昨晚撸了一个简易版的 Spring MVC 框架
想要了解Spring MVC框架的原理,探究框架是如何设计的,不错的学习方式是阅读源码,然后自己手写一个框架。本文带领大家简化的手写一个Spring MVC框架。
Spring框架对于Java后端程序员来说再熟悉不过了,以前只知道它用的反射实现的,但了解之后才知道有很多巧妙的设计在里面。
如果不看Spring的源码,你将会失去一次和大师学习的机会:它的代码规范,设计思想很值得学习。我们程序员大部分人都是野路子,不懂什么叫代码规范。写了一个月的代码,最后还得其他老司机花3天时间重构,相信大部分老司机都很头疼看新手的代码。
废话不多说,我们进入今天的正题,在Web应用程序设计中,MVC模式已经被广泛使用。SpringMVC以DispatcherServlet为核心,负责协调和组织不同组件以完成请求处理并返回响应的工作,实现了MVC模式。想要实现自己的SpringMVC框架,需要从以下几点入手:
了解SpringMVC运行流程及九大组件
梳理自己的SpringMVC的设计思路
实现自己的SpringMVC框架
一、了解SpringMVC运行流程及九大组件
1. SpringMVC的运行流程
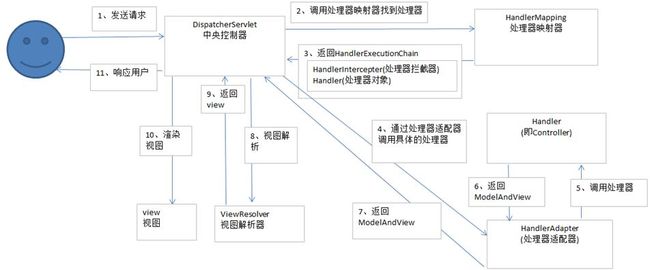
⑴ 用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet
⑵ DispatcherServlet收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器。
⑶ 处理器映射器根据请求url找到具体的处理器,生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如果有则生成)一并返回给DispatcherServlet。
⑷ DispatcherServlet通过HandlerAdapter处理器适配器调用处理器
⑸ 执行处理器(Controller,也叫后端控制器)。
⑹ Controller执行完成返回ModelAndView
⑺ HandlerAdapter将controller执行结果ModelAndView返回给DispatcherServlet
⑻ DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewReslover视图解析器
⑼ ViewReslover解析后返回具体View
⑽ DispatcherServlet对View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据填充至视图中)
⑾ DispatcherServlet响应用户。
从上面可以看出,DispatcherServlet有接收请求,响应结果,转发等作用。有了DispatcherServlet之后,可以减少组件之间的耦合度。
2. SpringMVC的九大组件
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
//用于处理上传请求。处理方法是将普通的request包装成MultipartHttpServletRequest,后者可以直接调用getFile方法获取File.
initMultipartResolver(context);
//SpringMVC主要有两个地方用到了Locale:一是ViewResolver视图解析的时候;二是用到国际化资源或者主题的时候。
initLocaleResolver(context);
//用于解析主题。SpringMVC中一个主题对应一个properties文件,里面存放着跟当前主题相关的所有资源、
//如图片、css样式等。SpringMVC的主题也支持国际化,
initThemeResolver(context);
//用来查找Handler的。
initHandlerMappings(context);
//从名字上看,它就是一个适配器。Servlet需要的处理方法的结构却是固定的,都是以request和response为参数的方法。
//如何让固定的Servlet处理方法调用灵活的Handler来进行处理呢?这就是HandlerAdapter要做的事情
initHandlerAdapters(context);
//其它组件都是用来干活的。在干活的过程中难免会出现问题,出问题后怎么办呢?
