Vue业务组件封装(二)Form表单
前言
这个系列主要是分享自己在工作中常用到的业务组件,以及如何对这些组件进行有效的封装和封装的思路。注:都是基于element ui进行二次封装。
封装组件的基本方法就是通过props和emit进行父子组件的传值和通信。利用插槽、组件等增加组件的可扩展性和复用性。
Form组件介绍
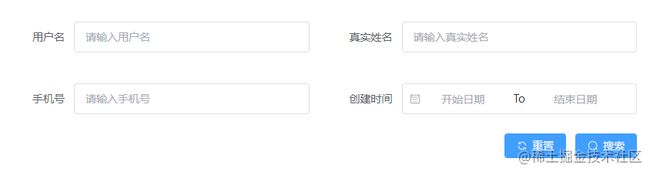
Form表单包含 输入框, 单选框, 下拉选择, 多选框 等用户输入的组件。使用表单,可以收集、验证和提交数据。
表单常用的地方是在搜索、信息提交、内容编辑以及新增。
搜索表单
编辑表单
Form组件封装思路
了解element Form组件代码
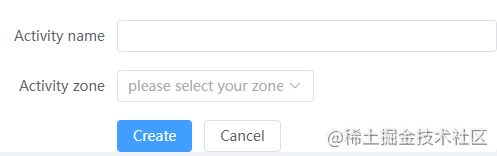
这里以最基本的Form代码为例进行分析:
Create
Cancel
const form = reactive({
name: '',
region: ''
})
基本表单
根据基本的Form代码,我们可以知道:
- 整个Form表单数据绑定在el-form上::model=“form”,form就是表单的数据对象。
- 表单里面的每一项是放在el-form-item标签里面,放入我们想渲染出来的组件,如输入框,单选等。
- 每个el-form-item中可以绑定了prop、label、rules等属性,我们可以在配置文件中配置对应属性的值进行绑定。
Form组件如何去封装
通过分析Form代码我们可以通过一个配置文件去遍历得到el-form-item,然后在el-form-item上面绑定我们需要的属性就可以得到我们想要的表单。
代码实现
配置文件
我们可以在页面文件夹下面新建一个文件夹config用于存放页面需要的各种配置文件,在里面新建我们表单的配置文件formConfig.ts:
import { IForm } from '@/components/Form/types'
import { rules } from '@/utils/validator'
export const modalConfig: IForm = {
formItems: [
{
field: 'name',
label: '用户名',
placeholder: '请输入用户名',
type: 'input',
rule: [{ required: true, message: 'Please input name', trigger: 'blur' }]
},
{
field: 'realname',
type: 'input',
label: '真实姓名',
placeholder: '请输入真实姓名',
rule: [
{ required: true, message: 'Please input realname', trigger: 'blur' }
]
},
{
field: 'password',
type: 'password',
label: '用户密码',
placeholder: '请输入密码',
isHidden: false,
rule: [
{ required: true, message: 'Please input password', trigger: 'blur' }
]
},
{
field: 'cellphone',
type: 'input',
label: '电话号码',
placeholder: '请输入电话号码',
rule: [
{
required: true,
message: '请输入正确手机号码',
validator: (rule: any, value: any) => /^1\d{10}$/.test(value)
}
]
},
{
field: 'departmentId',
type: 'select',
label: '部门',
placeholder: '请选择部门',
options: [],
rule: [
{
required: true,
message: 'Please input departmentId',
trigger: 'change'
}
]
},
{
field: 'roleId',
type: 'select',
label: '角色',
placeholder: '请选择角色',
options: [],
rule: [
{ required: true, message: 'Please input roleId', trigger: 'change' }
]
}
],
labelWidth: '80px',
colLayout: {
xl: 5,
lg: 8,
md: 12,
sm: 24,
xs: 24
}
}
formItems里面每一项就对应表单里的每一个el-form-item,里面的属性绑定到el-form-item上。
- field:必填,表示的是我们提交时的key,要与接口提供的字段名一致。
- type:必填,表示我们显示表单的种类。
- label:表单的标签文本。
- placeholder:输入框显示提示文案。
- options:选项,如select里面的options。
- rule:表单的校验规则,如果不是必填就不用写。
- labelWidth:表单label的宽度。
- colLayout:表单的布局,这里做了一个响应式设置。
还可以设置一些其他属性,具体根据实际业务需求。
新建LForm组件
我们在components文件夹下新建一个LForm表示我们封装的Form组件。基于El-Form组件的基本代码,我们写下LTable下代码内容:
Check all
{{ optionItem.label }}
{{ _item.label }}
{{ optionItem.label }}
{{ optionItem.label }}
{{ item.otherOptions.tip }}
![]()
选择上传文件
{{ item.otherOptions.tip }}
modelValue为双向绑定数据对象,通过modelValue[${item.field}]进行数据双向绑定。表单改变时调用handleValueChange方法更新数据到父组件,然后在父组件进行提交。
上传组件逻辑相对麻烦,这里将他们分别用hook进行了抽离:
use-uploadFile.ts:
import { ref } from 'vue'
import type { UploadProps, UploadRawFile, UploadInstance } from 'element-plus'
import { ElMessage, genFileId } from 'element-plus'
