opencv 插值方式
一、插值方式与resize()的关系
resize()函数里面包含插值的几种方式:
void resize(InputArray src,//输入,原图像,即待改变大小的图像;
OutputArray dst, //输出,改变大小之后的图像,这个图像和原图像具有相同的内容,只是大小和原图像不一样而已;
Size dsize, //输出图像的大小。如果这个参数不为0,那么就代表将原图像缩放到这个Size(width,height)指定的大小;如果这个参数为0,那么原图像缩放之后的大小就要通过下面的公式来计算:
double fx=0, // width方向的缩放比例,如果它是0,那么它就会按照(double)dsize.width/src.cols来计算;
double fy=0, //height方向的缩放比例,如果它是0,那么它就会按照(double)dsize.height/src.rows来计算;
int interpolation=INTER_LINEAR// 这个是指定插值的方式,图像缩放之后,肯定像素要进行重新计算的,就靠这个参数来指定重新计算像素的方式,有以下几种:
INTER_NEAREST - 最邻近插值
INTER_LINEAR - 双线性插值,如果最后一个参数你不指定,默认使用这种方法
INTER_AREA -区域插值 resampling using pixel area relation. It may be a preferred method for image decimation, as it gives moire’-free results. But when the image is zoomed, it is similar to the INTER_NEAREST method.
INTER_CUBIC - 4x4像素邻域内的双立方插值
INTER_LANCZOS4 - 8x8像素邻域内的Lanczos插值
);
使用注意事项:
dsize和fx/fy不能同时为0,
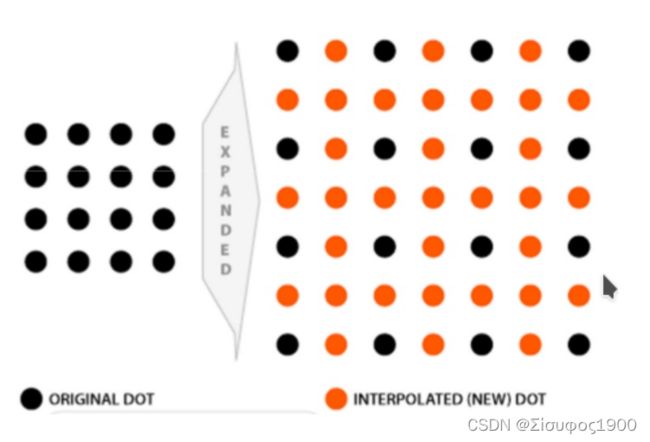
二、近邻插值INTER_NEAREST
最近邻插值法, 找到与之距离最相近的邻居(原来就存在的像素点, 黑点), 赋值与其相同。
实现opencv中常用的三种插值算法 - 简书
//最近邻域插值
//根据目标图像的像素点(浮点坐标)找到原始图像中的4个像素点,取距离该像素点最近的一个原始像素值作为该点的值。
#include(i, j) = src.at(y1, x1);
break;
case 1:
dst.at(i, j) = src.at(y1, x2);
break;
case 2:
dst.at(i, j) = src.at(y2, x1);
break;
case 3:
dst.at(i, j) = src.at(y2, x2);
break;
default:
assert(false);
}
}
}
double distance(const double x1, const double y1, const double x2, const double y2)//两点之间距离,这里用欧式距离
{
return (x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2)*(y1 - y2);//只需比较大小,返回距离平方即可
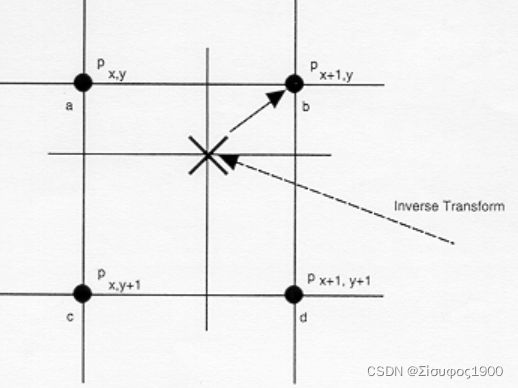
} 三、线性插值
已知两点(红色) ,在给出一个蓝点的x坐标, 求y。
//线性内插(双线性插值)
#include(y1, x1)), static_cast<double>(src.at(y2, x1)),
static_cast<double>(src.at(y1, x2)), static_cast<double>(src.at(y2, x2)) };
cv::Matx21d maty = {
y2 - y,
y - y1
};
auto val = (matx * matf * maty);
dst.at(i, j) = val(0,0);
}
} 四、双三次插值
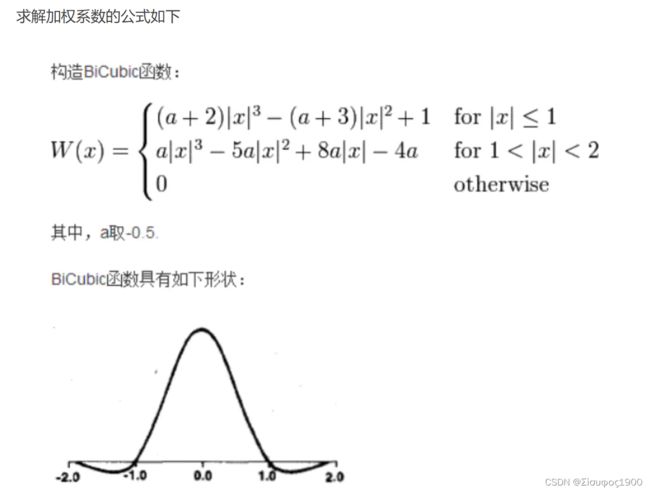
在数值分析这个数学分支中,双三次插值(英语:Bicubic interpolation)是二维空间中最常用的插值方法。在这种方法中,函数 f 在点 (x, y) 的值可以通过矩形网格中最近的十六个采样点的加权平均得到,在这里需要使用两个多项式插值三次函数,每个方向使用一个
双三次插值计算公式![]()
那么这个a(i, j)便是介绍里面所说的加权系数了,所以关键是要把它求解出来。
求解加强系数代码如下:
std::vector mycv::getW(double coor, double a)
{
std::vector w(4);
int base = static_cast(coor);//取整作为基准
double e = coor - static_cast(base);//多出基准的小数部分
std::vector tmp(4);//存放公式中 |x| <= 1, 1 < |x| < 2四个值
// 4 x 4的16个点,所以tmp[0]和tmp[4]距离较远,值在[1, 2]区间
