Machine Learning with Python Cookbook 学习笔记 第2章
Machine Learning with Python Cookbook 学习笔记 第2章
前言
- 本笔记是针对人工智能典型算法的课程中Machine Learning with Python Cookbook的学习笔记
- 学习的实战代码都放在代码压缩包中
- 实战代码的运行环境是python3.9 numpy 1.23.1
- (88条消息) 第一章学习笔记_五舍橘橘的博客-CSDN博客
Chapter 2
Loading Data
2.0 Introduction
The first step in any machine learning endeavor is to get the raw data into our system. The raw data might be a logfile, dataset file, or database. Furthermore, often we will want to retrieve data from multiple sources. The recipies in this chapter look at methods of loading data from a variety of sources, including CSV files and SQL databases. We also cover methods of generating simulated data with desirable properties for experimentation. Finally, while there are many ways to load data in the Python ecosystem, we will focus on using the pandas library’s extensive set of methods for loading external data, and using scikit-learn–an open source machine learning library in Python–for generating simulated data.
总结:
- 任何机器学习努力的第一步都是将原始数据输入我们的系统。
- 我们希望从多个数据源获得数据(pandas)
- 我们还可以通过工具生成数据(scikit-learn )
2.1 Loading a Sample Dataset
Problem
You want to load a prexisting sample dataset
Solution
scikit-learn comes with a number of popular datasets for you to use:
加载一个先前已经存在的数据源
sampleExample.py
# load scikit-learn's datasets
from sklearn import datasets
# 加载 digits 数据集
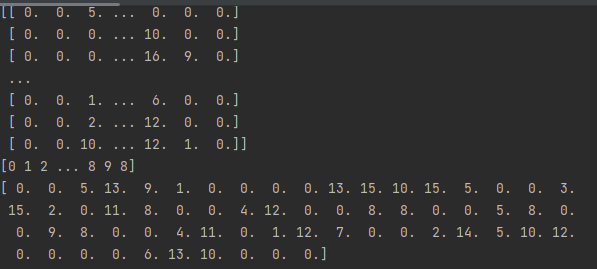
digits = datasets.load_digits()
# 创建 features matrix
features = digits.data
print(features)
# 创建 target vector
target = digits.target
print(target)
# 查看第一个 observation
print(features[0])
样例代码中含有scikit-learn库,需要单独安装
- 关于scikit-learn
#使用anaconda安装 4.12.0版本
conda install scikit-learn
scikit-learn,又写作sklearn,是一个开源的基于python语言的机器学习工具包。它通过NumPy, SciPy和Matplotlib等python数值计算的库实现高效的算法应用,并且涵盖了几乎所有主流机器学习算法。
scikit-learn中文社区:scikit-learn中文社区
-
关于datasets中的数据集
datasets.load_boston #波士顿房价数据集 datasets.load_breast_cancer #乳腺癌数据集 datasets.load_diabetes #糖尿病数据集 datasets.load_digits #手写体数字数据集 datasets.load_files datasets.load_iris #鸢尾花数据集 datasets.load_lfw_pairs datasets.load_lfw_people datasets.load_linnerud #体能训练数据集 datasets.load_mlcomp datasets.load_sample_image datasets.load_sample_images datasets.load_svmlight_file datasets.load_svmlight_files本例子使用的是手写体数字数据集
-
关于features matrix和target vector
features matrix:特征数据数组
target vector:标签数组
-
关于术语observation
Observation
A single unit in our level of observation—for example, a person, a sale, or a record.
observation理解下来应该是观测值的意思
Discussion
Often we do not want to go through the work of loading, transforming and cleaning a real-world dataset before we can explore some machine learning algorithm or method. Luckily, scikit-learn comes with some common datasets we can quickly load. These datasets are often called “toy” datasets because they are far smaller and cleaner than a dataset we would see in the real world. Some popular sample datasets in scikit-learn are:(给出了一些小型数据集)
load_boston
- Contains 503 observations on Boston housing prices. It is a good dataset for exploring regression algorithms.(包含503个观测值的波士顿房价数据集)
load_iris
- Contains 150 observations on the measurements of Iris flowers. It is a good dataset for exploring classification algorithms(150个样例的鸢尾花数据集 )
load_digits
- Cotnains 1,797 observations from images of handwritten digits. It is a good dataset for teaching image classification(手写数字数据集)
- 其他的数据集见上方
2.2 Creating a Simulated Dataset
Problem
You need to generate a dataset of simulated data
Solution
scikit-learn offers any methods for creating simulated data. Of those, three methods are particularly useful
When we want a dataset designed to be used with linear regression, make_regression is a good choice:
要求:生成模拟的数据集
线性回归数据集函数:make_regression
make_regressionExample.py
# load library
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression
# 生成 features matrix, target vector, and the true coefficients
features, target, coefficients = make_regression(n_samples=100, # 样本数量
n_features=3, # 特征
n_informative=3, # 参与建模的特征数
n_targets=1, # 因变量个数
noise=0.0, # 噪声
coef=True, # 是否输出coef标志
random_state=1) # 固定值表示每次调用参数一样的数据
# view feature matrix and target vector
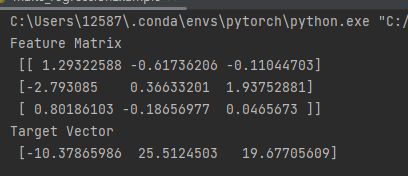
print("Feature Matrix \n {}".format(features[:3]))
print("Target Vector \n {}".format(target[:3]))
分类数据集:make_classification:
make_classificationExample.py
# load library
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
# generate features matrix and target vector
features, target = make_classification(n_samples = 100, # 样本个数
n_features = 3, # 特征数
n_informative = 3, # 参与建模的特征数
n_redundant = 0, # 冗余信息
n_classes = 2, # 类的个数
weights = [.25, .75], # 权重
random_state = 1) # 固定值表示每次调用参数一样的数据
# view feature matrix and target vector
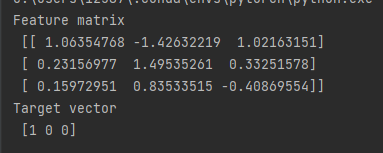
print("Feature matrix\n {}".format(features[:3]))
print("Target vector\n {}".format(target[:3]))
聚类数据集make_blobs
make_blobsExample.py
# load library
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
# generate feature_matrix and target vector
features, target = make_blobs(n_samples=100, # 样本数量
n_features=2, # 特征数量
centers=3, # 类别数(中心数)
cluster_std=0.5, # 每个类的方差
shuffle=True, # 是否洗乱数据
random_state=1) # 固定值表示每次调用参数一样的数据
# view feature matrix and target vector
print("Feature Matrix\n {}".format(features[:3]))
print("Target Vector\n {}".format(target[:3]))
Discussion
-
As might be apparent from the solutions, make regression returns a feature matrix of flaot values and a target vector of float values, while make_classification and make_blobs return a feature matrix of float values and a target vector of integers representing membership in a class.
(make_regression返回浮点值的特征矩阵和浮点值的目标向量,而 make_classification 和 make_blobs 返回浮点值的特征矩阵和表示类成员资格的整数目标向量。 )
-
scikit-learn’s simulated datasets offer extensive options to control the type of data generated.
(scikit-learn提供广泛选择来构建数据集)
-
In
make_regressionandmake_classification,n_informativedetermines the number of features that are used to generate the target vector. If n_informativeis less than the totla number of features (n_features), the resulting dataset will have redundant features that cna be identified through feature selection techniques(在
make_regression和make_classification中,n_informative决定了用于生成目标向量的特征数量。如果 n_informative小于特征总数 (n_features),则生成的数据集将具有冗余特征,这些特征可以通过特征选择技术识别) -
In addition,
make_classificationcontains aweightsparameter that allows us to simulate datasets with imbalanced classes. For example,weights = [.25, .75]would return a dataset with 25% of observations belonging to one class and 75% to the other(
make_classification包含一个weights参数,允许我们模拟具有不平衡类的数据集。例如,weights = [.25, .75]将返回一个数据集,其中 25% 的观察属于一个类,75% 属于另一个) -
For
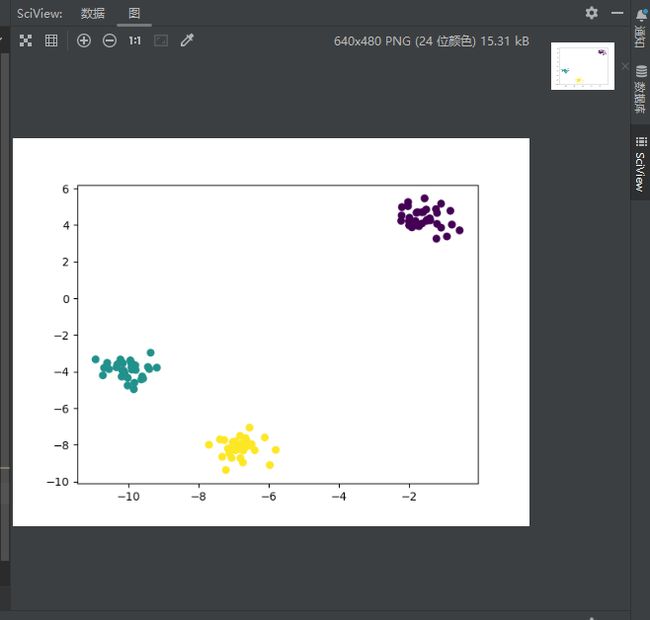
make_blobs, the centers parameter determines the number of clusters generated. Using thematplotlibvisualization library we can visualize the clusters generated bymake_blobs:
对于“make_blob”,centers 参数决定了生成的簇数。使用 matplotlib 可视化库,我们可以可视化 make_blobs 生成的集群:
需要安装matplotlib库
conda install matplotlib
# load library
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
# load library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# generate feature_matrix and target vector
features, target = make_blobs(n_samples=100, # 样本数量
n_features=2, # 特征数量
centers=3, # 类别数(中心数)
cluster_std=0.5, # 每个类的方差
shuffle=True, # 是否洗乱数据
random_state=1) # 固定值表示每次调用参数一样的数据
# view feature matrix and target vector
print("Feature Matrix\n {}".format(features[:3]))
print("Target Vector\n {}".format(target[:3]))
# view scatterplot
plt.scatter(features[:, 0], features[:, 1], c=target)
plt.show()
2.3 Loading a CSV File
Problem
You need to import a comma-separated values (CSV) file.
