HDLbits exercises 13(MORE CIRCUITS全部题)
目录
1\ RULE90
2\ RULE110
3\ CONWAY'S GAME OF LIFE 16X16*********
1\ RULE90
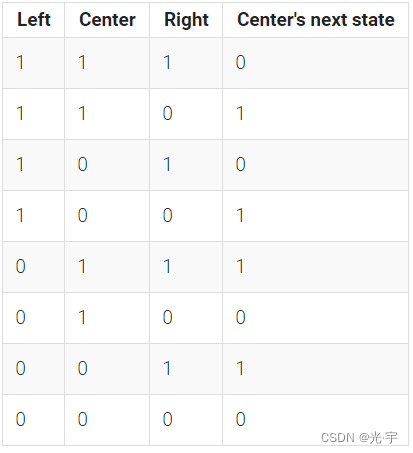
Rule 90 is a one-dimensional cellular automaton with interesting properties.(是一个具有有趣性质的一维元胞自动机。)
The rules are simple. There is a one-dimensional array of cells (on or off). At each time step, the next state of each cell is the XOR of the cell's two current neighbours. A more verbose way of expressing this rule is the following table, where a cell's next state is a function of itself and its two neighbours:(规则很简单。有一个单元格的一维数组(打开或关闭)。在每个时间步中,每个单元的下一个状态是该单元的两个当前邻居的异或。更详细的表达方式如下表所示,其中细胞的下一个状态是自身和两个相邻状态的函数:)
(The name "Rule 90" comes from reading the "next state" column: 01011010 is decimal 90.)
In this circuit, create a 512-cell system (q[511:0]), and advance by one time step each clock cycle. The load input indicates the state of the system should be loaded with data[511:0]. Assume the boundaries (q[-1] and q[512]) are both zero (off).((“规则90”这个名字来自于阅读“下一个州”列:01011010是十进制90。)在这个电路中,创建一个512单元系统(q[511:0]),每个时钟周期前进一个时间步。load输入指示系统的状态应该加载数据[511:0]。假设边界(q[-1]和q[512])都为零(关闭)。)
HINT:
对于初始状态q[511:0] = 1,前几次迭代为:
1
10
101
1000
10100
100010
1010101
10000000
这形成了半个sierpievski三角形。
CORRECT:
module top_module(
input clk,
input load,
input [511:0] data,
output [511:0] q );
always @(posedge clk)begin
if(load)begin
q <= data;
end
else begin
q <= {1'b0,q[511:1]}^{q[510:0],1'b0};
end
end
endmodule
2\ RULE110
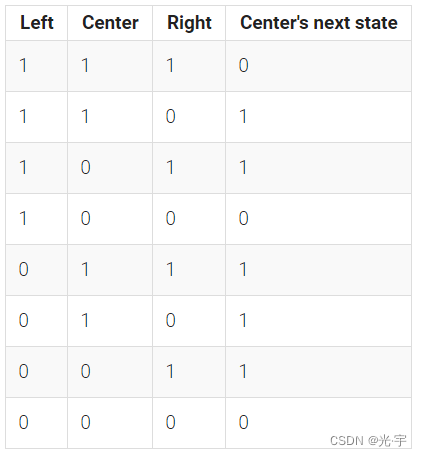
Rule 110 is a one-dimensional cellular automaton with interesting properties (such as being Turing-complete).
There is a one-dimensional array of cells (on or off). At each time step, the state of each cell changes. In Rule 110, the next state of each cell depends only on itself and its two neighbours, according to the following table:(有一个单元格的一维数组(打开或关闭)。在每个时间步中,每个单元的状态都发生变化。在110规则中,每个cell的下一个状态只依赖于它自己和它的两个邻居,如下表所示:)
(The name "Rule 110" comes from reading the "next state" column: 01101110 is decimal 110.)
In this circuit, create a 512-cell system (q[511:0]), and advance by one time step each clock cycle. The load input indicates the state of the system should be loaded with data[511:0]. Assume the boundaries (q[-1] and q[512]) are both zero (off).((“规则110”这个名字来自于阅读“下一个州”列:01101110是十进制110。)在这个电路中,创建一个512单元系统(q[511:0]),每个时钟周期前进一个时间步。load输入指示系统的状态应该加载数据[511:0]。假设边界(q[-1]和q[512])都为零(关闭)。)
HINT:
对于初始状态q[511:0] = 1,前几次迭代为:
1
11
111
1101
11111
110001
1110011
11010111
CORRECT:
module top_module(
input clk,
input load,
input [511:0] data,
output [511:0] q
);
always @(posedge clk)begin
if(load)begin
q <= data;
end
else begin
q <= (~{1'b0,q[511:1]} & q) | (q & ~{q[510:0],1'b0}) | {~{1'b0,q[511:1]} & {q[510:0],1'b0}} | {~q & {q[510:0],1'b0}};
end
end
endmodule
3\ CONWAY'S GAME OF LIFE 16X16*********
Conway's Game of Life is a two-dimensional cellular automaton.
