进阶——MyBatis-Plus快速入门
1、快速入门
官方链接:https://baomidou.com/guide/
导入Pom配置文件
创建springboot项目时选lombok和mysql就行,这里导入个mp的依赖
mysql mysql-connector-java runtime org.projectlombok lombok com.baomidou mybatis-plus-boot-starter 3.0.5 com.h2database h2 runtime org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-test test
连接数据库配置
#数据库连接配置 spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root #mysql5~8 驱动不同driver-class-name 8需要增加时区的配置serverTimezone=UTC #useSSL=false 安全连接 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis_plus?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
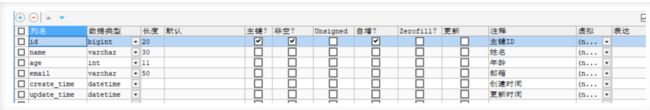
编写实体类
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
}
编写实体类对应的mapper接口
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.mapper.BaseMapper; import com.wsk.pojo.User; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; //在对应的接口上面继承一个基本的接口 BaseMapper @Repository//代表持久层 public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper{ //所有CRUD操作都编写完成了,不用像以前一样配置一大堆文件 }
在主启动类添加@MapperScan注解
package com.tpac;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@MapperScan("com.tpac.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class MybatisPlusApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MybatisPlusApplication.class, args);
}
}
进行Test测试
@SpringBootTest
class MybatisPlusApplicationTests {
//继承了BaseMapper,所有的方法都来自父类,我们也可以编写自己的扩展方法!
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
//参数是一个wrapper ,条件构造器,这里我们先不用 null
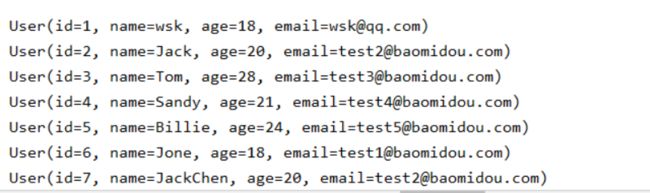
List userList = userMapper.selectList(null);//查询全部的用户
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
结果
2、配置日志
我们所有的sql是不可见的,我们希望知道他们是怎么执行的,所以要配置日志知道
#配置日志 log-impl:日志实现 mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
3、CRUD扩展
Insert
@Test//测试插入
public void insertTest(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("wsk");
user.setAge(18);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
Integer result = userMapper.insert(user); //会帮我们自动生成id
System.out.println(result); //受影响的行数
System.out.println(user); //通过日志发现id会自动回填
}
数据库插入的id的默认值为:全局的唯—id
主键生成策略
源码解释
public enum IdType {
AUTO, //数据库id自增
INPUT, //手动输入
ID_WORKER, //默认的全局唯一id
UUID, //全局唯一id uuid
NONE;//未设置主键
**
}
默认 : ID_WORKER 全局唯一Id
分布式系统唯一Id生成:分布式系统唯一ID生成方案汇总 - nick hao - 博客园
主键自增:AUTO 我们需要配置主键自增
我们需要配置主键自增
- 在实体类字段上配置@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
- 数据库字段一定是自增
手动输入:INPUT 就需要自己写id
- 在实体类字段上配置@TableId(type = IdType.INPUT)
Update
@Test//测试更新
public void updateTest(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(2L);//怎么改id??
//通过条件自动拼接动态Sql
user.setName("root");
user.setAge(12);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
int i = userMapper.updateById(user);//updateById,但是参数是个user
System.out.println(i);
}
自动填充
创建时间、更改时间! 这些操作一般都是自动化完成,我们不希望手动更新
阿里巴巴开发手册︰几乎所有的表都要配置 gmt_create、gmt_modified !而且需要自动化
方式一:数据库级别(工作中不允许修改数据库级别)
1、在表中增加字段:create_time,update_time
2、再次测试插入或更新方法,我们需要在实体类中同步!
private Date createTime;//驼峰命名 private Date updateTime;
3、查看结果
方式二:代码级别
1、删除数据库的默认值,更新操作!
2、实体类字段属性上需要增加注解
//字段 字段添加填充内容
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)//value = ("create_time"),
private Date createTime;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Date updateTime;
3、编写处理器来处理这个注解即可!
