PyTorch学习笔记(9)--神经网络:线性层
PyTorch学习笔记(9)–神经网络:线性层
本博文是PyTorch的学习笔记,第9次内容记录,主要介绍神经网络线性层的基本使用。
目录
- PyTorch学习笔记(9)--神经网络:线性层
- 1.什么是线性层
- 2.线性层
-
- 2.1线性激活函数相关参数
- 2.2线性层应用举例1
- 2.3线性层应用举例2
- 3.学习小结
1.什么是线性层
线性层又叫全连接层,其中每个神经元与上一层所有神经元相连,一个简单的线性层如下图所示:
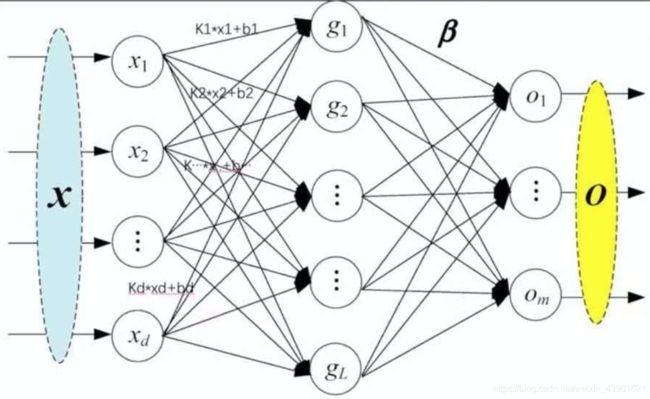
2.线性层
2.1线性激活函数相关参数
在PyTorch官网中,详细介绍了线性层的详细情况,线性函数为:torch.nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias=True, device=None, dtype=None),其中重要的3个参数in_features、out_features、bias说明如下:
- in_features:每个输入(x)样本的特征的大小
- out_features:每个输出(y)样本的特征的大小
- bias:如果设置为False,则图层不会学习附加偏差。默认值是True,表示增加学习偏置。
在上图中,in_features=d,out_features=L。
2.2线性层应用举例1
现以CIFAR10图片数据集为数据集,线性层实现代码如下:
# coding :UTF-8
# 文件功能: 代码实现神经网络--线性层功能
# 开发人员: dpp
# 开发时间: 2021/8/17 10:28 下午
# 文件名称: nn_linear.py
# 开发工具: PyCharm
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Linear
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("CIFAR10", train=False,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=64)
class Test(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Test, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = Linear(196608, 10)
def forward(self, input):
output = self.linear1(input)
return output
test = Test()
for data in dataloader:
imgs, targets = data
print(imgs.shape) # torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
output = torch.reshape(imgs, (1, 1, 1, -1))
print(output.shape) # torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 196608])
output = test(output)
print(output.shape) # torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 10])
上述的代码中Test类中实现线性函数self.linear1 = Linear(196608, 10),其中输入特征的大小为196608,输出特征的大小为10。output = torch.reshape(imgs, (1, 1, 1, -1))代码的功能是实现输入尺寸的重塑造,也就是将输入矩阵拉直。上述代码输出结果如下:
torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 196608])
torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 10])
torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 196608])
torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 10])
torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 196608])
torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 10])
...
2.3线性层应用举例2
除了使用reshape函数实现输入尺寸的修改,torch中还提供了flatten()函数实现将输入矩阵拉直。代码如下所示:
# coding :UTF-8
# 文件功能: 代码实现神经网络--线性层功能
# 开发人员: dpp
# 开发时间: 2021/8/17 10:28 下午
# 文件名称: nn_linear.py
# 开发工具: PyCharm
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Linear
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("CIFAR10", train=False,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=64)
class Test(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Test, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = Linear(196608, 10)
def forward(self, input):
output = self.linear1(input)
return output
test = Test()
for data in dataloader:
imgs, targets = data
print(imgs.shape) # torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
output = torch.flatten(imgs) # flatten()函数拉直输入数据
print(output.shape) # torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 196608])
output = test(output)
print(output.shape) # torch.Size([1, 1, 1, 10])
输出结果如下:
torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
torch.Size([196608])
torch.Size([10])
torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
torch.Size([196608])
torch.Size([10])
torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
torch.Size([196608])
torch.Size([10])
3.学习小结
在本文中总结了神经网络的线性层的基本使用方法,并通过构建一个类Test分别介绍了Linear()函数和flatten()函数的使用方法,在下一篇博文,将搭建一个简单的网络模型,并结合Sequential的使用。