MySQLⅡ增删查改
MySQL
- sql语句
-
- 表操作
-
- 增加
- 删除
- 查询
-
- 全列查询
- 指定列查询
- 查询字段为表达式
- 将所有数学成绩+10查询
- 查询总成绩
- 去重(distinct)
-
- 注意
- 排序(order by)
-
- 升序
- 降序
-
- 注意
- 总结
- 条件查询(where)
- 分页查询(limit)
- 修改
sql语句
表操作
增删查改(CURD)
以此student表为例:
drop table if exists student;
create table student(
id INT,
sn INT,
name VARCHAR(20),
qq_mail VARCHAR(20)
);
增加
- 单列全列插入
每次只能插入一行,且每一个字段要和数据库对应
insert into student values(1,1001,"张三","[email protected]");
insert into student values(2,1002,"李四","[email protected]");
- 指定列多行插入
insert into student(id,sn,name) values(3,1003,"王五"),(4,1004,"赵六");
//(id,sn,name)为指定列,数据之间用逗号隔开
如果没有指定某个字段的值,那么默认是NULL
- 插入数据,若存在,请忽略
insert ignore into student(id,sn) values(1,1001);
删除
删除整个表
delete from student;
删除表中某个数据
delete from student where id=1;
//删除id=1的行
mysql不允许在查询的同时删除原表数据
必须给原始数据表取一个别名再删除
查询
以exam_result表为例
drop table if exists exam_result;
create table exam_result (
id INT,
name VARCHAR(20),
chinese DECIMAL(3,1),
math DECIMAL(3,1),
english DECIMAL(3,1)
);
insert into exam_result (id,name, chinese, math, english)
values
(1,'A', 67, 98, 56),
(2,'B', 87.5, 78, 77),
(3,'C', 88, 98, 90),
(4,'D', 82, 84, 67),
(5,'E', 55.5, 85, 45),
(6,'F', 70, 73, 78.5),
(7,'G', 75, 65, 30),
(8,'H', 78, 32, 98);
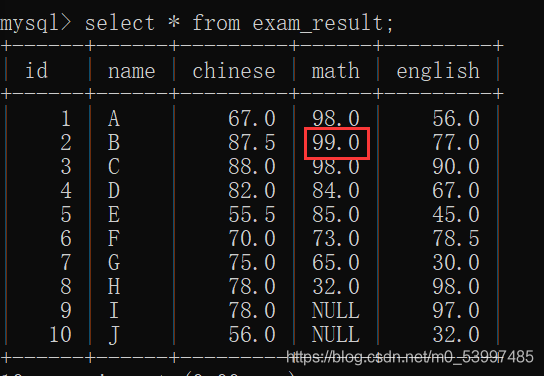
全列查询
select * from exam_result;
// * 代表当前表中的所有字段
指定列查询
select id,name from exam_result;
查询字段为表达式
select id,name,10 from exam_result;
//10:此列都为10
将所有数学成绩+10查询
select id,name,math+10 from exam_result;
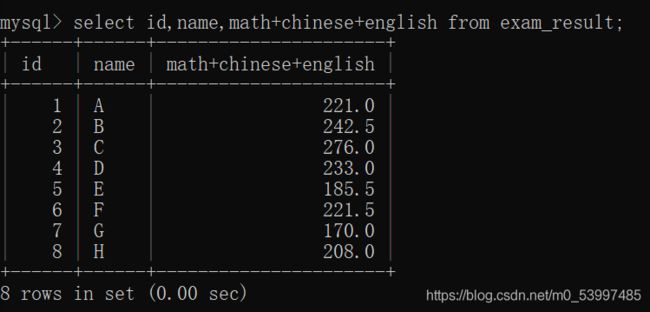
查询总成绩
select id,name,math+chinese+english from exam_result;
select id,name,math+chinese+english as 总成绩 from exam_result;
//as 可以省略
简化表明或列名,便于查看,不改变表本身名字
去重(distinct)
select distinct math from exam_result;
注意
若写为
//1.
select id,name,distinct math from exam_result;
//2.
select distinct math, id,name from exam_result;

并没有去重的原因是:去重针对的是所有的字段,只有当三个字段同时重复时,才会去重
排序(order by)
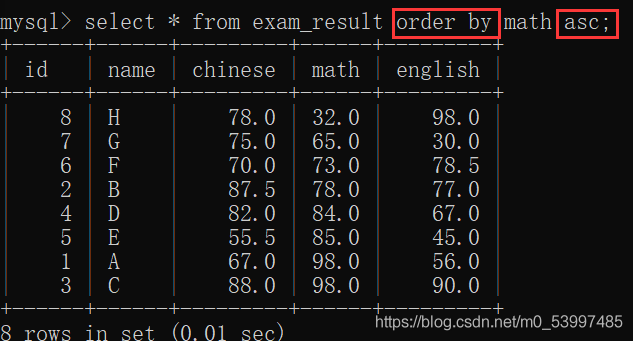
升序
将数学成绩从低到高排序,包括null
select * from exam_result order by math asc;
降序
将数学成绩从高到低排序,包括null
select * from exam_result order by math desc;
注意
desc 为关键字
eg:若要创建一个表名为desc的表,需要加`

