张正友相机标定(含python代码)笔记
张正友相机标定(含python代码)笔记
一、摘要
使用个人相机拍摄一组棋盘格标定图片,采用张正友相机标定法完成对拍摄设备进行标定的实验任务,求出相机的内、外参数,以及畸变参数并对实验得到的数据进行分析。
二、实验原理
(1)首先,从世界坐标系转换为相机坐标系,这一步是三维点到三维点的转换,包括 R,t (旋转矩阵和平移矩阵)等参数;

公式:
Xcam=R(Xw-Cw)
其中: R 表示旋转矩阵
X 表示 P 点在世界坐标系中的位置
Cw 表示相机原点 C 在世界坐标系中的位置
Xcam 表示 P 点在相机坐标系中的位置
(2)接着,是从相机坐标系转为图像坐标系,这一步是三维点到二维点的转换,包括 K (相机内参)等参数;

其中: C 点表示相机坐标系的中心点;
Z 轴表示相机坐标系的主轴;
π平面表示相机的像平面;
p 点表示主点,主轴与像平面相交的点;
C 点到 p 点的距离表示相机的焦距。
像平面上的 x 和 y 坐标轴是与相机坐标系上的 X 和 Y 坐标轴互相平行的; 相机坐标系是以 XYZ 三个轴组成的且原点在 C 点; 像平面坐标系是以 x ,y(小写)两个轴组成的且原点在 p 点

根据焦距与 Z 的关系,由相似三角形得:

偏移量
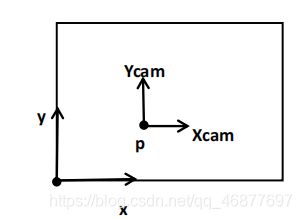
如上图所示,其中主点 p 是像平面坐标系的原点,但在图像坐标系中的位置为(px,py) 在这里,图形坐标系的原点是图片的左下角,所以可以得到:
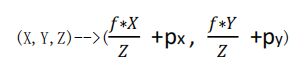

