YoloX引入注意力机制,CIoU、DIoU,DW卷积
本文以Bubbliiing的YoloX代码进行注意力机制的增加,原博文参考以下。
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44791964/article/details/120476949?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
在darknet中引入注意力机制
在darknet.py文件中加入以下代码。
'''注意力模块'''
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, ratio=16):
super(ChannelAttention, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.max_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(1)
self.f1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, in_planes // ratio, 1, bias=False)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.f2 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes // ratio, in_planes, 1, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avg_out = self.f2(self.relu(self.f1(self.avg_pool(x))))
max_out = self.f2(self.relu(self.f1(self.max_pool(x))))
out = self.sigmoid(avg_out + max_out)
return out
class SpatialAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, kernel_size=7):
super(SpatialAttention, self).__init__()
assert kernel_size in (3, 7), 'kernel size must be 3 or 7'
padding = 3 if kernel_size == 7 else 1
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size, padding=padding, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avg_out = torch.mean(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
max_out, _ = torch.max(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat([avg_out, max_out], dim=1)
x = self.conv(x)
return self.sigmoid(x)
class CBAM(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 3 convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, ratio=16, kernel_size=7): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super(CBAM, self).__init__()
self.channel_attention = ChannelAttention(c1, ratio)
self.spatial_attention = SpatialAttention(kernel_size)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.channel_attention(x) * x
out = self.spatial_attention(out) * out
return out
class SE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, r=16):
super(SE, self).__init__()
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.l1 = nn.Linear(c1, c1 // r, bias=False)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.l2 = nn.Linear(c1 // r, c1, bias=False)
self.sig = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avgpool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.l1(y)
y = self.relu(y)
y = self.l2(y)
y = self.sig(y)
y = y.view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y
'''注意力模块'''
基于MobileNet网络,我考虑在每一个bottleneck中引入se注意力机制。
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
# Standard bottleneck
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, shortcut=True, expansion=0.5, depthwise=False, act="silu",):
super().__init__()
hidden_channels = int(out_channels * expansion)
Conv = DWConv if depthwise else BaseConv
self.conv1 = BaseConv(in_channels, hidden_channels, 1, stride=1, act=act)
self.conv2 = Conv(hidden_channels, out_channels, 3, stride=1, act=act)
self.use_add = shortcut and in_channels == out_channels
'''注意力机制'''
self.se = SE(hidden_channels)
def forward(self, x):
'''注意力机制'''
y = self.conv2(self.se(self.conv1(x)))
# y = self.conv2(self.conv1(x))
if self.use_add:
y = y + x
return y
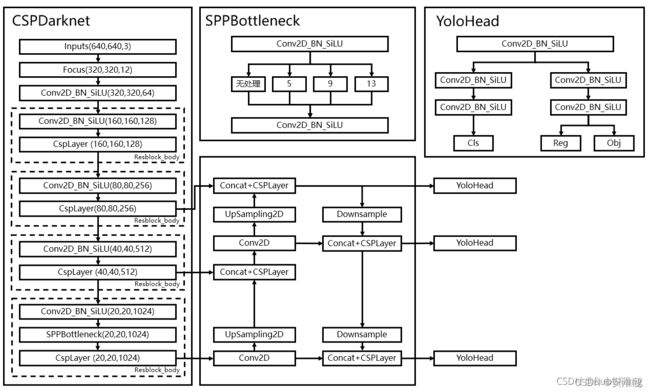
并在darknet.py中,输入到特征金字塔部分的80,80,256;40,40,512;20,20,1024的三个有效特征层分别加入CBAM注意力机制。
class CSPDarknet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dep_mul, wid_mul, out_features=("dark3", "dark4", "dark5"), depthwise=False, act="silu",):
super().__init__()
assert out_features, "please provide output features of Darknet"
self.out_features = out_features
Conv = DWConv if depthwise else BaseConv
base_channels = int(wid_mul * 64) # 64
base_depth = max(round(dep_mul * 3), 1) # 3