@Slf4j//日志
@Component//丢到springboot里 一定不要忘记把处理器加到Ioc容器中!
public class MyMetaObjectHandler extends MetaObjectHandler {//extends??
@Override//插入时的填充策略
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
log.info("==start insert ······==");
//setFieldValByName(java.lang.String fieldName, java.lang.Object fieldVal, org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject metaObject)
this.setFieldValByName("createTIme",new Date(),metaObject);
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
}
@Override//更新时的填充策略
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
log.info("==start update ······==");
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
}
}
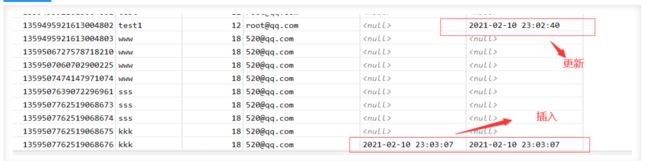
4、测试插入/更新,观察时间
@Test//测试插入
public void insertTest(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("live");
user.setAge(22);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
Integer result = userMapper.insert(user); //会帮我们自动生成id
System.out.println(result); //受影响的行数
System.out.println(user); //通过日志发现id会自动回填
}
@Test//测试更新
public void updateTest(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1359495921613004803L);
user.setName("test3");
user.setAge(18); //通过条件自动拼接动态Sql
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
int i = userMapper.updateById(user);//updateById,但是参数是个user
System.out.println(i);
}
乐观锁&悲观锁
在面试过程中经常被问到乐观锁/悲观锁,这个其实很简单
乐观锁:顾名思义十分乐观,他总是认为不会出现问题,无论干什么都不上锁!如果出现了问题,再次更新值测试
悲观锁:顾名思义十分悲观,他总是认为出现问题,无论干什么都会上锁!再去操作!
我们这里主要讲解 乐观锁机制!
乐观锁实现方式:
- 取出记录时,获取当前version
- 更新时,带上这个version
- 执行更新时,set version = newVersion where version = oldVersion
- 如果version不对,就更新失败
乐观锁:先查询,获得版本号 -- A update user set name = "wsk",version = version+1 where id = 1 and version = 1 -- B (B线程抢先完成,此时version=2,会导致A线程修改失败!) update user set name = "wsk",version = version+1 where id = 1 and version = 1
测试一下Mybatis-Plus乐观锁插件
1、给数据库中增加version字段
2、实体类加对应的字段
@Version//乐观锁version注解 private Integer version;
3、注册组件
//扫描mapper文件夹
@MapperScan("com.tpac.mapper")//交给mybatis做的,可以让这个配置类做扫描
@EnableTransactionManagement//自动管理事务
@Configuration//配置类
public class MyBatisPlusConfig {
//注册乐观锁插件
@Bean
public OptimisticLockerInterceptor optimisticLockerInterceptor(){
return new OptimisticLockerInterceptor();
}
}
4、测试一下
- 成功
@Test//测试乐观锁成功
public void testOptimisticLocker1(){
//1、查询用户信息
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
//2、修改用户信息
user.setAge(18);
user.setEmail("[email protected]");
//3、执行更新操作
userMapper.updateById(user);
}
- 失败
@Test//测试乐观锁失败 多线程下
public void testOptimisticLocker2(){
//线程1
User user1 = userMapper.selectById(1L);
user1.setAge(1);
user1.setEmail("[email protected]");
//模拟另外一个线程执行了插队操作
User user2 = userMapper.selectById(1L);
user2.setAge(2);
user2.setEmail("[email protected]");
userMapper.updateById(user2);
//自旋锁来多次尝试提交!
userMapper.updateById(user1);//如果没有乐观锁就会覆盖插队线程的值
}
Select
- 通过id查询单个用户
@Test//通过id查询单个用户
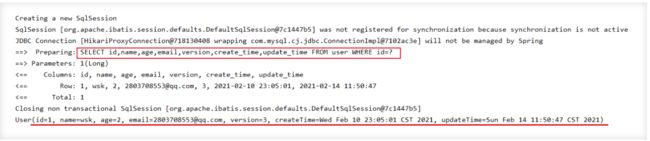
public void testSelectById(){
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
System.out.println(user);
}
- 通过id查询多个用户
@Test//通过id查询多个用户
public void testSelectBatchIds(){
List users = userMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1L, 2L, 3L));
users.forEach(System.out::println);
//System.out.println(users);
}
- 条件查询 通过map封装
@Test//通过条件查询之一 map
public void testMap(){
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
//自定义要查询的
map.put("name","www");
map.put("age",18);
List users = userMapper.selectByMap(map);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
分页查询
分页在网站的使用十分之多!