Solution
Use the pandas library’s read_csv to load a local or hosted CSV file:
需要安装pandas
conda install pandas
Pandas 教程 | 菜鸟教程 (runoob.com)
loadCSVExample.py
# load library
import pandas as pd
# create url
# 加载数据
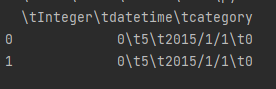
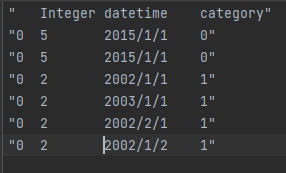
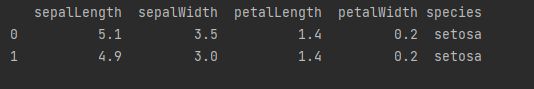
df = pd.read_csv("data.csv")
print(df.head(2))
因为无法打开课本中的csv文件
所以使用一个本地csv文件
得到结果
Discussion
- 加载之前快速查看文件内容通常很有用
- read_csv 有 30 多个参数,因此文档可能令人生畏。这些参数主要是为了让它能够处理各种 CSV 格式。
- pandas 的 sep 参数允许我们定义文件中使用的分隔符。
- header 参数允许我们指定标题行是否存在或存在于何处。如果标题行不存在,我们设置 header=None。
2.4 Loading an Excel File
Problem
You need to import an Excel spreadsheet
Solution
Use the pandas library’s read_excel to load an Excel spreadsheet:
用pandas打开excel文件
loadExcelExample.py
import pandas as pd
import ssl
# Python 从 2.7.9版本开始,就默认开启了服务器证书验证功能,如果证书校验不通过,则拒绝后续操作;这样可以防止中间人攻击,并使客户端确保服务器确实是它声称的身份。如果是自签名证书,由于一般系统的CA证书中不存在在自签名的CA证书内容,从而导致证书验证不通过。
ssl._create_default_https_context = ssl._create_unverified_context
# 因为原书的excel无法访问,所以替换了一个url
url = "https://www.sample-videos.com/xls/Sample-Spreadsheet-10-rows.xls"
# 加载url
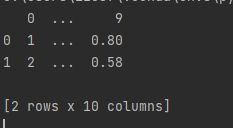
df = pd.read_excel(url, sheet_name=0, header=None)
# 打印前两行
print(df.head(2))
Discussion
- 附加参数 sheetname,它指定我们希望加载 Excel 文件中的哪个工作表。
- 如果我们需要加载多张工作表,请将它们作为列表包含在内。 例如, sheetname= [0,1,2, “Monthly Sales”] 将返回包含第一张、第二张和第三张工作表以及名为 Monthly Sales 的工作表的 pandas DataFrame 字典。
2.5 Loading a JSON File
Problem
You need to load a JSON file for data preprocessing
Solution
The pandas library provides read_json to convert a JSON file a pandas object:
加载json文件,使用read_json
# load library
import pandas as pd
# create url
url = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/domoritz/maps/master/data/iris.json'
# load data
df = pd.read_json(url, orient="columns")
# view first two rows
print(df.head(2))
Discussion
- orient 参数,它向 pandas 指示 JSON 文件的结构
- pandas 提供的另一个有用的工具是 json_normalize,它可以帮助将半结构化 JSON 数据转换为 pandas DataFrame。
2.6 Querying a SQL Database
Problem
You need to load data from a databaseu sing structured query language (SQL)
Solution
pandas’ read_sql_query allows us to make a SQL query to a database and load it:
读取sql中的内容
loadSqlExample.py
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
# 初始化数据库连接
# 按实际情况依次填写MySQL的用户名、密码、IP地址、端口、数据库名
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:444555@localhost:3306/lab5')
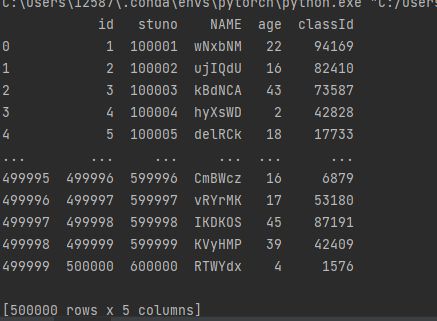
sql_query = 'select * from student;'
# 使用pandas的read_sql_query函数执行SQL语句,并存入DataFrame
df_read = pd.read_sql_query(sql_query, engine)
print(df_read)
(原书使用sqlite,本例子改成了mysql)
Discussion
create_engine创建一个mysql的数据连接read_sql_query将结果放到DataFrame
下一章:(89条消息) Machine Learning with Python Cookbook 学习笔记 第3章_五舍橘橘的博客-CSDN博客