[深度学习入门]知识蒸馏
论文:Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network
相关论文查找网站:
1. Connected Papers | Find and explore academic papers
2. https://paperswithcode.com/
3. 知识蒸馏在做什么?
将soft targets的结果作为标签进行训练stduent model,增加了更多的信息(物体间的相似度):
知识蒸馏主要是将大模型轻量化,以教师网络的输出(即通过数据集学到的各类检测物间的概率,概率中包含类与类间的隐式关系,即各类物体间的相似程度)作为学生网络的输入,以供学生网络学习轻量化模型。
4. 如何蒸馏?
通过温度T进行蒸馏(T用来将各类物体间的相似度进行放大或缩小):
当T=1时,pi就是标准的softmax;随着T的增加,softmax函数的概率分布函数就会变得更加平缓,也就是将各类之间的相似度拉得趋近于相同,如下图所示:
5. 损失函数:
损失函数分为两部分:
因为学生网络主要学习真实标签与教师网络传递过来的类间相似信息(这个信息就是教师网络输出检测目标的概率),所以其损失函数主要是学生网络和教师网络之间的蒸馏损失函数和学生网络与真实标签间的softmax:
1) 学生网络和教师网络之间蒸馏损失函数
教师网络和学生网络之间蒸馏损失函数基于T=t时计算的损失函数。
2)学生网络与真实标签间的softmax loss:
学生网络与真是标签间的softmax loss即为T=1时计算的损失函数。
代码:
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchinfo import summary
from tqdm import tqdm
torch.manual_seed(0)
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available else "cpu")
print("device : {}".format(device))
# cudnn加速卷积运算
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root="dataset/",
train=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True
)
test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root="dataset/",
train=False,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True
)
train_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset,batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset,batch_size=32,shuffle=False)
class TeacherModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=1, num_classes=10):
super(TeacherModel, self).__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(784,1200)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1200,1200)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(1200,num_classes)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=0.5)
def forward(self, x):
x = x.view(-1, 784)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
model = TeacherModel()
model = model.to(device)
summary(model)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
epochs = 6
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
# 训练集上训练模型权重
for data, targets in tqdm(train_dataloader):
data = data.to(device)
targets = targets.to(device)
# 前向预测
preds = model(data)
loss = criterion(preds, targets)
# 反向传播 优化权重
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 测试集上评估模型性能
model.eval()
num_correct = 0
num_samples = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x, y in test_dataloader:
x = x.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
preds = model(x)
predictions = preds.max(1).indices
num_correct += (predictions == y).sum()
num_samples += predictions.size(0)
acc = (num_correct/num_samples).item()
model.train()
print('Epoch:{}\t SingleTeacherAccurary:{:.4f}'.format(epoch+1, acc))
teacher_model = model
class StudentModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels=1, num_classes=10):
super(StudentModel, self).__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(784,20)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(20,20)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(20,num_classes)
# self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=0.5)
def forward(self, x):
x = x.view(-1, 784)
x = self.fc1(x)
# x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
# x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
# 从头训练学生模型
epochs = 3
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
# 训练集上训练模型权重
for data, targets in tqdm(train_dataloader):
data = data.to(device)
targets = targets.to(device)
# 前向预测
preds = model(data)
loss = criterion(preds, targets)
# 反向传播 优化权重
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 测试集上评估模型性能
model.eval()
num_correct = 0
num_samples = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x, y in test_dataloader:
x = x.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
preds = model(x)
predictions = preds.max(1).indices
num_correct += (predictions == y).sum()
num_samples += predictions.size(0)
acc = (num_correct/num_samples).item()
model.train()
print('Epoch:{}\t SingleStudentAccurary:{:.4f}'.format(epoch+1, acc))
# 准备好教师模型‘
teacher_model.eval()
# 准备新的学生模型
model = StudentModel()
model = model.to(device)
model.train()
temp = 7
hard_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
alpha = 0.3
# soft loss
soft_loss = nn.KLDivLoss(reduction="batchmean")
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
epochs = 3
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 训练集上训练模型权重
for data, targets in tqdm(train_dataloader):
data = data.to(device)
targets = targets.to(device)
# 教师模型
with torch.no_grad():
teacher_preds = teacher_model(data)
# 学生模型预测
student_preds = model(data)
student_loss = hard_loss(student_preds, targets)
# 计算蒸馏后预测结果及soft_loss
ditillation_loss = soft_loss(
F.softmax(student_preds / temp, dim=1),
F.softmax(teacher_preds / temp, dim=1),
)
# 将hardloss / soft_loss加权求和
loss = alpha * student_loss + (1 - alpha)*ditillation_loss
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 测试集上评估模型性能
model.eval()
num_correct = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for x, y in test_dataloader:
x = x.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
preds = model(x)
predictions = preds.max(1).indices
num_correct += (predictions == y).sum()
num_samples += predictions.size(0)
acc = (num_correct/num_samples).item()
model.train()
print('Epoch:{}\t TeacherStudentAccurary:{:.4f}'.format(epoch+1, acc))参考:
1. https://intellabs.github.io/distiller/knowledge_distillation.html
2. 【精读AI论文】知识蒸馏_哔哩哔哩_bilibili:demo代码来源
![[深度学习入门]知识蒸馏_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/129590c1779f4df39888ca8255eea670.jpg)
![[深度学习入门]知识蒸馏_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/9c636440889b45138f4680d92bf80326.jpg)
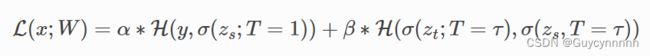
![[深度学习入门]知识蒸馏_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/180f0973aefe4f9f9117f6156e433782.jpg)