(Python)Gdal与Opencv遥感影像Sift匹配+RANSAC筛选并计算匹配RMSE精度
目录
- 简要介绍
- 代码
- 运行结果
简要介绍
SIFT,即尺度不变特征变换(Scale-invariant feature transform,SIFT),是用于图像处理领域的一种描述。这种描述具有尺度不变性,可在图像中检测出关键点,是一种局部特征描述子。 该方法于1999年由David Lowe 首先发表于计算机视觉国际会议(International Conference on Computer Vision,ICCV),2004年再次经David Lowe整理完善后发表于International journal of computer vision(IJCV)。
不仅在近景影像,SIFT在遥感影像也获得了极大的成功,本文旨在提供一个Demo,使用Python版本的Gdal读取遥感影像然后使用Opencv中的Sift等算法进行处理,还有给出一个计算匹精度RMSE的小工具。
代码
调用Opencv的SIFT进行匹配,使用单应性的RANSAC进行误匹配筛除。
from osgeo import gdal
import numpy as np
import cv2
import cmath
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from time import *
def readTIFF(tifpath, bandnum):
"""
Use GDAL to read data and transform them into arrays.
:param tifpath:tif文件的路径
:param bandnum:需要读取的波段
:return:该波段的数据,narray格式。len(narray)是行数,len(narray[0])列数
"""
image = gdal.Open(tifpath) # 打开影像
if image == None:
print(tifpath + "该tif不能打开!")
return
im_width = image.RasterXSize # 栅格矩阵的列数
im_height = image.RasterYSize # 栅格矩阵的行数
im_bands = image.RasterCount # 波段数
im_proj = image.GetProjection() # 获取投影信息坐标系
im_geotrans = image.GetGeoTransform() # 仿射矩阵
print('tif数据:{}个行,{}个列,{}层波段, 取出第{}层.'.format(im_width, im_height, im_bands, bandnum))
im_data = image.ReadAsArray(0, 0, im_width, im_height)
del image # 减少冗余
return im_data,im_proj, im_geotrans
def normalization(data):
_range = np.max(data) - np.min(data)
return (data - np.min(data)) / _range
def Tiff16to8bit(img_16):
if (np.max(img_16) - np.min(img_16) != 0):
# img_nrm = (img_16 - np.min(img_16)) / (np.max(img_16) - np.min(img_16)) #计算灰度范围,归一化
img_nrm = normalization(img_16)
img_8 = np.uint8(255 * img_nrm)
return img_8
def imagexy2geo(trans, row, col):
px = trans[0] + col * trans[1] + row * trans[2]
py = trans[3] + col * trans[4] + row * trans[5]
return px, py
def geo2imagexy(trans, x, y):
a = np.array([[trans[1], trans[2]], [trans[4], trans[5]]])
b = np.array([x - trans[0], y - trans[3]])
return np.linalg.solve(a, b) # 使用numpy的linalg.solve进行二元一次方程的求解
def SIFT(img_l, img_r):
sift = cv2.SIFT_create()
kp1, des1 = sift.detectAndCompute(img_l, None)
kp2, des2 = sift.detectAndCompute(img_r, None)
# 创建设置FLANN匹配
FLANN_INDEX_KDTREE = 0
index_params = dict(algorithm=FLANN_INDEX_KDTREE, trees=5)
search_params = dict(checks=50)
flann = cv2.FlannBasedMatcher(index_params, search_params)
matches = flann.knnMatch(des1, des2, k=2)
# store all the good matches as per Lowe's ratio test.
good = []
# 舍弃大于0.7的匹配,初步筛除
for m, n in matches:
if m.distance < 0.7 * n.distance:
good.append(m)
MIN_MATCH_COUNT = 10 # 设置最低特征点匹配数量为10
if len(good) > MIN_MATCH_COUNT:
# 获取关键点的坐标
src_pts = np.float32([kp1[m.queryIdx].pt for m in good]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
dst_pts = np.float32([kp2[m.trainIdx].pt for m in good]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
# 计算变换矩阵和MASK
M, mask = cv2.findHomography(src_pts, dst_pts, cv2.RANSAC, 3.0)
#M, mask = cv2.findFundamentalMat(src_pts, dst_pts, cv2.FM_RANSAC, 1.0)
matchesMask = mask.ravel().tolist()
calRMSE(src_pts, dst_pts, M, mask)#计算匹配算的精度)
else:
print("Not enough matches are found - %d/%d" % (len(good), MIN_MATCH_COUNT))
matchesMask = None
draw_params = dict(matchColor=(0, 255, 255),
singlePointColor=None,
matchesMask=matchesMask,
flags=2)
row_l, col_l = img_l.shape
row_r, col_r = img_r.shape
img_show = np.empty((max(row_l, row_r), col_l + col_r))
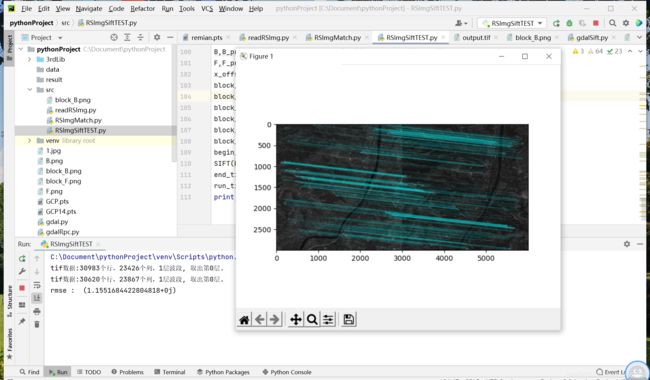
img_show = cv2.drawMatches(img_l,kp1,img_r,kp2,good,None,**draw_params)
#plt.imshow(img_show), plt.show()
def calRMSE(src_pts,dst_pts,M,mask):
# 求残差
sum_H = 0 #残差和
num = 0 #参与统计的总个数
for i, j, m in zip(src_pts, dst_pts, mask):
P_src = np.float32([i[0][0],i[0][1],1]).reshape((-1, 1))
P = np.matmul(M, P_src) #通过计算出的矩阵预测点
p = np.float32([P[0] / P[2], P[1] / P[2]]) #从齐次矩阵变为2维点
j = j.T
distance = np.linalg.norm(p - j)
if (m == True):
sum_H += distance
num += 1
rmse = cmath.sqrt(sum_H/num)
print("rmse : ",rmse)
return rmse
B,B_proj, B_geotrans = readTIFF('D:\\SongshanZY3\\ortho\\BWDSC.tif', 1)
F,F_proj, F_geotrans = readTIFF('D:\\SongshanZY3\\ortho\\FWDSC.tif', 1)
x_offset,y_offset = 5000,6000
block_size_x = 3000
block_size_y = 3000
block_B = B[y_offset:y_offset + block_size_y,x_offset:x_offset + block_size_x]
block_F = F[y_offset:y_offset + block_size_y,x_offset:x_offset + block_size_x]
block_B = Tiff16to8bit(block_B)
block_F = Tiff16to8bit(block_F)
begin_time = time()
SIFT(block_B,block_F)
end_time = time()
run_time = end_time-begin_time
print ('匹配耗时运行时间:',run_time,'s') #该循环程序运行时间: 1.4201874732