1、原始的limit分页
2、pageHelper第三方插件
3、MybatisPlus其实也内置了分页插件!
如何使用:
1、配置拦截器组件
//分页插件
@Bean
public PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor() {
return new PaginationInterceptor();
}
2、直接使用page对象即可
@Test//测试分页查询
public void testPage(){
//参数一current:当前页 参数二size:页面大小
//使用了分页插件之后,所有的分页操作都变得简单了
Page page = new Page<>(2,5);
userMapper.selectPage(page,null);
page.getRecords().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("总页数==>"+page.getTotal());
}
Delete
基本的删除任务:
@Test
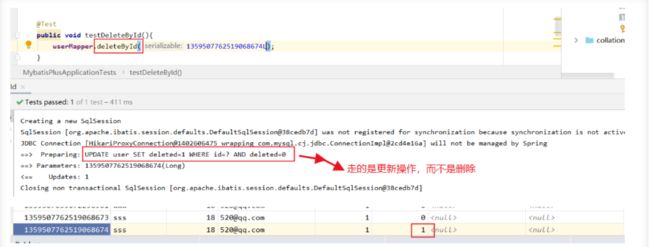
public void testDeleteById(){
userMapper.deleteById(1359507762519068681L);
}
@Test
public void testDeleteBatchIds(){
userMapper.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1359507762519068675L,1359507762519068676L));
}
@Test
public void testD(){
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("age","18");
map.put("name","lol");
userMapper.deleteByMap(map);
}
我们在工作中会遇到一些问题:逻辑删除!
逻辑删除
物理删除:从数据库中直接删除
逻辑删除:在数据库中没有被删除,而是通过一个变量来使他失效! deleted=0 ==> deleted=1
管理员可以查看被删除的记录!防止数据的丢失,类似于回收站!
测试一下:
1、在数据表中增加一个deleted字段
2、实体类中添加对应属性
@TableLogic//逻辑删除注解 private Integer deleted;
3、配置!
//逻辑删除组件
@Bean
public ISqlInjector sqlInjector(){
return new LogicSqlInjector();
}
#配置逻辑删除 没删除的为0 删除的为1 mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-delete-value=1 mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-not-delete-value=0
4、测试一下删除
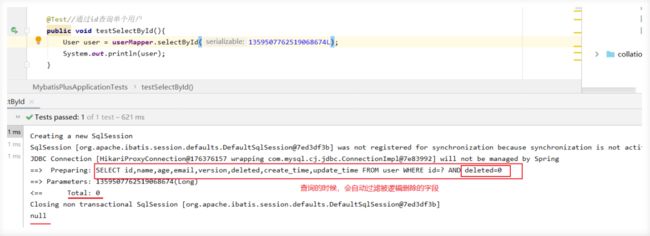
发现: 记录还在,deleted变为1
再次测试查询被删除的用户,发现查询为空
以上所有的CRUD及其扩展操作,我们都必须精通掌握!会大大提高工作写项目的效率!
4、性能分析插件
我们在平时的开发中,会遇到一些满Sql。测试、druid···
MybatisPlus也提供了性能分析插件,如果超过这个时间就停止运行!
性能分析拦截器作用:用于输出每条sql语句及其执行时间
1、导入插件
//性能分析插件
@Bean
@Profile({"dev","test"})//设置dev开发、test测试 环境开启 保证我们的效率
public PerformanceInterceptor performanceInterceptor(){
PerformanceInterceptor performanceInterceptor = new PerformanceInterceptor();
performanceInterceptor.setMaxTime(100);//设置sql最大执行时间*ms,如果超过了则不执行
performanceInterceptor.setFormat(true);//开启sql格式化
return performanceInterceptor;
}
注意: 要在SpringBoot中配置环境为dev或test环境!