type fn = (value: any, field: string) => void
export const useUploadFile = (props: any, handleValueChange: fn) => {
const uploadRef = ref()
// 文件移除
const handleRemove: UploadProps['onRemove'] = (file, uploadFiles) => {
handleValueChange('', 'file')
}
// 在 before-upload 钩子中限制用户上传文件的格式和大小
const beforeFileUpload: UploadProps['beforeUpload'] = (
rawFile: UploadRawFile
) => {
if (props.type && !props.type.includes(rawFile.type as any)) {
const formatStr = props.type.join(',')
ElMessage.error(`File must be ${formatStr} format`)
return false
} else if (props.size && rawFile.size / 1024 / 1024 > props.size) {
ElMessage.error(`File size can not exceed ${props.size}MB!`)
return false
}
return true
}
// 文件上传成功时的钩子
const handleFileSuccess: UploadProps['onSuccess'] = (
response,
uploadFile
) => {
handleValueChange(uploadFile.raw, 'file')
}
// 文件替换
const handleExceed: UploadProps['onExceed'] = (files: File[]) => {
console.log(uploadRef.value, 'upload.value')
uploadRef.value && uploadRef.value.clearFiles()
const file = files[0] as UploadRawFile
file.uid = genFileId()
uploadRef.value && uploadRef.value.handleStart(file)
}
return [
uploadRef,
handleRemove,
beforeFileUpload,
handleFileSuccess,
handleExceed
]
}
use-uploadImg.ts:
import { ref, toRefs } from 'vue'
import type { UploadProps, UploadRawFile, UploadFile } from 'element-plus'
import { ElMessage } from 'element-plus'
type fn = (value: any, field: string) => void
export const useUploadImg = (props: any, handleValueChange: fn) => {
const { modelValue } = toRefs(props)
const imageUrl = ref(modelValue.value.img)
// 图片上传
// 在 before-upload 钩子中限制用户上传文件的格式和大小
const beforeAvatarUpload = (rawFile: UploadRawFile, otherOptions: any) => {
if (otherOptions.type && !otherOptions.type.includes(rawFile.type as any)) {
const formatStr = otherOptions.type.join(',')
ElMessage.error(`Avatar picture must be ${formatStr} format`)
return false
} else if (props.size && rawFile.size / 1024 / 1024 > otherOptions.size) {
ElMessage.error(`Avatar picture size can not exceed ${props.size}MB!`)
return false
}
return true
}
// 上传成功时的钩子
const handleAvatarSuccess: UploadProps['onSuccess'] = (
response,
uploadFile: UploadFile
) => {
handleValueChange(uploadFile.raw, 'img')
imageUrl.value = URL.createObjectURL(uploadFile.raw as any)
}
return [imageUrl, beforeAvatarUpload, handleAvatarSuccess]
}
hooks文件将我们组件需要用到的方法和属性进行返回。
效果
总结
Form组件的封装思路就是通过配置文件生成一个基本的表单,然后配合数据的双向绑定得到我们提交的数据。
exceed ${props.size}MB!`)
return false
}
return true
}
// 上传成功时的钩子
const handleAvatarSuccess: UploadProps[‘onSuccess’] = (
response,
uploadFile: UploadFile
) => {
handleValueChange(uploadFile.raw, ‘img’)
imageUrl.value = URL.createObjectURL(uploadFile.raw as any)
}
return [imageUrl, beforeAvatarUpload, handleAvatarSuccess]
}
hooks文件将我们组件需要用到的方法和属性进行返回。
[外链图片转存中...(img-jmfo1oPW-1656318443637)]
效果
### 总结
Form组件的封装思路就是通过配置文件生成一个基本的表单,然后配合数据的双向绑定得到我们提交的数据。