三、实验器材
1 摄像设备:手机型号 vivo X27(V1829A)
2标定图像:打印的 7×14 棋盘格(图像 10–50张),一个格子宽度 为 18mm
3Python(代码)
四、实验流程
1.准备图片。采用手机摄像机定焦拍摄不同角度的图片
2. 对每张图片提取角点信息
3. 对每张图片,进一步提取亚像素角点信息
4. 相机标定
5. 畸变矫正,计算内外参数和畸变系数 6. 画坐标轴,和三维立体盒子.
五、python代码
1.生成棋盘格
import cv2
import sys
import numpy as np
image = np.ones([1080, 1920, 3], np.uint8) * 255
x_nums = 14
y_nums = 7
square_pixel = 120 # 1080/9 = 120 pixels
x0 = square_pixel
y0 = square_pixel
def DrawSquare():
flag = -1
for i in range(y_nums):
flag = 0 - flag
for j in range(x_nums):
if flag > 0:
color = [0,0,0]
else:
color = [255,255,255]
cv2.rectangle(image,(x0 + j*square_pixel,y0 + i*square_pixel),
(x0 + j*square_pixel+square_pixel,y0 + i*square_pixel+square_pixel),color,-1)
flag = 0 - flag
cv2.imwrite('D:/chess_map_14x7.bmp',image)
if __name__ == '__main__':
DrawSquare()
2.相机标定
import cv2
import numpy as np
import glob
#criteria:角点精准化迭代过程的终止条件
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER, 30, 0.001)
#棋盘格模板规格
len = 18#黑白格长度
w = 6
h = 13
# 世界坐标系中的棋盘格点,例如(0,0,0), (1,0,0), (2,0,0) ....,(8,5,0),去掉Z坐标,记为二维矩阵
world_point = np.zeros((w*h, 3), np.float32)#初始化一个6*13行3列的矩阵,类型为float
#把每一个世界坐标的xy赋值[:,:2]中,:表示列表的所有字列表全部,:2表示从1截止到第二个数字
world_point[:, :2] = np.mgrid[0:w*len:len, 0:h*len:len].T.reshape(-1, 2)
# 储存棋盘格角点的世界坐标和图像坐标对
world_points = [] # 在世界坐标系中的三维点
imgpoints = [] # 在图像平面的二维点
j=1
images = glob.glob('*.jpg')#读取所有jpg文件
for fname in images:
img = cv2.imread(fname)
#将图片缩小
img = cv2.resize(img,None,fx=0.4, fy=0.4, interpolation = cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 找到棋盘格角点
#寻找角点,存入corners,ret是找到角点的flag(如果找到角点则为true)
ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray, (w, h), None)
# 如果找到足够点对,将其存储起来
if ret is True:
cv2.cornerSubPix(gray, corners, (11, 11), (-1, -1), criteria)
#加入到世界坐标系
world_points.append(world_point)
#角点加入到图像坐标系
imgpoints.append(corners)
# 将角点在图像上显示
cv2.drawChessboardCorners(img, (w, h), corners, ret)
cv2.imshow('findCorners', img)
cv2.waitKey(1)
print(str(j)+"完成\n")
j+=1
else:
print('错误')
j+=1
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
#求解摄像机的内在参数和外在参数。mtx 内参数矩阵,dist 畸变系数,rvecs 旋转向量,tvecs 平移向量
ret, mtx, dist, rvecs, tvecs = cv2.calibrateCamera(world_points, imgpoints, gray.shape[::-1], None, None)
# 找棋盘格角点
# 去畸变
img2 = cv2.imread('1.jpg')
img2= cv2.resize(img2,None,fx=0.4, fy=0.4, interpolation = cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
cv2.imshow("畸变图像", img2)
cv2.waitKey(100)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
h, w = img2.shape[:2]
#内参数矩阵
newcameramtx, roi = cv2.getOptimalNewCameraMatrix(mtx, dist, (w, h), 0, (w, h)) # 自由比例参数
#校正后图像
dst = cv2.undistort(img2, mtx, dist, None, newcameramtx)
cv2.imwrite('calibresult.png', dst)
f = open('内参数矩阵.txt', 'w+')
f.write('内参数矩阵:\n'+str(newcameramtx)+'\n')
f.close()
print('内参数输出完毕')
f = open('外参数矩阵.txt', 'w+')
#得到旋转矩阵与平移
for t in range(0,j-1):#向量变为矩阵
newrvecs=cv2.Rodrigues(rvecs[t].ravel())
newtvecs=cv2.Rodrigues(tvecs[t].ravel())
f.write('第'+str(t+1)+'张图像的外参数矩阵:\n'+'(1)旋转矩阵:\n'+str(newrvecs[0])+'\n'+'(2)平移矩阵:\n'+str(newtvecs[0])+'\n')
t+=1
f.close()
print('外参数输出完毕')
f = open('畸变系数.txt', 'w+')
f.write('畸变系数:\n'+str(dist)+'\n')
f.close()
print('结果输出完毕')
np.savez('data.npz', mtx= mtx, dist= dist,rvecs=rvecs,tvecs=tvecs)
print('*.npz文件输出完毕')
3.画三维坐标轴与立方体
import cv2
import numpy as np
import glob
#加载数据
with np.load('data.npz') as X:
#加载上一部生成的参数
mtx, dist, _, _= [X[i] for i in ('mtx','dist','rvecs','tvecs')]
#criteria:角点精准化迭代过程的终止条件
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER, 30, 0.001)
#棋盘格模板规格
len = 18#黑白格长度
w = 6
h = 13
#画坐标轴和立方体
def draw(img, corners, imgpts,imgpts2):
corner=tuple(corners[0].ravel())#ravel()方法将数组维度拉成一维数组
# img要画的图像,corner起点,tuple终点,颜色,粗细
img= cv2.line(img, corner, tuple(imgpts2[0].ravel()), (255,0,0), 8)
img= cv2.line(img, corner, tuple(imgpts2[1].ravel()), (0,255,0), 8)
img= cv2.line(img, corner, tuple(imgpts2[2].ravel()), (0,0,255), 8)
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
cv2.putText(img,'X',tuple(imgpts2[0].ravel()+2), font, 1,( 255,0,0),2,cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(img,'Y',tuple(imgpts2[1].ravel()+2), font, 1,( 0,255,0),2,cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(img,'Z',tuple(imgpts2[2].ravel()+2), font, 1,( 0,0,255),2,cv2.LINE_AA)
imgpts= np.int32(imgpts).reshape(-1,2)#draw ground floor in green
for i,j in zip(range(4),range(4,8)):#正方体顶点逐个连接
img= cv2.line(img, tuple(imgpts[i]), tuple(imgpts[j]),(255,215,0),3)#draw top layer in red color
#imgpts[4:]是八个顶点中上面四个顶点
#imgpts[:4]是八个顶点中下面四个顶点
#用函数drawContours画出上下两个盖子,它的第一个参数是原始图像,第二个参数是轮廓,一个python列表,第三个参数是轮廓的索引(当设置为-1时绘制所有轮廓)
img = cv2.drawContours(img, [imgpts[4:]],-1,(255,215,0),3)
img = cv2.drawContours(img, [imgpts[:4]],-1,(255,215,0),3)
return img
objp= np.zeros((w*h,3), np.float32)
objp[:,:2] = np.mgrid[0:w*len:len,0:h*len:len].T.reshape(-1,2)
axis = np.float32([[0,0,0], [0,2*len,0], [2*len,2*len,0], [2*len,0,0],
[0,0,-2*len],[0,2*len,-2*len],[2*len,2*len,-2*len],[2*len,0,-2*len] ])
axis2= np.float32([[3*len,0,0], [0,3*len,0], [0,0,-3*len]]).reshape(-1,3)
images = glob.glob('*.jpg')
i=1;
for fname in images:
img = cv2.imread(fname)
img = cv2.resize(img,None,fx=0.4, fy=0.4, interpolation = cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 找到棋盘格角点
#寻找角点,存入corners,ret是找到角点的flag
ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray, (w, h), None)
if ret is True:
corners2= cv2.cornerSubPix(gray,corners,(11,11),(-1,-1),criteria)
#求解物体位姿的需要
_,rvecs, tvecs, inliers =cv2.solvePnPRansac(objp, corners2, mtx, dist)
#projectPoints()根据所给的3D坐标和已知的几何变换来求解投影后的2D坐标。
#imgpts是整体的8个顶点
imgpts,_=cv2.projectPoints(axis, rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist)
#imgpts2是三个坐标轴的x,y,z划线终点
imgpts2, _ =cv2.projectPoints(axis2, rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist)
img=draw(img,corners2,imgpts,imgpts2)
cv2.imshow('世界坐标系与小盒子',img)
cv2.imwrite(str(i)+'.png', img)
cv2.waitKey(1000)
i+=1;
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
print("完毕")




