使用Python对图像进行不同级别量化QP,使用RLE计算压缩比,并计算对应的PSNR
1.效果图
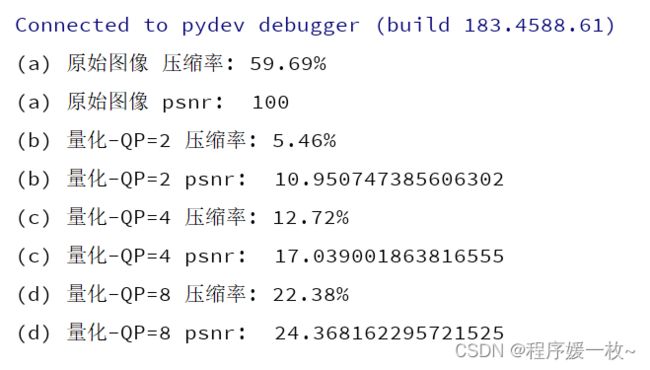
原图 VS QP=2 VS QP=4 VS QP=8效果图如下:
QP量化是指把原始图像按像素级别划分取值。如QP=2,则<128 取0,>128取128.
QP=4,则<64取0,<128取64,<192取128,<256取192.
QP=8,则<32取0,<64取32,<96取64,<128取96,<160取128,<192取160,<224取192,<256取224.

可以看出QP越大,压缩率越大,同时psnr越大,这表示跟原图相似性越好,越接近原图像。
PSNR 最小值为 0,PSNR 越大,两张图像差异越小;PSNR 计算简单,物理意义清晰,但是这种基于 MSE 的评价指标并不能很好的按人眼的感受来衡量两张图像的相似度
原始灰度图像 VS 原始图像rle后再反解码回去效果图如下:

原始灰度图像 VS qp=2图像rle后再反解码回去效果图如下:

原始灰度图像 VS qp=4图像rle后再反解码回去效果图如下:

原始灰度图像 VS qp=8图像rle后再反解码回去效果图如下:

2. 原理
-
量化(Quantization)旨在将图像像素点对应亮度的连续变化区间转换为单个特定值的过程,即将原始灰度图像的空间坐标幅度值离散化。量化等级越多,图像层次越丰富,灰度分辨率越高,图像的质量也越好;量化等级越少,图像层次欠丰富,灰度分辨率越低,会出现图像轮廓分层的现象,降低了图像的质量。
QP量化是指把原始图像按像素级别划分取值。如QP=2,则<128 取0,>128取128.
QP=4,则<64取0,<128取64,<192取128,<256取192.
QP=8,则<32取0,<64取32,<96取64,<128取96,<160取128,<192取160,<224取192,<256取224. -
行程编码(RLE) 在图像压缩上,行程编码一般用于压缩二值化图像,因为它是基于重复的压缩算法,比如:
二维图像降维后(压缩前):0 0 0 0 0 255 255 255 0 0 255
行程编码压缩后:5 0 3 255 2 0 1 255
(压缩格式为:数量+像素+数量+像素…)
如果有大量的像素连续重复,那么压缩率会更高。 -
PSNR(峰值信噪比,Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio),用于衡量两张图像之间差异,例如压缩图像与原始图像,评估压缩图像质量;复原图像与ground truth,评估复原算法性能等。