#设置开发环境 spring.profiles.active=dev
2、测试使用
@Test
void contextLoads() {
//参数是一个wrapper ,条件构造器,这里我们先不用 null
//查询全部的用户
List userList = userMapper.selectList(null);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
使用性能分析插件,可以帮助我们提高效率!
5、条件构造器
十分重要:Wrapper 记住查看输出的SQL进行分析
1、测试一
@Test
public void testWrapper1() {
//参数是一个wrapper ,条件构造器,和刚才的map对比学习!
//查询name不为空,email不为空,age大于18的用户
QueryWrapper wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper
.isNotNull("name")
.isNotNull("email")
.ge("age",18);
List userList = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
测试二
@Test
public void testWrapper2() {
//查询name=wsk的用户
QueryWrapper wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("name","wsk");
//查询一个数据selectOne,若查询出多个会报错
//Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: *
//若出现多个结果使用list或map
User user = userMapper.selectOne(wrapper);//查询一个数据,若出现多个结果使用list或map
System.out.println(user);
}
测试三
@Test
public void testWrapper3() {
//查询age在10-20之间的用户
QueryWrapper wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.between("age", 10, 20);//区间
Integer count = userMapper.selectCount(wrapper);//输出查询的数量selectCount
System.out.println(count);
}
测试四
@Test
public void testWrapper4() {
//模糊查询
QueryWrapper wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper
.notLike("name","s")
.likeRight("email","t");//qq% 左和右?
List> maps = userMapper.selectMaps(wrapper);
maps.forEach(System.out::println);
}
测试五
@Test
public void testWrapper5() {
//模糊查询
// SELECT id,name,age,email,version,deleted,create_time,update_time
//FROM user
//WHERE deleted=0 AND id IN
//(select id from user where id<5)
QueryWrapper wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//id 在子查询中查出来
wrapper.inSql("id","select id from user where id<5");
List
测试六
@Test
public void testWrapper6() {
QueryWrapper wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//通过id进行降序排序
wrapper.orderByDesc("id");
List userList = userMapper.selectList(wrapper);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
Mysql => JDBC => Mybatis => MybatisPlus
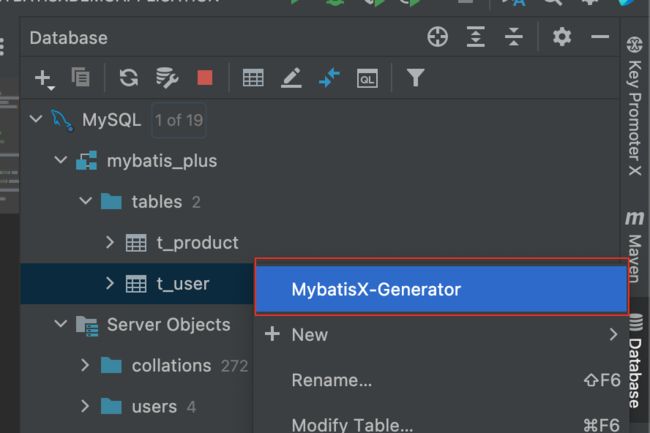
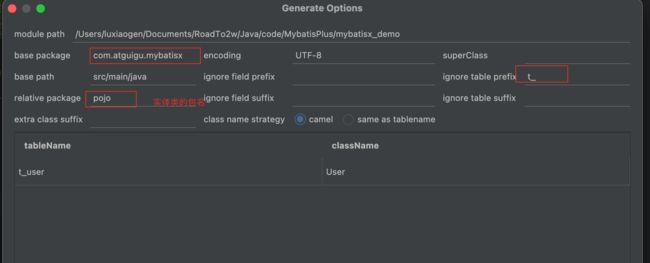
6、MyBatisX插件
MyBatis-Plus为我们提供了强大的mapper和service模板,能够大大的提高开发效率
但是在真正开发过程中,MyBatis-Plus并不能为我们解决所有问题,例如一些复杂的SQL,多表 联查,我们就需要自己去编写代码和SQL语句,我们该如何快速的解决这个问题呢,这个时候可 以使用MyBatisX插件
MyBatisX一款基于 IDEA 的快速开发插件,为效率而生
MyBatisX插件用法