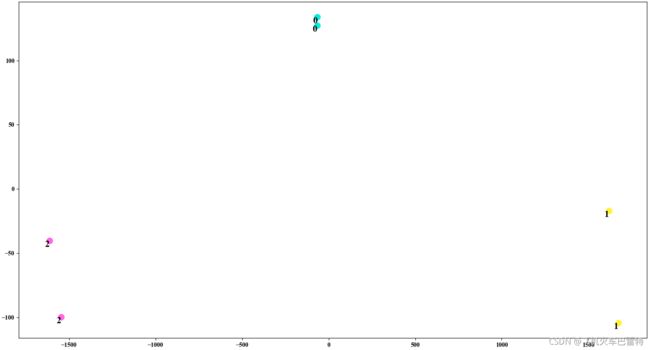
PCA降维+Python matplotlib绘制动态散点图
代码
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
def main():
# 打开交互模式
plt.ion()
# 设置plt参数
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (9 * 1920 / 1080, 9)
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Times New Roman']
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.06, right=0.94, top=0.92, bottom=0.08)
# 根据循环动态显示散点的变化
for i in range(1000):
# 清空当前的图
plt.clf()
# 设置plt参数
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (9 * 1920 / 1080, 9)
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Times New Roman']
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.06, right=0.94, top=0.92, bottom=0.08)
# 加载散点数据
xs, ys, ls, cs = get_data(i)
# 绘制散点
for index in range(len(xs)):
x = xs[index]
y = ys[index]
label = ls[index]
color = cs[index]
plt.scatter(x, y, c=color, s=90)
plt.text(x, y, label, fontsize=15, verticalalignment="top", horizontalalignment="right")
plt.draw()
# 暂停0.1秒
plt.pause(0.1)
# 切片:切成两边,一边是xs,另一边是ys
def row2col(data_list):
xs = [] # x list
ys = [] # y list
n = len(data_list)
for i in range(n):
xs.append(data_list[i][0])
ys.append(data_list[i][1])
return xs, ys
# 根据step动态更新数据
def get_data(step):
# 散点可取的颜色
color_1 = "#0CECDD" # teal
color_2 = "#FFF338" # yellow
color_3 = "#FF67E7" # pink
color_4 = "#C400FF" # purple
color_5 = "#170055" # navy
color_6 = "#3E00FF" # blue
color_7 = "#B5FFD9" # green
# 数据的增量(用于更新数据)
increment = [[0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1], [-0.1, -0.1, 0.1, 0.1], [0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1], [-0.1, 0.1, -0.1, 0.1], [0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1], [-0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1]]
data_list = [[0, 1, 2, -1], [20, 20, 20, -21], [999, 800, 798, 901], [900, 808, 805, 903], [-505, -606, -790, -1000], [-580, -616, -800, -1024]]
# 更新数据
for i in range(len(data_list)):
row = data_list[i]
for j in range(len(row)):
data_list[i][j] = data_list[i][j] + step * increment[i][j]
# 使用PCA对高维数据进行降维(得到2维数据)
pca_tool = PCA(n_components=2)
reduced_data_list = pca_tool.fit_transform(data_list)
# 对降维后的数据进行切片
xs, ys = row2col(reduced_data_list)
# 获取数据的标签、颜色(用于可视化)
clas_list = [0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]
colr_list = [color_1, color_1, color_2, color_2, color_3, color_3]
# 返回数据
return xs, ys, clas_list, colr_list
# 程序入口
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
效果