MOVI_BLKSIZE-1)) ? 1 : 0);
image[i].used_blk = blkcnt;
printf("%s RFS.. %ld, %ld ", rw ? "writing":"reading",
start_blk, blkcnt);
sprintf(run_cmd,"mmc %s 0 0x%lx 0x%lx 0x%lx",
rw ? "write":"read",
addr, start_blk, blkcnt);
run_command(run_cmd, 0);
printf("completed\n");
return 1;
}
return 1;
usage:
printf("Usage:\n%s\n", cmdtp->usage);
return -1;
}
二、init_raw_area_table函数分析
注意到上面的do_movi函数中频繁用到member_t *image这个变量。
其中member_t是struct member结构体的别名,这个结构体的一个实例就表示一个分区的信息。
/*
* start_blk: start block number for image
* used_blk: blocks occupied by image
* size: image size in bytes
* attribute: attributes of image
* 0x1: u-boot parted (BL1)
* 0x2: u-boot (BL2)
* 0x4: kernel
* 0x8: root file system
* 0x10: environment area
* 0x20: reserved
* description: description for image
* by scsuh
*/
typedef struct member {
uint start_blk;
uint used_blk;
uint size;
uint attribute; /* attribute of image */
char description[16];
} member_t; /* 32 bytes */在/common/cmd_movi.c文件中,init_raw_area_table函数构建了一个raw分区表。
raw分区表的数据类型如下(这个数据类型的一个实例就是一个raw分区表):
/*
* magic_number: 0x24564236
* start_blk: start block number for raw area
* total_blk: total block number of card
* next_raw_area: add next raw_area structure
* description: description for raw_area
* image: several image that is controlled by raw_area structure
* by scsuh
*/
typedef struct raw_area {
uint magic_number; /* to identify itself */
uint start_blk; /* compare with PT on coherency test */
uint total_blk;
uint next_raw_area; /* should be sector number */
char description[16];
member_t image[15];
} raw_area_t; /* 512 bytes *///定义raw_area_t数据类型的一个变量raw_area_control,即定义一个分区表
//后面将填充这个变量的image[]成员(image[]成员表示具体分区的信息)
raw_area_t raw_area_control;
int init_raw_area_table (block_dev_desc_t * dev_desc)
{
struct mmc *host = find_mmc_device(dev_desc->dev);
/* when last block does not have raw_area definition. */
if (raw_area_control.magic_number != MAGIC_NUMBER_MOVI) {
int i = 0;
member_t *image;
u32 capacity;
if (host->high_capacity) {
capacity = host->capacity;
#ifdef CONFIG_S3C6410
if(IS_SD(host))
capacity -= 1024;
#endif
} else {
capacity = host->capacity;
}
dev_desc->block_read(dev_desc->dev,
capacity - (eFUSE_SIZE/MOVI_BLKSIZE) - 1,
1, &raw_area_control);
if (raw_area_control.magic_number == MAGIC_NUMBER_MOVI) {
return 0;
}
dbg("Warning: cannot find the raw area table(%p) %08x\n",
&raw_area_control, raw_area_control.magic_number);
/* add magic number */
raw_area_control.magic_number = MAGIC_NUMBER_MOVI;
/* init raw_area will be 16MB */
raw_area_control.start_blk = 16*1024*1024/MOVI_BLKSIZE;
raw_area_control.total_blk = capacity;
raw_area_control.next_raw_area = 0;
strcpy(raw_area_control.description, "initial raw table");
image = raw_area_control.image;//指向分区表的开头位置
#if defined(CONFIG_EVT1)
#if defined(CONFIG_FUSED)
