推荐算法学习-MXNET 矩阵分解应用实例
案例:Matrix-factorization
平台:MXNET
数据源下载: https://grouplens.org/datasets/movielens/
Step1. 自定义 DataIter和DataBatch,用于装载训练数据
源码:
import mxnet as mx
class SimpleBatch(object):
def __init__(self, data, label, pad=0):
self.data = data
self.label = label
self.pad = pad
class SimpleBatch(object):
def __init__(self, data, label, pad=0):
self.data = data
self.label = label
self.pad = pad
class CustDataIter:
def __init__(self, data_names, data_gen, data_shape,
label_names, label_gen, label_shape,ctx, batch_size,total_batches):
self.data_names = data_names
self.label_names = label_names
self.data_gen = data_gen
self.label_gen = label_gen
self.data_shape = data_shape
self.label_shape = label_shape
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.total_batches = total_batches
self.cur_batch = 0
# self.ctx = ctx
def __iter__(self):
return self
def reset(self):
self.cur_batch = 0
def __next__(self):
return self.next()
@property
def provide_data(self):
return zip(self.data_names,self.data_shape)
@property
def provide_label(self):
return zip(self.label_names,self.label_shape)
def next(self):
if self.cur_batch < self.total_batches:
data = []
for tdata in self.data_gen:
_data = tdata[self.cur_batch*self.batch_size:(self.cur_batch+1)*self.batch_size]
data.append(mx.nd.array(_data))
assert len(data) > 0, "Empty batch data."
label = []
for tlabel in self.label_gen:
_label = tlabel[self.cur_batch*self.batch_size:(self.cur_batch+1)*self.batch_size]
label.append(mx.nd.array(_label))
assert len(label) > 0, "Empty batch label."
self.cur_batch += 1
# print('Return batch %d' % self.cur_batch)
return SimpleBatch(data, label)
else:
raise StopIterationStep2. 加载电影文件数据,原始数据有4列,分别是User, Item, Rating,Timestamp,我们只会用到前面的3列
import numpy as np
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)def loadData(fname):
user = []
item = []
score = []
with open(fname) as f:
f.readline() #skip first line
while 1:
line = f.readline()
if line == '':#end of file:
break
tks = line.strip().split('\t')
if len(tks) != 4:
continue
user.append(tks[0])
item.append(tks[1])
score.append(tks[2])
return (user,item,score)Step3. 定义MXNET 训练网络。使用2个embedding 层来向量化 user和item,用于提取隐藏变量。然后进行内积,按列相加,并flatten成2D tensor,在传给linear regression output。
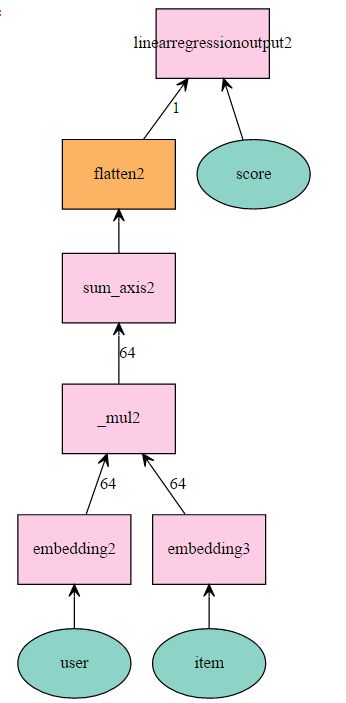
比如总共有n个user,m个item,定义最大的维度是k,则我们把user 表从(n,) embedding成为(n,k),每个user变成 一个k 维vector。 同理,Item变成 (m,k)。 每次输入一批size=batch的数据,则embedding后的shape是(batch,k)。 内积之后的shape仍然是(batch,k)。在用 sum_axis(axis=1),沿着列相加,最终变成 shape=(batch,)的vector,其中每一个元素分别对应的就是每个用户对item的rating。 我们再把这个vector flatten成 2-D数据 (batch,1),则最终传给output 层。 output层使用简单的线性输出即可。
