人工智能实践:Tensorflow笔记 Class 6:循环神经网络
目录
6.1 循环核
1.循环核
2.按时间步展开
6.2 循环计算层
1.层数
2.Tensorflow描述循环计算层
6.3 循环计算过程(Ⅰ)
步骤
代码
6.4 循环计算过程(Ⅱ)
步骤
代码
6.5 Embeddng编码
输入一个字母
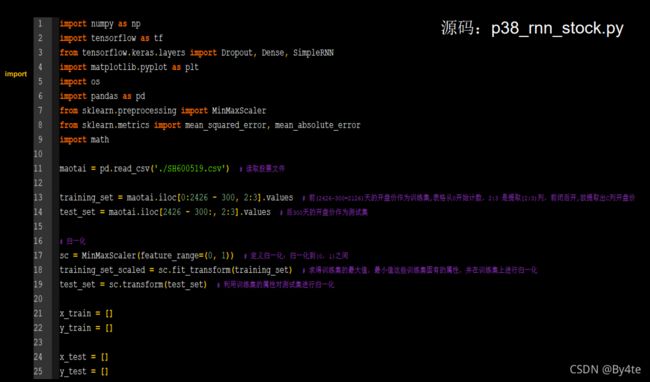
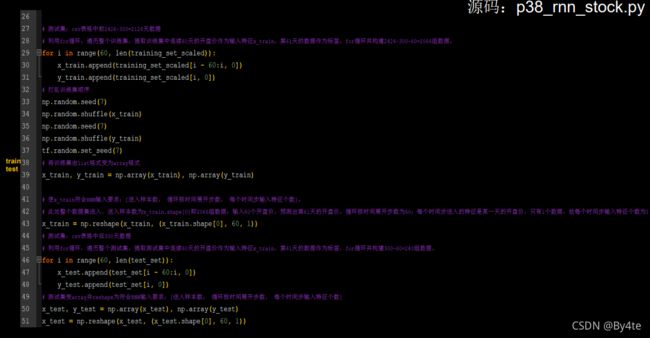
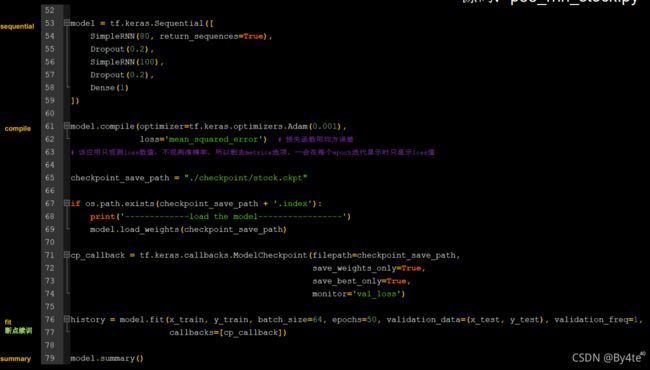
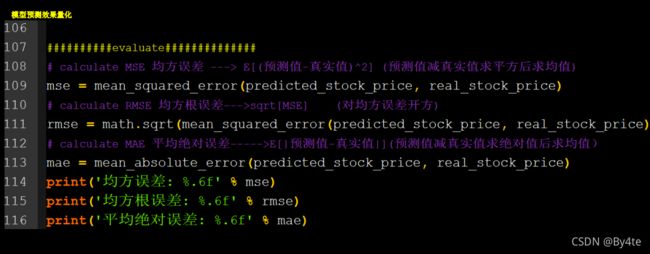
6.6 RNN实现股票预测
6.7 LSTM实现股票预测
6.8 GRU实现股票预测
6.1 循环核
复习:卷积就是特征提取器(CBAPD),借助卷积核提取空间特征后,送入全连接网络
1.循环核
参数时间共享,循环层提取时间信息
2.按时间步展开
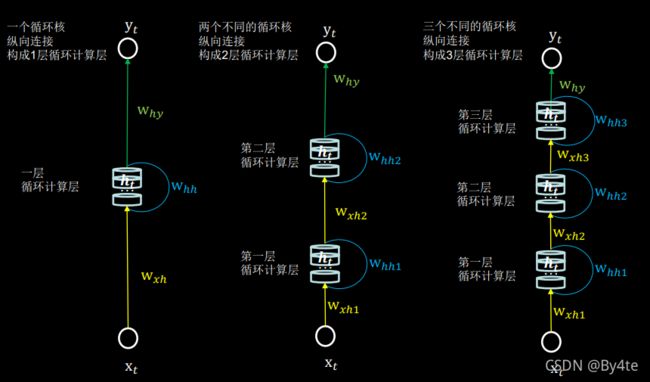
6.2 循环计算层
1.层数
向输出方向增长
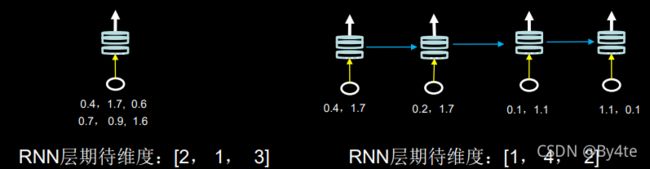
2.Tensorflow描述循环计算层
数据送入RNN时,x_train维度=[送入样本数、循环核时间展开步数、每个时间步输入特征个数]
6.3 循环计算过程(Ⅰ)
步骤
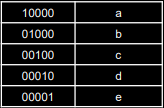
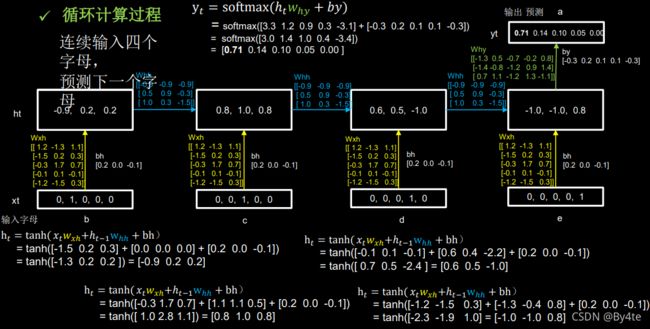
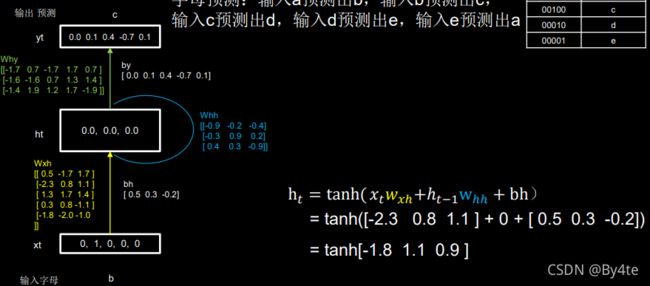
字母预测任务:
词向量空间:
随机生成why,wxh,whh三个参数矩阵,记忆体个数为3。
过程:
 代码
代码
#导入库
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense,SimpleRNN
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
#输入
input_word='abcde'
#为使字母输入神经网络将其编为数字
w_to_id={'a':0,'b':1,'c':2,'d':3,'e':4}
#将数字编为独热码
id_to_onehot={0:[1.,0.,0.,0.,0.],1:[0.,1.,0.,0.,0.],2:[0.,0.,1.,0.,0.],3:[0.,0.,0.,1.,0.],
4:[0.,0.,0.,0.,1.]}
#训练用的特征及标签
x_train=[id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c']],
id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e']]]
y_train=[w_to_id['b'],w_to_id['c'],w_to_id['d'],w_to_id['e'],w_to_id['a']]
#打乱训练集顺序
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(x_train)
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(y_train)
tf.random.set_seed(7)
#将输入特征变为RNN层期待的形状
#第一个维度:样本数
#第二个维度:循环核时间展开步数
#第三个维度:每个时间步输入特征的个数
x_train=np.reshape(x_train,(len(x_train),1,5)) #5即字母对应的独热码,有五个数
y_train=np.array(y_train)
#搭建循环层
model=tf.keras.Sequential([
SimpleRNN(3), #三个记忆体
Dense(5,activation='softmax') #全连接层
])
#设置优化器、准确度函数、损失函数
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.01),
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy'])
checkpoint_save_path='./checkpoint/rnn_onehot_lprel.ckpt'
#保存模型及其参数
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path+'.index'):
print('load the model')
model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path)