The "game" is played on a two-dimensional grid of cells, where each cell is either 1 (alive) or 0 (dead). At each time step, each cell changes state depending on how many neighbours it has:
- 0-1 neighbour: Cell becomes 0.
- 2 neighbours: Cell state does not change.
- 3 neighbours: Cell becomes 1.
- 4+ neighbours: Cell becomes 0.
(这个“游戏”是在二维细胞网格上进行的,每个细胞要么是1(活的),要么是0(死的)。在每个时间步中,每个细胞根据它有多少邻居而改变状态:
0-1邻居:Cell变为0。
2 neighbors: Cell状态不变。
3个邻居:细胞变成1。
4+邻居:Cell变为0。)
The game is formulated for an infinite grid. In this circuit, we will use a 16x16 grid. To make things more interesting, we will use a 16x16 toroid, where the sides wrap around to the other side of the grid. For example, the corner cell (0,0) has 8 neighbours: (15,1), (15,0), (15,15), (0,1), (0,15), (1,1), (1,0), and (1,15). The 16x16 grid is represented by a length 256 vector, where each row of 16 cells is represented by a sub-vector: q[15:0] is row 0, q[31:16] is row 1, etc. (This tool accepts SystemVerilog, so you may use 2D vectors if you wish.)
(这个游戏是为无限网格设计的。在这个电路中,我们将使用16x16的网格。为了让事情更有趣,我们将使用一个16x16的环面,其中的边绕到网格的另一边。例如,角落里的细胞(0,0)有8个邻国:(15,1),(15 0),(15、15)(0,1),(0,15),(1,1),(1,0)和(1,15)。16x16网格由长度256的向量表示,其中每一行16个单元格由子向量表示:q[15:0]是第0行,q[31:16]是第1行,等等(该工具接受SystemVerilog,因此如果您愿意,您可以使用2D向量)。)
- load: Loads data into q at the next clock edge, for loading initial state.
- q: The 16x16 current state of the game, updated every clock cycle.
The game state should advance by one timestep every clock cycle.
John Conway, mathematician and creator of the Game of Life cellular automaton, passed away from COVID-19 on April 11, 2020.
(load:在下一个时钟边缘将数据加载到q中,用于加载初始状态。
q: 16x16的游戏当前状态,每个时钟周期更新。
游戏状态应该在每个时钟周期中前进一个时间步。
数学家、生命游戏细胞自动机的创造者约翰·康威于2020年4月11日因COVID-19去世。)
HINT:
A test case that's easily understandable and tests some boundary conditions is the blinker 256'h7. It is 3 cells in row 0 columns 0-2. It oscillates between a row of 3 cells and a column of 3 cells (in column 1, rows 15, 0, and 1).(一个容易理解并测试一些边界条件的测试用例是闪烁灯256'h7。它是第0行第0-2列的3个单元格。它在一行3个单元格和一列3个单元格之间振荡(在第1列、第15行、第0行和第1行中)。)
CORRECT:
module top_module(
input clk,
input load,
input [255:0] data,
output [255:0] q );
reg [3:0] count;
integer i;
always @(posedge clk)begin
if(load)begin
q <= data;
end
else begin
for(i=0;i<256;i++)begin
if(i == 0)begin
count = q[255] + q[240] + q[241] + q[15] + q[1] + q[31] + q[16] + q[17];
end
else if(i == 15)begin
count = q[254] + q[255] + q[240] + q[14] + q[0] + q[30] + q[31] + q[16];
end
else if(i == 240)begin
count = q[239] + q[224] + q[225] + q[255] + q[241] + q[15] + q[0] + q[1];
end
else if(i == 255)begin
count = q[238] + q[239] + q[224] + q[254] + q[240] + q[15] + q[0] + q[14];
end
else if( i>0 && i<15)begin
count = q[239+i]+q[240+i]+q[241+i]+q[i-1]+q[i+1]+q[i+15]+q[i+16]+q[i+17];
end
else if(i>240 && i<255)begin
count = q[i-17]+q[i-16]+q[i-15]+q[i-1]+q[i+1]+q[i-239]+q[i-240]+q[i-241];
end
else if( i%16 == 0)begin
count = q[i-1]+q[i-16]+q[i-15]+q[i+15]+q[i+1]+q[i+31]+q[i+16]+q[i+17];
end
else if(i % 16 == 15)begin
count = q[i-17]+q[i-16]+q[i-31]+q[i-1]+q[i-15]+q[i+15]+q[i+16]+q[i+1];
end
else begin
count = q[i-17]+q[i-16]+q[i-15]+q[i-1]+q[i+1]+q[i+15]+q[i+16]+q[i+17];
end
case(count)
4'd2:q[i] <= q[i];
4'd3:q[i] <= 1'b1;
default:q[i] <= 1'b0;
endcase
end
end
end
endmodule