def plain_net(k,max_user,max_item): # input user = mx.symbol.Variable('user') item = mx.symbol.Variable('item') score = mx.symbol.Variable('score') # user feature lookup user = mx.symbol.Embedding(data = user, input_dim = max_user, output_dim = k) # item feature lookup item = mx.symbol.Embedding(data = item, input_dim = max_item, output_dim = k) # predict by the inner product, which is elementwise product and then sum pred = user * item pred = mx.symbol.sum_axis(data = pred, axis = 1) pred = mx.symbol.Flatten(data = pred) # loss layer pred = mx.symbol.LinearRegressionOutput(data = pred, label = score) return pred
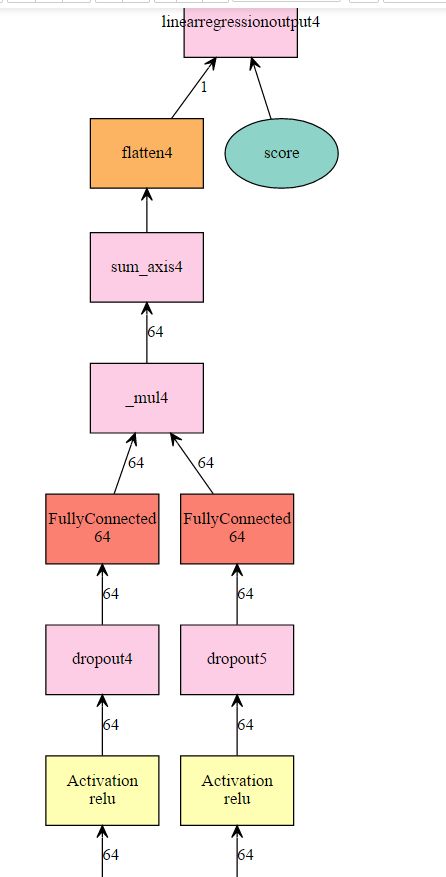
def get_one_layer_mlp(hidden, k,max_user,max_item): # input user = mx.symbol.Variable('user') item = mx.symbol.Variable('item') score = mx.symbol.Variable('score') # user latent features user = mx.symbol.Embedding(data = user, input_dim = max_user, output_dim = k,name='User_Embedding') user = mx.symbol.Activation(data = user, act_type="relu") #add dropout user = mx.symbol.Dropout(data = user, p = 0.5) user = mx.symbol.FullyConnected(data = user, num_hidden = hidden) # item latent features item = mx.symbol.Embedding(data = item, input_dim = max_item, output_dim = k,name='Item_Embedding') item = mx.symbol.Activation(data = item, act_type="relu") #add dropout item = mx.symbol.Dropout(data = item, p = 0.5) item = mx.symbol.FullyConnected(data = item, num_hidden = hidden) # predict by the inner product pred = user * item pred = mx.symbol.sum_axis(data = pred, axis = 1) pred = mx.symbol.Flatten(data = pred) # loss layer pred = mx.symbol.LinearRegressionOutput(data = pred, label = score) return pred
![]()
Step4. 训练函数。
def train(network,data_train_iter,data_valid_iter, context, num_epoch,learning, learning_rate):import logging logging.getLogger().setLevel(logging.DEBUG) model = mx.mod.Module( symbol = network, context=context, data_names=['user', 'item'], label_names=['score'] ) model.fit(train_data = data_train_iter, eval_data =data_valid_iter, optimizer =learning, optimizer_params={'learning_rate':learning_rate,}, #'momentum':0.9,'wd':0.00005 eval_metric = 'RMSE', num_epoch = num_epoch, ) return model def trainingModel(): TRAIN_DIR = 'PycharmProjects/mxnetlearn/data/movie/ml-100k/' user,item,score = loadData(TRAIN_DIR+'u1.base') # user,item,score = loadData(TRAIN_DIR+'ratings.csv') # t_user,t_item,t_score=loadData(TRAIN_DIR+'u1.test') data = np.array([user,item]) print (data.shape) label = np.array([score]) # t_data = np.array([t_user,t_item]) # t_label = np.array([t_score]) context = mx.gpu() BATCH_SIZE = 800 kdims = 64 num_epoch = 5 trainIter = CustDataIter(['user','item'],data,[(BATCH_SIZE,),(BATCH_SIZE,)], ['score'],label,[(BATCH_SIZE,)],context,BATCH_SIZE,data.shape[1]/BATCH_SIZE) # testIter = CustDataIter(['user','item'],t_data,[(BATCH_SIZE,),(BATCH_SIZE,)], # ['score'],t_label,[(BATCH_SIZE,)],context,BATCH_SIZE,t_data.shape[1]/BATCH_SIZE) import pandas as pd pd_user=pd.Series(user).unique() user_nd=mx.nd.array(pd_user) pd_item=pd.Series(item).unique() item_nd=mx.nd.array(pd_item) max_user = user_nd.shape[0] max_item = item_nd.shape[0] net =get_one_layer_mlp(hidden=64,k=kdims,max_user=max_user,max_item=max_item) # mx.viz.plot_network(network,shape={'data':(128,3,227,227),'data2':(128,300)}) ##Train module mode = train(net,trainIter,None,context,num_epoch=num_epoch,learning = 'sgd',learning_rate=0.05) #save model mode.save_checkpoint('data/matrixfactor_model_checkpoint',0) # load model mode = reloadModel(context=context,batch=BATCH_SIZE,fname='data/matrixfactor_model_checkpoint') #print embedded matrix W_user = mode.get_params()[0]['User_Embedding_weight'] usermatrix = forwardEmbedding(maxinputdim=max_user,W=W_user,K=kdims,dataname='user',data=user_nd,context=context) print (usermatrix) W_item = mode.get_params()[0]['Item_Embedding_weight'] itemmatrix = forwardEmbedding(maxinputdim=max_item,W=W_item,K=kdims,dataname='item',data=item_nd,context=context) print (itemmatrix)if __name__ == '__main__': trainingModel()
Step5. 结果
采用RMSE进行衡量,迭代1000次以后,基本可以达到0.9
INFO:root:Epoch[0] Train-RMSE=2.347769 INFO:root:Epoch[0] Time cost=0.850 INFO:root:Epoch[1] Train-RMSE=1.115457 INFO:root:Epoch[1] Time cost=0.409 INFO:root:Epoch[2] Train-RMSE=1.115395 INFO:root:Epoch[2] Time cost=0.410 INFO:root:Epoch[3] Train-RMSE=1.115343 INFO:root:Epoch[3] Time cost=0.397 INFO:root:Epoch[4] Train-RMSE=1.115271 INFO:root:Epoch[4] Time cost=0.393 INFO:root:Saved checkpoint to "data/matrixfactor_model_checkpoint-0000.params"
Step6. 衍生应用
展开embedding 层的结果,可以得到user和item的向量表示。每个元素代表了其中一个隐藏属性。因此可以对这些user或者item进行K-means等聚类。从而获取相邻用户群,后者相似item。获取embedding层输出代码如下:
# load model
mode = reloadModel(context=context,batch=BATCH_SIZE,fname='data/matrixfactor_model_checkpoint')
#print embedded matrix
W_user = mode.get_params()[0]['User_Embedding_weight']
# usermatrix = forwardEmbedding(maxinputdim=max_user,W=W_user,K=kdims,dataname='user',data=user_nd,context=context)
# print (usermatrix)
usermatrix = mx.nd.Embedding(user_nd,W_user,user_nd.shape[0],kdims).asnumpy()
print('------------user matrix------------')
print (usermatrix)
W_item = mode.get_params()[0]['Item_Embedding_weight']
# itemmatrix = forwardEmbedding(maxinputdim=max_item,W=W_item,K=kdims,dataname='item',data=item_nd,context=context)
itemmatrix = mx.nd.Embedding(item_nd,W_item,item_nd.shape[0],kdims).asnumpy()
print('------------item matrix------------')
print (itemmatrix)