//这就需要有一个专门的角色对异常情况进行处理,在SpringMVC中就是HandlerExceptionResolver。
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
//有的Handler处理完后并没有设置View也没有设置ViewName,这时就需要从request获取ViewName了,
//如何从request中获取ViewName就是RequestToViewNameTranslator要做的事情了。
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
//ViewResolver用来将String类型的视图名和Locale解析为View类型的视图。
//View是用来渲染页面的,也就是将程序返回的参数填入模板里,生成html(也可能是其它类型)文件。
initViewResolvers(context);
//用来管理FlashMap的,FlashMap主要用在redirect重定向中传递参数。
initFlashMapManager(context);
}二、梳理SpringMVC的设计思路
本文只实现自己的@Controller、@RequestMapping、@RequestParam注解起作用,其余SpringMVC功能读者可以尝试自己实现。
1、读取配置
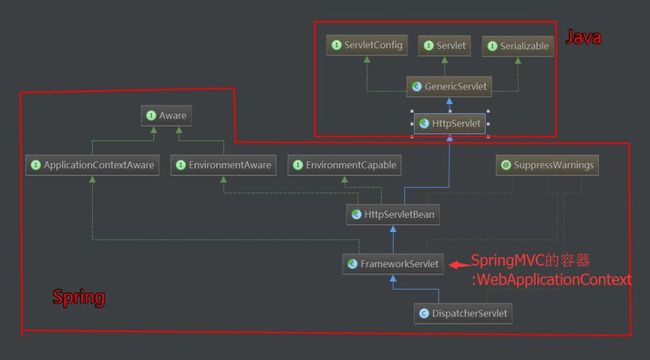
从图中可以看出,SpringMVC本质上是一个Servlet,这个 Servlet 继承自 HttpServlet。FrameworkServlet负责初始化SpringMVC的容器,并将Spring容器设置为父容器。
因为本文只是实现SpringMVC,对于Spring容器不做过多讲解(有兴趣同学可以看看我另一篇文章:向spring大佬低头--大量源码流出解析)。
为了读取web.xml中的配置,我们用到ServletConfig这个类,它代表当前Servlet在web.xml中的配置信息。通过web.xml中加载我们自己写的MyDispatcherServlet和读取配置文件。
2、初始化阶段
在前面我们提到DispatcherServlet的initStrategies方法会初始化9大组件,但是这里将实现一些SpringMVC的最基本的组件而不是全部,按顺序包括:
加载配置文件
扫描用户配置包下面所有的类
拿到扫描到的类,通过反射机制,实例化。并且放到ioc容器中(Map的键值对 beanName-bean) beanName默认是首字母小写
初始化HandlerMapping,这里其实就是把url和method对应起来放在一个k-v的Map中,在运行阶段取出
3、运行阶段
每一次请求将会调用doGet或doPost方法,所以统一运行阶段都放在doDispatch方法里处理,它会根据url请求去HandlerMapping中匹配到对应的Method,然后利用反射机制调用Controller中的url对应的方法,并得到结果返回。按顺序包括以下功能:
异常的拦截
获取请求传入的参数并处理参数
通过初始化好的handlerMapping中拿出url对应的方法名,反射调用
三、实现自己的SpringMVC框架
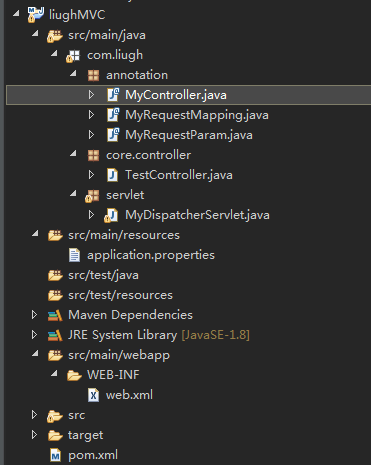
工程文件及目录:
首先,新建一个maven项目,在pom.xml中导入以下依赖:
4.0.0
com.liugh
liughMVC
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
war
UTF-8
1.8
1.8
1.8
javax.servlet
javax.servlet-api
3.0.1
provided
接着,我们在WEB-INF下创建一个web.xml,如下配置:
MySpringMVC
com.liugh.servlet.MyDispatcherServlet
contextConfigLocation
application.properties
1
MySpringMVC
/*
application.properties文件中只是配置要扫描的包到SpringMVC容器中。
scanPackage=com.liugh.core创建自己的Controller注解,它只能标注在类上面:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyController {
/**
* 表示给controller注册别名
* @return
*/
String value() default "";
}RequestMapping注解,可以在类和方法上:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyRequestMapping {
/**
* 表示访问该方法的url
* @return
*/
String value() default "";
}RequestParam注解,只能注解在参数上
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface MyRequestParam {
/**
* 表示参数的别名,必填
* @return
*/
String value();
}然后创建MyDispatcherServlet这个类,去继承HttpServlet,重写init方法、doGet、doPost方法,以及加上我们第二步分析时要实现的功能:
public class MyDispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet{
private Properties properties = new Properties();
private List classNames = new ArrayList<>();
private Map ioc = new HashMap<>();
private Map handlerMapping = new HashMap<>();
private Map controllerMap =new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
//1.加载配置文件
doLoadConfig(config.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation"));
//2.初始化所有相关联的类,扫描用户设定的包下面所有的类
doScanner(properties.getProperty("scanPackage"));
//3.拿到扫描到的类,通过反射机制,实例化,并且放到ioc容器中(k-v beanName-bean) beanName默认是首字母小写
doInstance();
//4.初始化HandlerMapping(将url和method对应上)
initHandlerMapping();
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
//处理请求
doDispatch(req,resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
resp.getWriter().write("500!! Server Exception");
}
}
private void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception {
if(handlerMapping.isEmpty()){
return;
}
String url =req.getRequestURI();
String contextPath = req.getContextPath();
url=url.replace(contextPath, "").replaceAll("/+", "/");
if(!this.handlerMapping.containsKey(url)){
resp.getWriter().write("404 NOT FOUND!");
return;
}
Method method =this.handlerMapping.get(url);
//获取方法的参数列表
Class[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
//获取请求的参数
Map parameterMap = req.getParameterMap();
//保存参数值
Object [] paramValues= new Object[parameterTypes.length];