cp_callback=tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path,
save_weights_only=True,
save_best_only=True,
monitor='loss')
history=model.fit(x_train,y_train,batch_size=32,epochs=100,callbacks=[cp_callback])
model.summary()
file=open('./weights.txt','w')
for v in model.trainable_variables:
file.write(str(v.name)+'\n')
file.write(str(v.shape)+'\n')
file.write(str(v.numpy())+'\n')
file.close()
acc=history.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy']
loss=history.history['loss']
#绘制准确率、损失函数曲线
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.plot(acc,label='training accuracy')
plt.title('training accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.plot(loss,label='training loss')
plt.title('training loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
#预测
preNum=int(input('input your number:')) #输入需要预测的任务量
for i in range(preNum):
alphabet1=input('input test alphabet:') #输入一个字母
alphabet=[id_to_onehot[w_to_id[alphabet1]]] #转换为独热码
alphabet=np.reshape(alphabet,(1,1,5))
result=model.predict([alphabet]) #预测
pred=tf.argmax(result,axis=1) #预测结果最大值
pred=int(pred)
tf.print(alphabet1+'->'+input_word[pred])6.4 循环计算过程(Ⅱ)
连续输入四个字母,预测下一个字母
步骤
代码
#导入库
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense,SimpleRNN
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
#输入
input_word='abcde'
#为使字母输入神经网络将其编为数字
w_to_id={'a':0,'b':1,'c':2,'d':3,'e':4}
#将数字编为独热码
id_to_onehot={0:[1.,0.,0.,0.,0.],1:[0.,1.,0.,0.,0.],2:[0.,0.,1.,0.,0.],3:[0.,0.,0.,1.,0.],
4:[0.,0.,0.,0.,1.]}
#训练用的特征及标签
x_train=[
[id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d']]],
[id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e']]],
[id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a']]],
[id_to_onehot[w_to_id['d']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b']]],
[id_to_onehot[w_to_id['e']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['a']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['b']],id_to_onehot[w_to_id['c']]],
]
y_train=[w_to_id['e'],w_to_id['a'],w_to_id['b'],w_to_id['c'],w_to_id['d']]
#打乱训练集顺序
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(x_train)
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(y_train)