PSNR 最小值为 0,PSNR 越大,两张图像差异越小;
PSNR 计算简单,物理意义清晰,但是这种基于 MSE 的评价指标并不能很好的按人眼的感受来衡量两张图像的相似度
3. 源码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# By:Eastmount
# 1. 对图像进行 QP=2,QP=4,QP=8的量化并展示
# 2. 采用行程编码(RLE),计算压缩比;
# 3. 进行解码(反量化),并计算不同量化级别的PSNR值。
# python ask_img_qa_rle_psnr.py
import cv2
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 读取原始图像
img = cv2.imread('ml.jpg')
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 获取图像高度和宽度
height = img.shape[0]
width = img.shape[1]
# 创建一幅图像
new_img1 = np.zeros((height, width, 3), np.uint8)
new_img2 = np.zeros((height, width, 3), np.uint8)
new_img3 = np.zeros((height, width, 3), np.uint8)
# 图像量化等级为2的量化处理
for i in range(height):
for j in range(width):
for k in range(3): # 对应BGR三分量
if img[i, j][k] < 128:
gray = 0
else:
gray = 128
new_img1[i, j][k] = np.uint8(gray)
# 图像量化等级为4的量化处理
for i in range(height):
for j in range(width):
for k in range(3): # 对应BGR三分量
if img[i, j][k] < 64:
gray = 0
elif img[i, j][k] < 128:
gray = 64
elif img[i, j][k] < 192:
gray = 128
else:
gray = 192
new_img2[i, j][k] = np.uint8(gray)
# 图像量化等级为8的量化处理
for i in range(height):
for j in range(width):
for k in range(3): # 对应BGR三分量
if img[i, j][k] < 32:
gray = 0
elif img[i, j][k] < 64:
gray = 32
elif img[i, j][k] < 96:
gray = 64
elif img[i, j][k] < 128:
gray = 96
elif img[i, j][k] < 160:
gray = 128
elif img[i, j][k] < 192:
gray = 160
elif img[i, j][k] < 224:
gray = 192
else:
gray = 224
new_img3[i, j][k] = np.uint8(gray)
# 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
# 显示图像
titles = ['(a) 原始图像', '(b) 量化-QP=2', '(c) 量化-QP=4', '(d) 量化-QP=8']
images = [img, new_img1, new_img2, new_img3]
for i in range(4):
plt.subplot(2, 2, i + 1), plt.imshow(images[i], 'gray'),
plt.title(titles[i])
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
# 2. RLE计算压缩比
def rle(title, origin, img):
grayorigin = cv2.cvtColor(origin, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
grayimg = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
rows, cols = grayimg.shape
img = grayimg.flatten() # 把灰度化后的二维图像降维为一维列表
data = []
image3 = []
count = 1
# 行程压缩编码
for i in range(len(img) - 1):
if (count == 1):
image3.append(img[i])
if img[i] == img[i + 1]:
count = count + 1
if i == len(img) - 2:
image3.append(img[i])
data.append(count)
else:
data.append(count)
count = 1
if (img[len(img) - 1] != img[-1]):
image3.append(img[len(img) - 1])
data.append(1)
# 压缩率
ys_rate = len(image3) / len(img) * 100
print(str(title) + ' 压缩率: %.2f%s' % (ys_rate, '%'))
# 行程编码RLE解码
rec_image = []
for i in range(len(data)):
for j in range(data[i]):
rec_image.append(image3[i])
rec_image = np.reshape(rec_image, (rows, cols))
cv2.imshow('grayorigin VS ' + str(title) + 'res', np.hstack([grayorigin, rec_image])) # 重新输出二值化图像
cv2.waitKey(0)
plt.subplot()
plt.imshow(np.hstack([grayorigin, rec_image]), 'gray')
plt.title('grayOrigin VS ' + str(title) + '')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
print(str(title) + ' psnr: ', psnr2(grayorigin, rec_image))
# 3. 计算psnr
# 计算灰度图的psnr
def psnr1(img1, img2):
# compute mse
# mse = np.mean((img1-img2)**2)
mse = np.mean((img1 / 1.0 - img2 / 1.0) ** 2)
# compute psnr
if mse < 1e-10:
return 100
psnr1 = 20 * math.log10(255 / math.sqrt(mse))
return psnr1
# 计算彩色图的psnr
def psnr2(img1, img2):
mse = np.mean((img1 / 255.0 - img2 / 255.0) ** 2)
if mse < 1e-10:
return 100
psnr2 = 20 * math.log10(1 / math.sqrt(mse))
return psnr2
for i in range(0, 4):
rle(titles[i], images[0], images[i])
参考
- 对图像进行qp量化
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42233962/article/details/105482765
- psnr计算
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43605641/article/details/118088814