# -----------------------------------------------#
# 引入cbam注意力机制
# -----------------------------------------------#
self.cbam1 = CBAM(base_channels * 4)
self.cbam2 = CBAM(base_channels * 8)
self.cbam3 = CBAM(base_channels * 16)
self.stem = Focus(3, base_channels, ksize=3, act=act)
self.dark2 = nn.Sequential(
Conv(base_channels, base_channels * 2, 3, 2, act=act),
CSPLayer(base_channels * 2, base_channels * 2, n=base_depth, depthwise=depthwise, act=act),
)
self.dark3 = nn.Sequential(
Conv(base_channels * 2, base_channels * 4, 3, 2, act=act),
CSPLayer(base_channels * 4, base_channels * 4, n=base_depth * 3, depthwise=depthwise, act=act),
)
self.dark4 = nn.Sequential(
Conv(base_channels * 4, base_channels * 8, 3, 2, act=act),
CSPLayer(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 8, n=base_depth * 3, depthwise=depthwise, act=act),
)
self.dark5 = nn.Sequential(
Conv(base_channels * 8, base_channels * 16, 3, 2, act=act),
SPPBottleneck(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 16, activation=act),
CSPLayer(base_channels * 16, base_channels * 16, n=base_depth, shortcut=False, depthwise=depthwise, act=act),
)
def forward(self, x):
outputs = {}
x = self.stem(x)
outputs["stem"] = x
x = self.dark2(x)
outputs["dark2"] = x
#---------------------------------------------------------#
# dark3的输出为80, 80, 256,是一个有效特征层,引入cbam模块
#---------------------------------------------------------#
x = self.dark3(x)
x1 = self.cbam1(x)
outputs["dark3"] = x1
#--------------------------------------------------------#
# dark4的输出为40, 40, 512,是一个有效特征层,引入cbam模块
#--------------------------------------------------------#
x = self.dark4(x)
x2 = self.cbam2(x)
outputs["dark4"] = x2
#--------------------------------------------------------#
# dark5的输出为20, 20, 1024,是一个有效特征层,引入cbam模块
#--------------------------------------------------------#
x = self.dark5(x)
x3 = self.cbam3(x)
outputs["dark5"] = x3
return {k: v for k, v in outputs.items() if k in self.out_features}
在特征金字塔中加入注意力机制
在特征金字塔中每个上采样和下采样之后使用注意力机制。
在nets/yolo.py中的YOLOPAFPN类加入以下代码。
in_channels = [256, 512, 1024]
'''注意力机制'''
self.cbam1 = CBAM(c1 = int(in_channels[1] * width))
self.cbam2 = CBAM(c1 = int(in_channels[0] * width))
self.cbam3 = CBAM(c1 = int(in_channels[0] * width))
self.cbam4 = CBAM(c1 = int(in_channels[1] * width))
- 其中*width部分是为了适应不同大小的网络对于通道数的要求。
- int类型指定了输入通道数的整数类型,否则会报错。
TypeError: empty() received an invalid combination of arguments - got (tuple, dtype=NoneType, device=NoneType), but expected one of:
在对应的采样部分加入
P5_upsample = self.cbam1(P5_upsample)
P4_upsample = self.cbam2(P4_upsample)
P3_downsample = self.cbam3(P3_downsample)
P4_downsample = self.cbam4(P4_downsample)
训练即可,只增加了少量的运算量。
DW卷积的实现
学习发现大佬的darknet.py文件里已经集成了DW卷积,但是没有使用。
class DWConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, ksize, stride=1, act="silu"):
super().__init__()
self.dconv = BaseConv(in_channels, in_channels, ksize=ksize, stride=stride, groups=in_channels, act=act,)
self.pconv = BaseConv(in_channels, out_channels, ksize=1, stride=1, groups=1, act=act)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.dconv(x)
return self.pconv(x)
DW卷积是否开启使用是由depthwise参数控制的。
我这里使用yolo_x.pth进行训练,想使用DW卷积大大减少参数量(具体可以达到接近50%的参数量减少)。
修改nets/yolo.py中的
depthwise = True if phi == 'x' else False
并且在train.py中修改
phi = 'x'
即可。
使用混合精度训练
train.py中修改为True,注意版本号。
# fp16 是否使用混合精度训练
# 可减少约一半的显存、需要pytorch1.7.1以上
fp16 = True
使用双线性插值进行上采样
在net/yolo.py中更改
'''mode有更改,有'nearest', 'linear', 'bilinear', 'bicubic' and trilinear'''
self.upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear')
不使用预训练权重直接开始训练
因为在bottleneck中引入了se注意力模块,因此无法直接读取.pth与训练权重,因此直接从头开始训练。
train.py脚本里model_path设置为空。
model_path = ''
Freeze_Train设置成False
Freeze_Train = False
使用DIoU,CIoU进行训练
