基于VGG卷积神经网络的图像识别代码实现
VGG模型介绍
VGG(Oxford Visual Geometry Group)模型是2014年ILSVRC竞赛的第二名,,由Karen Simonyan和Andrew Zisserman实现。VGG是卷积神经网络模型,是在AlexNet的基础上做的改进。
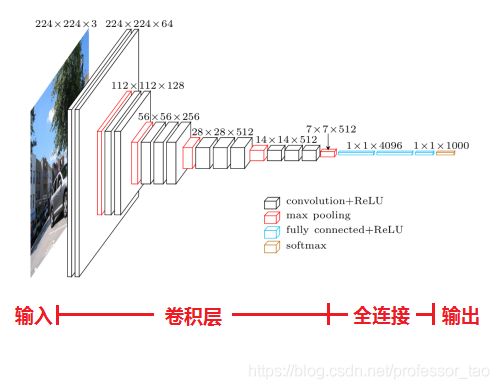
TensorFLow的keras库中集成有VGG16、VGG19模型,可以打印模型的结构,下面以VGG16为例进行模型结构说明:
from tensorflow.python.keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16
model = VGG16()
print(model.summary())
VGG模型打印结果
Model: "vgg16"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 224, 224, 3)] 0
_________________________________________________________________
block1_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 64) 1792
_________________________________________________________________
block1_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 224, 224, 64) 36928
_________________________________________________________________
block1_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 112, 112, 64) 0
_________________________________________________________________
block2_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128) 73856
_________________________________________________________________
block2_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 128) 147584
_________________________________________________________________
block2_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 56, 56, 128) 0
_________________________________________________________________
block3_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 295168
_________________________________________________________________
block3_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080
_________________________________________________________________
block3_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 56, 56, 256) 590080
_________________________________________________________________
block3_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 28, 28, 256) 0
_________________________________________________________________
block4_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 1180160
_________________________________________________________________
block4_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block4_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block4_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 0
_________________________________________________________________
block5_conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block5_conv2 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block5_conv3 (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 512) 2359808
_________________________________________________________________
block5_pool (MaxPooling2D) (None, 7, 7, 512) 0
_________________________________________________________________
flatten (Flatten) (None, 25088) 0
_________________________________________________________________
fc1 (Dense) (None, 4096) 102764544
_________________________________________________________________
fc2 (Dense) (None, 4096) 16781312
_________________________________________________________________
predictions (Dense) (None, 1000) 4097000
=================================================================
Total params: 138,357,544
Trainable params: 138,357,544
Non-trainable params: 0
基于VGG实现图像识别
本文从网络上找了两张动物的图片,一种是哈士奇,一直是美洲豹,通过VGG模型对图像进行
类的识别。
哈士奇:

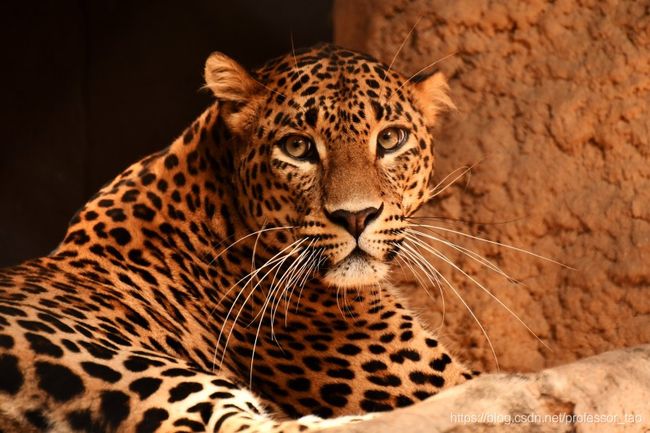
美洲豹:

代码实现
由于VGG模型是集成好的,所以只需要调用相应的API就能实现图像识别任务。
哈士奇识别
from tensorflow.python.keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16,decode_predictions,preprocess_input
from tensorflow.python.keras.preprocessing.image import load_img,img_to_array
model = VGG16()
# 将输入图片变为(224,224)的固定大小
image = load_img("./dog.jpeg",target_size=(224,224))
# 将图片转换为3维数组
image = img_to_array(image)
# 图片变成4维,满足VGG模型的输入要求
image = image.reshape(1,image.shape[0],image.shape[1],image.shape[2])
# 对输入图片进行数据预处理
image = preprocess_input(image)
# 对图片的类别进行预测
y_predict = model.predict(image)
# 对预测结果进行解码
label = decode_predictions(y_predict)
res = label[0][0]
print("预测的类别为:%s,概率为:(%.2f%%)",(res[1],res[2]*100))
运行结果
预测的类别为:Siberian_husky,概率为:(51.18%)
美洲豹识别
from tensorflow.python.keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16,decode_predictions,preprocess_input
from tensorflow.python.keras.preprocessing.image import load_img,img_to_array
model = VGG16()
# 将输入图片变为(224,224)的固定大小
image = load_img("./leopard.jpg",target_size=(224,224))
# 将图片转换为3维数组
image = img_to_array(image)
# 图片变成4维,满足VGG模型的输入要求
image = image.reshape(1,image.shape[0],image.shape[1],image.shape[2])
# 对输入图片进行数据预处理
image = preprocess_input(image)
# 对图片的类别进行预测
y_predict = model.predict(image)
# 对预测结果进行解码
label = decode_predictions(y_predict)
res = label[0][0]
print("预测的类别为:%s,概率为:(%.2f%%)",(res[1],res[2]*100))
运行结果
预测的类别为:leopard,概率为:(62.83%)
总结
本文介绍了VGG模型,并基于TensorFlow.Keras中集成的API搭建了VGG模型。通过两张动物图片验证了模型在图像识别任务中的准确性。