浅析C#Image类
进来初学C#,为了让记忆更深刻一点,避免日后需要用时反复做同样的工作,决定把现在查到的一些资料,和自己的一些理解记录下来。
使用C#读图并不困难。Image类中提供了FromFile()函数,可以直接把指定了路径与文件名的图片载入到Image类的各种派生类中;FromFile函数在MSDN中的声明如下:![]()
C#自身提供了Picture Box控件,新建工程选择Windows应用程序,命名为Picture_Viewer,首先在添加控件OpenFileDialog,命名为ofdSelectPicture,然后添加Picture Box,命名为picShowPicture,同时添加button按钮,命名为btnSelectPicture。效果如下:
直接双击button按钮,进入代码段编辑如下代码:
if (ofdSelectPicture.ShowDialog()==DialogResult.OK)
{
picShowPicture.Image = Image.FromFile(ofdSelectPicture.FileName);
this.Text = string.Concat("Picture View(" + ofdSelectPicture.FileName + ")");
}
对于码农来讲,更重要的应该是对于Image类应该如何使用,对像素值的访问和操作。于是查看MSDN发现:
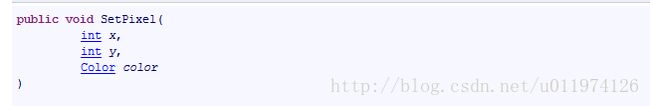
Image类只提供了 GetType ,ToString 等方法,以及Height ,Width等属性,并未提供对数据成员的操作的方法。但是在Image 的派生类Bitmap类中,GetPixel 和 SetPixel等方法,可以方便的对图像的像素值进行操作。以SetPixel在MSDN中的声明为例:
x和y分表表示像素点的行列坐标,color为要设置的像素值的颜色值。实例如下:
public static bool GetRGB(Bitmap Source, out int[,] R, out int[,] G, out int[,] B)
{
try
{
int iWidth = Source.Width;
int iHeight = Source.Height;
// 注意这个地方图像的两维方向与数组两维的方向是转置的关系
R = new int[iHeight, iWidth];
G = new int[iHeight, iWidth];
B = new int[iHeight, iWidth];
for (int i = 0; i < iHeight; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < iWidth; j++)
{
Color colCurr = Source.GetPixel(j, i);
R[i, j] = colCurr.R;
G[i, j] = colCurr.G;
B[i, j] = colCurr.B;
}
}
return true;
}
catch (Exception)
{
R = null;
G = null;
B = null;
return false;
}
}然而,这种对于像素值的操作看似很简单,很方便,却是以牺牲时间代价为前提的。实验发现,对于一副640*480的图像的操作需要话费1至2分钟,更别提在图像上做其他的处理了。
由于C#托管代码中不能使用指针(经验证,即使是在unsafe代码中用指针操作,速度仍然很慢),因此我们就不能像C++里面一样直接利用指针在内存中完成读写操作。好在.NET Framework提供了托管内存与非托管内存之间的读写功能,一个强大的Marshal类,使得我们快速读写图像的像素信息成为可能。
需要提到的就是Marshal.Copy 方法 ,该方法用于将托管数组复制到非托管内存指针,或者从非托管内存指针复制到托管数组中。Marshal.Copy 的重载方法很多,
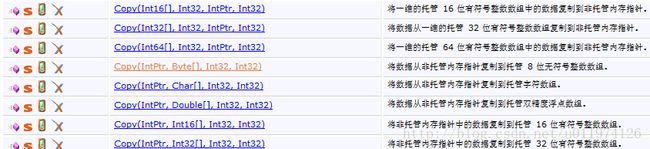
我值列出上图中橙色部分在MSDN中的声明:
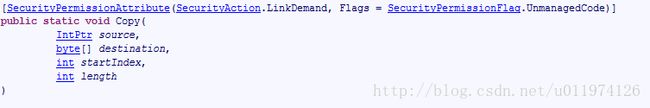
其中,source 为内存指针,从中进行复制,destination为要复制到的数组,startIndex为数组中COPY开始位置的从零开始的索引,length为要复制的数组中的元素的数目。
然后再来看一下Bitmap类中的LockBits方法,该方法用于将Bitmap锁定到系统内存中,MSDN的声明如下:


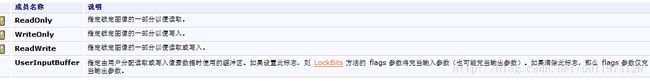
其中,rect指定要锁定的Bitmap区域,flags指定Bitmap的访问级别,format指定Bitmap的数据格式。flags的取值如下:
由于LockBits的返回值类型为System.Drawing.Imaging.BitmapData,下面对BitmapData做一下介绍:

要用到的即是Scan0和Stride方法,下面列出用Marshal类对Bitmap数据的操作的代码:
try { int iWidth = Source.Width; int iHeight = Source.Height; Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(0, 0, iWidth, iHeight); System.Drawing.Imaging.BitmapData bmpData = Source.LockBits(rect, System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageLockMode.ReadWrite, Source.PixelFormat); IntPtr iPtr = bmpData.Scan0; int iBytes = iWidth * iHeight * 3; byte[] PixelValues = new byte[iBytes]; System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.Copy(iPtr, PixelValues, 0, iBytes); Source.UnlockBits(bmpData); // 注意这个地方图像的两维方向与数组两维的方向是转置的关系 R = new int[iHeight, iWidth]; G = new int[iHeight, iWidth]; B = new int[iHeight, iWidth]; int iPoint = 0; for (int i = 0; i < iHeight; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < iWidth; j++) { // 注意,Windows 中三基色的排列顺序是 BGR 而不是 RGB! B[i, j] = Convert.ToInt32(PixelValues[iPoint++]); G[i, j] = Convert.ToInt32(PixelValues[iPoint++]); R[i, j] = Convert.ToInt32(PixelValues[iPoint++]); } } return true; } catch (Exception) { R = null; G = null; B = null; return false; } }这段代码仅仅适合于像素是24位RGB的图像(8位R、8位B和8位G,不包含Alpha通道,Format24bppRgb),如果要其它像素格式的(可以参见System.Drawing.Imaging.PixelFormat的成员),回写则与之相反,把需要写入的像素信息先写到byte数组中,再调用Marshal.Copy的第一个重载方法即可。代码如下:////// 由灰度矩阵创建位图 /// /// 灰度矩阵(取值0~255) ///矩阵对应的位图 public static Bitmap FromGray(int[,] Gray) { int iWidth = Gray.GetLength(1); int iHeight = Gray.GetLength(0); Bitmap Result=new Bitmap(iWidth,iHeight,System.Drawing.Imaging.PixelFormat.Format24bppRgb); Rectangle rect=new Rectangle(0,0,iWidth,iHeight); System.Drawing.Imaging.BitmapData bmpData = Result.LockBits(rect, System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageLockMode.ReadWrite, System.Drawing.Imaging.PixelFormat.Format24bppRgb); IntPtr iPtr = bmpData.Scan0; int iStride = bmpData.Stride; int iBytes = iWidth * iHeight * 3; byte[] PixelValues = new byte[iBytes]; int iPoint=0; for (int i=0;i参考资料:MSDN、http://ustc.blog.hexun.com/9374788_d.html。