tmp[0] = 1.0 + e;// 1 < x < 2
tmp[1] = e;//x <= 1
tmp[2] = 1.0 - e;// x <= 1
tmp[3] = 2.0 - e;// 1 < x < 2
//按照bicubic公式计算系数w
// x <= 1
w[1] = (a + 2.0) * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[1], 3)) - (a + 3.0) * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[1], 2)) + 1;
w[2] = (a + 2.0) * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[2], 3)) - (a + 3.0) * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[2], 2)) + 1;
// 1 < x < 2
w[0] = a * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[0], 3)) - 5.0 * a * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[0], 2)) + 8.0*a*std::abs(tmp[0]) - 4.0*a;
w[3] = a * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[3], 3)) - 5.0 * a * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[3], 2)) + 8.0*a*std::abs(tmp[3]) - 4.0*a;
return w;
}
求解出来之后,wx和wy就是4x4组成的16个系数,与插值所需要用到4x4的16个点相匹配。插值步骤的关键代码
//4x4数量的点(rr, cc) -> (y, x)
std::vector > src_arr = {
{ src.at(rr - 1, cc - 1), src.at(rr, cc - 1), src.at(rr + 1, cc - 1), src.at(rr + 2, cc - 1)},
{ src.at(rr - 1, cc), src.at(rr, cc), src.at(rr + 1, cc), src.at(rr + 2, cc)},
{ src.at(rr - 1, cc + 1), src.at(rr, cc + 1), src.at(rr + 1, cc + 1), src.at(rr + 2, cc + 1)},
{ src.at(rr - 1, cc + 2), src.at(rr, cc + 2), src.at(rr + 1, cc + 2), src.at(rr + 2, cc + 2)}
};
for(int p = 0; p < 3; ++p)
for (int q = 0; q < 3; ++q)
{
//val(p, q) = w(p,q) * src(p, q)
val += wr[p] * wc[q] * static_cast(src_arr[p][q]);
}
assert(i < dst.rows && j < dst.cols);
dst.at(i, j) = static_cast(val);
//双三次插值
#include
#include
#include
#include
namespace mycv {
void bicubicInsterpolation(cv::Mat& src, cv::Mat& dst, const int rows, const int cols);
std::vector getW(double coor, double a = -0.5);//a默认-0.5
}//mycv
int main(void)
{
cv::Mat img = cv::imread("lena.jpg", 0);
if (img.empty()) return -1;
cv::Mat dst;
mycv::bicubicInsterpolation(img, dst, 600, 600);
cv::imshow("img", img);
cv::imshow("dst", dst);
cv::waitKey(0);
return 0;
}//main
void mycv::bicubicInsterpolation(cv::Mat& src, cv::Mat& dst, const int rows, const int cols)
{
dst = cv::Mat(rows, cols, src.type(), cv::Scalar::all(0));//初始化dst
//比例尺
double row_scale = static_cast(src.rows) / rows;
double col_scale = static_cast(src.cols) / cols;
switch (src.channels())
{
case 1://灰度