tf.random.set_seed(7)
#将输入特征变为RNN层期待的形状
#第一个维度:样本数
#第二个维度:循环核时间展开步数
#第三个维度:每个时间步输入特征的个数
x_train=np.reshape(x_train,(len(x_train),4,5)) #5即字母对应的独热码,有五个数
y_train=np.array(y_train)
#搭建循环层
model=tf.keras.Sequential([
SimpleRNN(3), #三个记忆体
Dense(5,activation='softmax') #全连接层
])
#设置优化器、准确度函数、损失函数
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.01),
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy'])
checkpoint_save_path='./checkpoint/rnn_onehot_lprel.ckpt'
#保存模型及其参数
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path+'.index'):
print('load the model')
model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path)
cp_callback=tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path,
save_weights_only=True,
save_best_only=True,
monitor='loss')
history=model.fit(x_train,y_train,batch_size=32,epochs=100,callbacks=[cp_callback])
model.summary()
file=open('./weights.txt','w')
for v in model.trainable_variables:
file.write(str(v.name)+'\n')
file.write(str(v.shape)+'\n')
file.write(str(v.numpy())+'\n')
file.close()
acc=history.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy']
loss=history.history['loss']
#绘制准确率、损失函数曲线
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.plot(acc,label='training accuracy')
plt.title('training accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.plot(loss,label='training loss')
plt.title('training loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
#预测
preNum=int(input('input your number:')) #输入需要预测的任务量
for i in range(preNum):
alphabet1=input('input test alphabet:') #输入一个字母
alphabet=[id_to_onehot[w_to_id[a]] for a in alphabet1] #转换为独热码
alphabet=np.reshape(alphabet,(1,4,5))
result=model.predict([alphabet]) #预测
pred=tf.argmax(result,axis=1) #预测结果最大值
pred=int(pred)
tf.print(alphabet1+'->'+input_word[pred])6.5 Embeddng编码
独热码具有一定的局限性
使用Embedding编码
 输入一个字母
输入一个字母
#导入库
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense,SimpleRNN,Embedding5
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
#输入
input_word='abcde'
#为使字母输入神经网络将其编为数字
w_to_id={'a':0,'b':1,'c':2,'d':3,'e':4}
#将数字编为独热码
