自回归移动平均模型(ARMA)-平稳序列
自回归滑动平均模型(ARMA模型,Auto-Regression and Moving Average Model)是研究时间序列的重要方法,由自回归模型(AR模型)与滑动平均模型(MA模型)为基础“混合”而成,具有适用范围广、预测误差小的特点。ARMA原理分析,见此篇博客。
1. 导入python中的相关模块
import tushare as ts
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import statsmodels.tsa.api as smtsa
from statsmodels.tsa.stattools import adfuller as ADF
from statsmodels.tsa.arima_model import ARMA
from statsmodels.stats.diagnostic import acorr_ljungbox as acorr
from statsmodels.graphics.tsaplots import plot_acf, plot_pacf
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
2. 载入数据集
本模型使用的为某股票公开数据集
ts.set_token('46af5ae83a803c592eeff2620f87402fea47911650b115cf1f671f64')
pro = ts.pro_api()
data = pro.daily(ts_code='000001.SZ', start_date='20100101', end_date='20200101')
data.sort_values(by='trade_date', inplace=True)
data.reset_index(drop='True', inplace=True)
data# 查看data数据
| ts_code | trade_date | open | high | low | close | pre_close | change | pct_chg | vol | amount | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 000001.SZ | 20100104 | 24.52 | 24.58 | 23.68 | 23.71 | 24.37 | -0.66 | -2.7100 | 241922.76 | 5.802495e+05 |
| 1 | 000001.SZ | 20100105 | 23.75 | 23.90 | 22.75 | 23.30 | 23.71 | -0.41 | -1.7300 | 556499.82 | 1.293477e+06 |
| 2 | 000001.SZ | 20100106 | 23.25 | 23.25 | 22.72 | 22.90 | 23.30 | -0.40 | -1.7200 | 412143.13 | 9.444537e+05 |
| 3 | 000001.SZ | 20100107 | 22.90 | 23.05 | 22.40 | 22.65 | 22.90 | -0.25 | -1.0900 | 355336.85 | 8.041663e+05 |
| 4 | 000001.SZ | 20100108 | 22.50 | 22.75 | 22.35 | 22.60 | 22.65 | -0.05 | -0.2200 | 288543.06 | 6.506674e+05 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 2356 | 000001.SZ | 20191225 | 16.45 | 16.56 | 16.24 | 16.30 | 16.40 | -0.10 | -0.6098 | 414917.98 | 6.796646e+05 |
| 2357 | 000001.SZ | 20191226 | 16.34 | 16.48 | 16.32 | 16.47 | 16.30 | 0.17 | 1.0429 | 372033.86 | 6.103818e+05 |
| 2358 | 000001.SZ | 20191227 | 16.53 | 16.93 | 16.43 | 16.63 | 16.47 | 0.16 | 0.9715 | 1042574.72 | 1.741473e+06 |
| 2359 | 000001.SZ | 20191230 | 16.46 | 16.63 | 16.10 | 16.57 | 16.63 | -0.06 | -0.3608 | 976970.31 | 1.603153e+06 |
| 2360 | 000001.SZ | 20191231 | 16.57 | 16.63 | 16.31 | 16.45 | 16.57 | -0.12 | -0.7242 | 704442.25 | 1.154704e+06 |
2361 rows × 11 columns
填补data中的缺失值
data = data.iloc[:, 1:]
data = data.fillna(method='ffill')# 用前一个非缺失值去填充该缺失值
data.head()
| trade_date | open | high | low | close | pre_close | change | pct_chg | vol | amount | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 20100104 | 24.52 | 24.58 | 23.68 | 23.71 | 24.37 | -0.66 | -2.71 | 241922.76 | 5.802495e+05 |
| 1 | 20100105 | 23.75 | 23.90 | 22.75 | 23.30 | 23.71 | -0.41 | -1.73 | 556499.82 | 1.293477e+06 |
| 2 | 20100106 | 23.25 | 23.25 | 22.72 | 22.90 | 23.30 | -0.40 | -1.72 | 412143.13 | 9.444537e+05 |
| 3 | 20100107 | 22.90 | 23.05 | 22.40 | 22.65 | 22.90 | -0.25 | -1.09 | 355336.85 | 8.041663e+05 |
| 4 | 20100108 | 22.50 | 22.75 | 22.35 | 22.60 | 22.65 | -0.05 | -0.22 | 288543.06 | 6.506674e+05 |
data = data[['trade_date', 'open', 'close', 'high', 'low']]
data.plot(subplots=True, figsize=(10, 12))
plt.title(' zhangshang stock attributes from 2010-01-01 to 2020-01-01')
plt.show()
3. 平稳性检验
#平稳性检验
adf = ADF(data['close'])
if adf[1] > 0.05:# adf[i]表示对data['close']数据进行1阶差分
print(u'原始序列经检验不平稳,p值为:%s'%(adf[1]))
else:
print(u'原始序列经检验平稳,p值为:%s'%(adf[1]))
原始序列经检验平稳,p值为:0.017668059342580877
4. 白噪声检验
p值越大表示数据是随机的可能性越大,随机性很大的数据没有研究意义。
#采用LB统计量的方法进行白噪声检验
p = acorr(data['close'], lags=1)
if p[1] < 0.05:
print(u'原始序列非白噪声序列,p值为:%s'%p[1])
else:
print(u'原始序列为白噪声序列,p值为:%s'%p[1])
原始序列非白噪声序列,p值为:[0.]