yolo.training.py中修改class IOUloss
class IOUloss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, reduction="none", loss_type="iou"):
super(IOUloss, self).__init__()
self.reduction = reduction
self.loss_type = loss_type
def forward(self, pred, target):
assert pred.shape[0] == target.shape[0]
# pred,target为xywh格式
pred = pred.view(-1, 4)
target = target.view(-1, 4)
# tl:top_left, br:bottom_right
tl = torch.max(
(pred[:, :2] - pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] - target[:, 2:] / 2)
)
br = torch.min(
(pred[:, :2] + pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] + target[:, 2:] / 2)
)
# torch.prob为算矩阵乘积,pred[:, 2:]为wh,算出来为面积
area_p = torch.prod(pred[:, 2:], 1)
area_g = torch.prod(target[:, 2:], 1)
# en应该是一个比例吧!交集所占两个框所接最小外界矩形面积的比例
en = (tl < br).type(tl.type()).prod(dim=1)
# torch.prod(br - tl, 1)为最小外接矩形的面积,giou需要用到
area_i = torch.prod(br - tl, 1) * en
# 并集的面积
area_u = area_p + area_g - area_i
iou = (area_i) / (area_u + 1e-16)
if self.loss_type == "iou":
loss = 1 - iou ** 2
elif self.loss_type == "giou":
c_tl = torch.min(
(pred[:, :2] - pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] - target[:, 2:] / 2)
)
c_br = torch.max(
(pred[:, :2] + pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] + target[:, 2:] / 2)
)
# 最小外接矩形的面积
area_c = torch.prod(c_br - c_tl, 1)
# area_c.clamp(1e-16)意义为将area_c的值下限设为1e-16,防止报错
giou = iou - (area_c - area_u) / area_c.clamp(1e-16)
# giou.clamp(min=-1.0, max=1.0)将giou值域限制为(-1,1),实际上giou的值也就是这个值
loss = 1 - giou.clamp(min=-1.0, max=1.0)
# 尝试加入diou,ciou
elif self.loss_type == 'diou':
c_tl = torch.min(
(pred[:, :2] - pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] - target[:, 2:] / 2)
)
c_br = torch.max(
(pred[:, :2] + pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] + target[:, 2:] / 2)
)
# 最大外界矩形对角线长度c^2
w_c = (c_br - c_tl)[:, 0]
h_c = (c_br - c_tl)[:, 1]
c = w_c ** 2 + h_c ** 2
# 中心点距离平方d^2
w_d = (pred[:, :2] - target[:, :2])[:, 0]
h_d = (pred[:, :2] - target[:, :2])[:, 1]
d = w_d ** 2 + h_d ** 2
# 求diou
diou = iou - d/c
loss = 1 - diou.clamp(min=-1.0, max=1.0)
elif self.loss_type == 'ciou':
c_tl = torch.min(
(pred[:, :2] - pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] - target[:, 2:] / 2)
)
c_br = torch.max(
(pred[:, :2] + pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] + target[:, 2:] / 2)
)
# 最大外界矩形对角线长度c^2
w_c = (c_br - c_tl)[:, 0]
h_c = (c_br - c_tl)[:, 1]
c = w_c ** 2 + h_c ** 2
# 中心点距离平方d^2
w_d = (pred[:, :2] - target[:, :2])[:, 0]
h_d = (pred[:, :2] - target[:, :2])[:, 1]
d = w_d ** 2 + h_d ** 2
# 求diou
diou = iou - d / c
w_gt = target[:, 2]
h_gt = target[:, 3]
w = pred[:, 2]
h = pred[:, 3]
with torch.no_grad():
arctan = torch.atan(w_gt / h_gt) - torch.atan(w / h)
v = (4 / (math.pi ** 2)) * torch.pow(arctan, 2)
s = 1 - iou
alpha = v / (s + v)
ciou = diou - alpha * v
loss = 1-ciou.clamp(min=-1.0, max=1.0)
if self.reduction == "mean":
loss = loss.mean()
elif self.reduction == "sum":
loss = loss.sum()
return loss
使用GIoU、DIoU、CIoU Loss进行训练
具体GIoU、DIoU、CIoU有什么改进可以参考我的一篇博文。
https://blog.csdn.net/shayinzzh/article/details/124336574
yolo_training.py文件中修改如下:
self.iou_loss = IOUloss(reduction="none", loss_type="ciou")
想使用什么种类的iou修改loss_type即可。
发现的一些问题
在summary.py中使用s模型
m = YoloBody(80, 's').to(device)
参数量为
Total params: 9,083,365
Trainable params: 9,083,365
Non-trainable params: 0
使用DW卷积之后,报错
RuntimeError: CUDA out of memory.
使用DW卷积就是减少参数量,为什么会报显存不足的问题,很难理解。
理解:代替普通Conv2D的是DW卷积和PW卷积,相当于两层卷积代替一层卷积,虽然网络的参数量减少了,但是网络层数加深了,因此运行会报显存不足的问题。
在summary.py中使用tiny模型
参数量为
Total params: 5,120,709
Trainable params: 5,120,709
Non-trainable params: 0
使用DW卷积之后
Total params: 2,078,853
Trainable params: 2,078,853
Non-trainable params: 0
正常运行,可见使用DW卷积可以大大减少可训练的参数量。
具体对精度的影响还未测试。