总结
- order by asc 和 order by 默认为 从低到高 排序
- order by desc 为 从高到低 排序
- 对于MySQL的关键字,用作变量名时,要加符号`
- 对于要排序的字段为NULL时,asc NULL 在最前,desc NULL 在最后
- 可以对多个字段进行排序,优先级随书写顺序
查询各科成绩,按数学降序,英语升序,语文升序的方式显示
select * from exam_result order by math desc,chinese,english;
条件查询(where)
- 查询数学成绩>80的同学及成绩
select id,name,math from exam_result where math > 80;
- 查询数学成绩>80的同学及成绩,并升序排序
select id,name,math from exam_result where math > 80 order by math;
- 查询数学成绩=98的同学及成绩
select id,name,math from exam_result where math = 98;

注意:若成绩为null,则不能使用=,是查不到的,要使用<=>
- 查询数学成绩!=98的同学及成绩
select id,name,math from exam_result where math != 98;

注意:若成绩为null,则不能使用!=,是查不到的,要使用<>
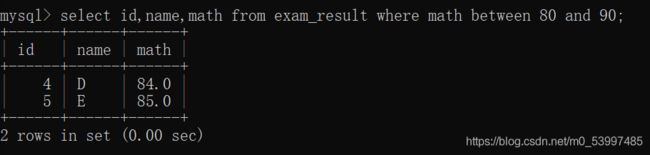
- 查询数学成绩在80~90
select id,name,math from exam_result where math between 80 and 90;
select id,name,math from exam_result where math >= 80 and math <= 90;

所以,between … and 的区间为闭区间,eg:[80,90]
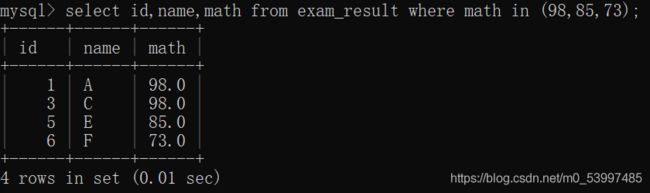
- 查询数学成绩为98,85,73的同学
select id,name,math from exam_result where math in (98,85,73);
select id,name,math from exam_result where math = 98 or math = 85 or math = 73;
- 查询数学成绩是否为null
我们先插入几个为数学成绩为null的同学
insert into exam_result (id,name,chinese,english) values(9,'I',78,97);
insert into exam_result (id,name,chinese,english) values(10,'J',56,32);
select id,name,math from exam_result where math is null;
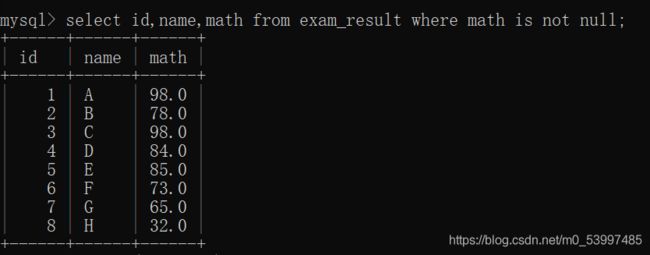
查询数学成绩不为null
select id,name,math from exam_result where math is not null;
- 模糊查询
查询名字包含“三”的
select * from exam_result where name like '%三%';
//代表一定是 三 开头的
select * from exam_result where name like '三%';
//代表一定是 三 结尾的
select * from exam_result where name like '%三';
%:代表通配符,表示任意数量的字符
-:表示一个字符
//代表一定是 三× 两个字
select * from exam_result where name like '三_';
//代表一定是 三×× 三个字
select * from exam_result where name like '三_ _';
注意:and 优先级 高于 or,同时使用时要加括号
分页查询(limit)
原因:数据量太大时,一次性查找数据的时候,系统会执行SQL语句,查询需要时间,这时有可能系统就会被卡住,所以,一般采取的优化的方案就是用 分页查询
原理:每次只查询,当前页需要显示的数据即可
如果 每页10条数据,那么只查询10条数据,每次点击下一页的时候,又会请求查询10条数据。这样就提高了效率
//方法1
select * from exam_result limit s,n;
//s 表示偏移位置 n 表示数据个数
//即从s开始取n个数据
eg:
select * from exam_result limit 0,5;

如果n的值过大,只会查询到能查询到的内容
如果s的值过大,SQL不会报错,但是什么也查不到
如果没有写s,默认是从0偏移开始取n个
select * from exam_result limit 5;
//方法2
select * from exam_result limit n offset s;
eg:
select * from exam_result limit 5 offset 0;
修改
- 将B同学的数学成绩修改为99
update exam_result set math = 99 where name = 'B';
- 将C同学的数学成绩改为60,语文成绩改为80
update exam_result set math = 60,chinese = 80 where name = 'C';
- 将总成绩倒数前三的同学的数学成绩+30
对于复杂的sql语句可以使用分步式思想,最终写出语句
①找出总成绩倒数前三的同学
select id,name,chinese+math+english sum from exam_result order by chinese+math+english limit 3;

注意:这里只要有一门成绩为null,则总成绩就为null
因为 null不能使用任何运算符与其他字段或变量进行运算
所以不建议order by 与 limit 一起使用
②更新数学成绩
update exam_result set math = math + 30;
最终写法为:
update exam_result set math = math + 30 order by chinese+math+english limit 3;