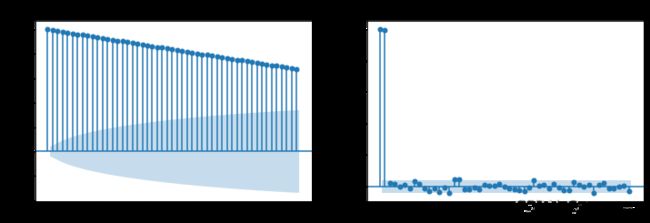
5. 模型识别
# 定义绘图函数plotds
def plotds (xt, nlag=30, fig_size=(12,8)):
if not isinstance(xt, pd.Series): #判断xt是否是pd.Series类型数据,不是则转化为该类型数据
xt = pd.Series(xt)
plt.figure(figsize=fig_size)
plt.plot(xt)# 原始数据时序图
plt.title("Time Series")
plt.show()
plt.figure(figsize=fig_size)
layout = (2, 2)
ax_acf = plt.subplot2grid(layout, (1, 0))
ax_pacf = plt.subplot2grid(layout, (1, 1))
plot_acf(xt, lags=nlag, ax=ax_acf)# 自相关图
plot_pacf(xt, lags=nlag, ax=ax_pacf)# 偏自相关图
plt.show()
return None
plotds(data['close'].dropna(), nlag=50)
#定阶
data_df = data.copy()
aicVal = []
for ari in range(1, 3):
for maj in range(0,5):
try:
arma_obj = smtsa.ARMA(data_df.close.tolist(), order=(ari, maj))\
.fit(maxlag=30, method='mle', trend='nc')
aicVal.append([ari, maj, arma_obj.aic])
except Exception as e:
print(e)
aicVal
[[1, 0, 1958.0143376009719],
[1, 1, 1958.7504776249589],
[1, 2, 1960.3388645021796],
[1, 3, 1962.0299202559945],
[1, 4, 1963.6365504220475],
[2, 0, 1958.7847615798437],
[2, 1, 1960.5080165518111],
[2, 2, 1957.0524190412552],
[2, 3, 1959.0187650693679],
[2, 4, 1961.0165491508224]]
6. 训练模型
从aicVal的结果可以看到模型阶数为(2,2)时,AIC最小为1957.0524190412552,故选择(2,2)阶数的模型。
arma_obj_fin = smtsa.ARMA(data_df['close'].tolist(), order=(2, 2)).fit(maxlag=30, method='mle', trend='nc', disp=False)
arma_obj_fin.summary()
| Dep. Variable: | y | No. Observations: | 2361 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model: | ARMA(2, 2) | Log Likelihood | -973.526 |
| Method: | mle | S.D. of innovations | 0.365 |
| Date: | Thu, 06 May 2021 | AIC | 1957.052 |
| Time: | 19:06:47 | BIC | 1985.887 |
| Sample: | 0 | HQIC | 1967.551 |
| coef | std err | z | P>|z| | [0.025 | 0.975] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ar.L1.y | 0.0320 | nan | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| ar.L2.y | 0.9676 | nan | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| ma.L1.y | 0.9468 | nan | nan | nan | nan | nan |
| ma.L2.y | -0.0329 | 0.020 | -1.628 | 0.103 | -0.073 | 0.007 |
| Real | Imaginary | Modulus | Frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR.1 | 1.0002 | +0.0000j | 1.0002 | 0.0000 |
| AR.2 | -1.0333 | +0.0000j | 1.0333 | 0.5000 |
| MA.1 | -1.0200 | +0.0000j | 1.0200 | 0.5000 |
| MA.2 | 29.7678 | +0.0000j | 29.7678 | 0.0000 |
7.模型拟合效果
#plot the curves
data_df["ARMA"] = arma_obj_fin.predict()
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))
plt.plot(data_df['close'].iloc[-100:], color='b', label='Actual')
plt.plot(data_df["ARMA"].iloc[-100:], color='r', linestyle='--', label='ARMA(2,2)_pre')
plt.xlabel('index')
plt.ylabel('close price')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
8. 模型预测
fig = arma_obj_fin.plot_predict(len(data_df)-50, len(data_df)+10)
predict = arma_obj_fin.predict(start=1, end=len(data_df)+10)
predict[-10:]
array([16.44779647, 16.45696253, 16.44202199, 16.4504122 , 16.43622479,
16.44388842, 16.43040644, 16.43738965, 16.42456844, 16.43091446])