for(int i = 2; i < dst.rows - 2; ++i)
for (int j = 2; j < dst.cols - 2; ++j)
{
//计算系数w
double r = static_cast(i * row_scale);
double c = static_cast(j * col_scale);
//防止越界
if (r < 1.0) r += 1.0;
if (c < 1.0) c += 1.0;
std::vector wr = mycv::getW( r);
std::vector wc = mycv::getW( c);
//最后计算插值得到的灰度值
double val = 0;
int cc = static_cast(c);
int rr = static_cast(r);
//防止越界
if (cc > src.cols - 3)
{
cc = src.cols - 3;
}
if (rr > src.rows - 3) rr = src.rows - 3;
assert(0 <= (rr - 1) && 0 <= (cc - 1) && (rr + 2) < src.rows && (cc + 2) < src.cols);
//4x4数量的点(rr, cc) -> (y, x)
std::vector > src_arr = {
{ src.at(rr - 1, cc - 1), src.at(rr, cc - 1), src.at(rr + 1, cc - 1), src.at(rr + 2, cc - 1)},
{ src.at(rr - 1, cc), src.at(rr, cc), src.at(rr + 1, cc), src.at(rr + 2, cc)},
{ src.at(rr - 1, cc + 1), src.at(rr, cc + 1), src.at(rr + 1, cc + 1), src.at(rr + 2, cc + 1)},
{ src.at(rr - 1, cc + 2), src.at(rr, cc + 2), src.at(rr + 1, cc + 2), src.at(rr + 2, cc + 2)}
};
for(int p = 0; p < 3; ++p)
for (int q = 0; q < 3; ++q)
{
//val(p, q) = w(p,q) * src(p, q)
val += wr[p] * wc[q] * static_cast(src_arr[p][q]);
}
assert(i < dst.rows && j < dst.cols);
dst.at(i, j) = static_cast(val);
}
break;
case 3://彩色(原理一样多了两个通道而已)
break;
default:
break;
}
}
std::vector mycv::getW(double coor, double a)
{
std::vector w(4);
int base = static_cast(coor);//取整作为基准
double e = coor - static_cast(base);//多出基准的小数部分
std::vector tmp(4);//存放公式中 |x| <= 1, 1 < |x| < 2四个值
// 4 x 4的16个点,所以tmp[0]和tmp[4]距离较远,值在[1, 2]区间
tmp[0] = 1.0 + e;// 1 < x < 2
tmp[1] = e;//x <= 1
tmp[2] = 1.0 - e;// x <= 1
tmp[3] = 2.0 - e;// 1 < x < 2
//按照bicubic公式计算系数w
// x <= 1
w[1] = (a + 2.0) * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[1], 3)) - (a + 3.0) * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[1], 2)) + 1;
w[2] = (a + 2.0) * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[2], 3)) - (a + 3.0) * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[2], 2)) + 1;
// 1 < x < 2
w[0] = a * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[0], 3)) - 5.0 * a * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[0], 2)) + 8.0*a*std::abs(tmp[0]) - 4.0*a;
w[3] = a * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[3], 3)) - 5.0 * a * std::abs(std::pow(tmp[3], 2)) + 8.0*a*std::abs(tmp[3]) - 4.0*a;
return w;
}