android中的享元模式,设计模式之享元模式
作用
也叫蝇量模式。“享”:共享,“元”:对象。
常用于系统底层开发,解决系统的性能问题。像数据库连接池,池里都是创建好的连接对象,无需再创建直接拿来用。解决重复创建对象造成内存浪费的问题。
经典的应用场景就是池技术了,String常量池、数据库连接池、缓冲池。
也可理解为为业务加一层缓存。
原理
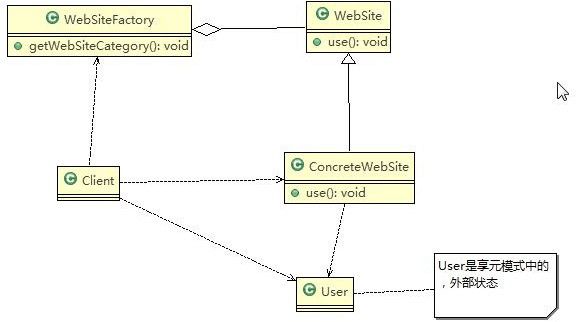
Flyweight:抽象的享元角色,是产品的抽象类,同时定义出对象的外部状态和内部状态的接口或实现。
ConcreteFlyweight:具体的享元角色,是具体的产品类,实现抽象角色,定义相关业务。
UnsharedConcreteFlyweight:不可共享的角色,一般不会出现在享元工厂。
FlyweightFactory:享元工厂类,用于构建一个池容器(集合),同时提供从池中获取对象的方法。
内部状态:指对象共享出来的信息,存储在享元对象内部且不会随环境的改变而改变。
外部状态:指对象得以依赖的一个标记,是随环境改变而改变的、不可共享的状态。
案例
抽象的享元角色
public abstract class Website {
public abstract void use(User user);
}
具体的享元角色
内部状态:type
外部状态:User
public class ConcreteWebsite extends Website {
private String type;
public ConcreteWebsite(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
@Override
public void use(User user) {
System.out.println(user.getName() + "正在使用" + type + "网站");
}
}
不可共享的角色
public class User {
private String name;
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
享元工厂类
public class WebsiteFactory {
private Map cache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public Website getWebsite(String type) {
if (!cache.containsKey(type)) {
cache.put(type, new ConcreteWebsite(type));
}
return cache.get(type);
}
public int getCacheSize() {
return cache.size();
}
}
调用
public class Client {
//Tom正在使用新闻网站
//Jack正在使用博客网站
//Smith正在使用博客网站
//Alice正在使用博客网站
//2
public static void main(String[] args) {
WebsiteFactory factory = new WebsiteFactory();
Website news = factory.getWebsite("新闻");
news.use(new User("Tom"));
Website blog = factory.getWebsite("博客");
blog.use(new User("Jack"));
Website blog2 = factory.getWebsite("博客");
blog2.use(new User("Smith"));
Website blog3 = factory.getWebsite("博客");
blog3.use(new User("Alice"));
System.out.println(factory.getCacheSize());
}
}
源码
java.lang.Integer#valueOf(int)
valueOf:享元工厂类中的方法,提供对象。
i:内部状态。
Integer:具体的享元角色。
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
调用:
Integer x = Integer.valueOf("127");
Integer y = Integer.valueOf("127");
System.out.println(x == y);//true