/* image 0 should be fwbl1 */
image[0].start_blk = (eFUSE_SIZE/MOVI_BLKSIZE);
image[0].used_blk = MOVI_FWBL1_BLKCNT;
image[0].size = FWBL1_SIZE;
image[0].attribute = 0x0;
strcpy(image[0].description, "fwbl1");
dbg("fwbl1: %d\n", image[0].start_blk);
#endif
#endif
/* image 1 should be bl2 */
#if defined(CONFIG_EVT1)
#if defined(CONFIG_FUSED)
image[1].start_blk = image[0].start_blk + MOVI_FWBL1_BLKCNT;
#else
image[1].start_blk = (eFUSE_SIZE/MOVI_BLKSIZE);
#endif
#else
image[1].start_blk = capacity - (eFUSE_SIZE/MOVI_BLKSIZE) -
MOVI_BL1_BLKCNT;
#endif
image[1].used_blk = MOVI_BL1_BLKCNT;
image[1].size = SS_SIZE;
image[1].attribute = 0x1;
strcpy(image[1].description, "u-boot parted");
dbg("bl1: %d\n", image[1].start_blk);
/* image 2 should be environment */
#if defined(CONFIG_EVT1)
image[2].start_blk = image[1].start_blk + MOVI_BL1_BLKCNT;
#else
image[2].start_blk = image[1].start_blk - MOVI_ENV_BLKCNT;
#endif
image[2].used_blk = MOVI_ENV_BLKCNT;
image[2].size = CFG_ENV_SIZE;
image[2].attribute = 0x10;
strcpy(image[2].description, "environment");
dbg("env: %d\n", image[2].start_blk);
/* image 3 should be bl2 */
#if defined(CONFIG_EVT1)
image[3].start_blk = image[2].start_blk + MOVI_ENV_BLKCNT;
#else
image[3].start_blk = image[2].start_blk - MOVI_BL2_BLKCNT;
#endif
image[3].used_blk = MOVI_BL2_BLKCNT;
image[3].size = PART_SIZE_BL;
image[3].attribute = 0x2;
strcpy(image[3].description, "u-boot");
dbg("bl2: %d\n", image[3].start_blk);
/* image 4 should be kernel */
#if defined(CONFIG_EVT1)
image[4].start_blk = image[3].start_blk + MOVI_BL2_BLKCNT;
#else
image[4].start_blk = image[3].start_blk - MOVI_ZIMAGE_BLKCNT;
#endif
image[4].used_blk = MOVI_ZIMAGE_BLKCNT;
image[4].size = PART_SIZE_KERNEL;
image[4].attribute = 0x4;
strcpy(image[4].description, "kernel");
dbg("knl: %d\n", image[4].start_blk);
/* image 5 should be RFS */
#if defined(CONFIG_EVT1)
image[5].start_blk = image[4].start_blk + MOVI_ZIMAGE_BLKCNT;
#else
image[5].start_blk = image[4].start_blk - MOVI_ROOTFS_BLKCNT;
#endif
image[5].used_blk = MOVI_ROOTFS_BLKCNT;
image[5].size = PART_SIZE_ROOTFS;
image[5].attribute = 0x8;
strcpy(image[5].description, "rfs");
dbg("rfs: %d\n", image[5].start_blk);
for (i=6; i<15; i++) {
raw_area_control.image[i].start_blk = 0;
raw_area_control.image[i].used_blk = 0;
}
}
}
由于CONFIG_FUSED 宏没有定义,故总共5个分区:
| image数组 | 扇区号 | 分区名 | 大小 |
|---|---|---|---|
| image[1] | 1-16 | u-boot parted,即BL1 | 8KB |
| image[2] | 17-48 | environment | 16KB |
| image[3] | 49-1072 | u-boot,即BL2 | 512KB |
| image[4] | 1073-9264 | kernel | 4MB |
| image[5] | 9265-62512 | rfs,即rootfs | 26MB |
注意,这里定义的image[5]的扇区号与大小,好像不是很适合实际情况?
movi命令下的分区表、fastboot命令下的分区表,两者相辅相成,利用movi或者fastboot flash命令时,参数中的bootLoader、kernel、system等标签都可以从这两张表中找到对应的地址。
关于fastboot命令下的分区表,见博客如何将镜像烧写至iNand(fastboot命令的源码分析)。