id_to_onehot={0:[1.,0.,0.,0.,0.],1:[0.,1.,0.,0.,0.],2:[0.,0.,1.,0.,0.],3:[0.,0.,0.,1.,0.],
4:[0.,0.,0.,0.,1.]}
#训练用的特征及标签
x_train=[w_to_id['a'],w_to_id['b'],w_to_id['c'],w_to_id['d'],w_to_id['e']]
y_train=[w_to_id['b'],w_to_id['c'],w_to_id['d'],w_to_id['e'],w_to_id['a']]
#打乱训练集顺序
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(x_train)
np.random.seed(7)
np.random.shuffle(y_train)
tf.random.set_seed(7)
#将输入特征变为RNN层期待的形状
#第一个维度:样本数
#第二个维度:循环核时间展开步数
#第三个维度:每个时间步输入特征的个数
x_train=np.reshape(x_train,(len(x_train),1)) #5即字母对应的独热码,有五个数
y_train=np.array(y_train)
#搭建循环层
model=tf.keras.Sequential([
Embedding(5,2),
SimpleRNN(3), #三个记忆体
Dense(5,activation='softmax') #全连接层
])
#设置优化器、准确度函数、损失函数
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.01),
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=False),
metrics=['sparse_categorical_accuracy'])
checkpoint_save_path='./checkpoint/rnn_onehot_lprel.ckpt'
#保存模型及其参数
if os.path.exists(checkpoint_save_path+'.index'):
print('load the model')
model.load_weights(checkpoint_save_path)
cp_callback=tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(filepath=checkpoint_save_path,
save_weights_only=True,
save_best_only=True,
monitor='loss')
history=model.fit(x_train,y_train,batch_size=32,epochs=100,callbacks=[cp_callback])
model.summary()
file=open('./weights.txt','w')
for v in model.trainable_variables:
file.write(str(v.name)+'\n')
file.write(str(v.shape)+'\n')
file.write(str(v.numpy())+'\n')
file.close()
acc=history.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy']
loss=history.history['loss']
#绘制准确率、损失函数曲线
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.plot(acc,label='training accuracy')
plt.title('training accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.plot(loss,label='training loss')
plt.title('training loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
#预测
preNum=int(input('input your number:')) #输入需要预测的任务量
for i in range(preNum):
alphabet1=input('input test alphabet:') #输入一个字母
alphabet=[w_to_id[alphabet1]] #转换为独热码
alphabet=np.reshape(alphabet,(1,1))
result=model.predict([alphabet]) #预测
pred=tf.argmax(result,axis=1) #预测结果最大值
pred=int(pred)
tf.print(alphabet1+'->'+input_word[pred])