//方法的参数列表
for (int i = 0; i param : parameterMap.entrySet()) {
String value =Arrays.toString(param.getValue()).replaceAll("\\[|\\]", "").replaceAll(",\\s", ",");
paramValues[i]=value;
}
}
}
//利用反射机制来调用
try {
method.invoke(this.controllerMap.get(url), paramValues);//第一个参数是method所对应的实例 在ioc容器中
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void doLoadConfig(String location){
//把web.xml中的contextConfigLocation对应value值的文件加载到流里面
InputStream resourceAsStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(location);
try {
//用Properties文件加载文件里的内容
properties.load(resourceAsStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//关流
if(null!=resourceAsStream){
try {
resourceAsStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
private void doScanner(String packageName) {
//把所有的.替换成/
URL url =this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/"+packageName.replaceAll("\\.", "/"));
File dir = new File(url.getFile());
for (File file : dir.listFiles()) {
if(file.isDirectory()){
//递归读取包
doScanner(packageName+"."+file.getName());
}else{
String className =packageName +"." +file.getName().replace(".class", "");
classNames.add(className);
}
}
}
private void doInstance() {
if (classNames.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
for (String className : classNames) {
try {
//把类搞出来,反射来实例化(只有加@MyController需要实例化)
Class clazz =Class.forName(className);
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)){
ioc.put(toLowerFirstWord(clazz.getSimpleName()),clazz.newInstance());
}else{
continue;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
continue;
}
}
}
private void initHandlerMapping(){
if(ioc.isEmpty()){
return;
}
try {
for (Entry entry: ioc.entrySet()) {
Class clazz = entry.getValue().getClass();
if(!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyController.class)){
continue;
}
//拼url时,是controller头的url拼上方法上的url
String baseUrl ="";
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)){
MyRequestMapping annotation = clazz.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class);
baseUrl=annotation.value();
}
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if(!method.isAnnotationPresent(MyRequestMapping.class)){
continue;
}
MyRequestMapping annotation = method.getAnnotation(MyRequestMapping.class);
String url = annotation.value();
url =(baseUrl+"/"+url).replaceAll("/+", "/");
handlerMapping.put(url,method);
controllerMap.put(url,clazz.newInstance());
System.out.println(url+","+method);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 把字符串的首字母小写
* @param name
* @return
*/
private String toLowerFirstWord(String name){
char[] charArray = name.toCharArray();
charArray[0] += 32;
return String.valueOf(charArray);
}
} 这里我们就开发完了自己的SpringMVC,现在我们测试一下:
@MyController
@MyRequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@MyRequestMapping("/doTest")
public void test1(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@MyRequestParam("param") String param){
System.out.println(param);
try {
response.getWriter().write( "doTest method success! param:"+param);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@MyRequestMapping("/doTest2")
public void test2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){
try {
response.getWriter().println("doTest2 method success!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
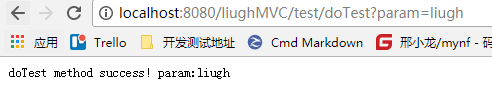
}访问 http://localhost:8080/liughMVC/test/doTest?param=liugh 如下:
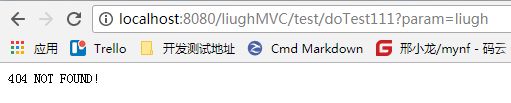
访问一个不存在的试试:
到这里我们就大功告成了!
源码地址:https://github.com/qq53182347/liughMVC
来源:my.oschina.net/liughDevelop/blog/1622646
往期推荐
基于 Spring Boot+Bootstrap 的迷你天猫商城项目,可二次开发接私活!
重磅推荐:一款功能强大、非常全面的Java权限认证框架!
Spring最常用的7大类注解,史上最强整理!
SpringCloud+SpringBoot+OAuth2+Spring Security+Redis实现的微服务统一认证授权
IDEA的后缀自动补全候选项都在这里了,求求你这些代码别手写了!
Spring Boot + Vue + Shiro 实现前后端分离,写得太好了!
基于springBoot 实现webSocket方式的扫码登录