Spring Security登录流程分析
本文内容来自王松老师的《深入浅出Spring Security》,自己在学习的时候为了加深理解顺手抄录的,有时候还会写一些自己的想法
登录流程分析
要搞请求Spring Security认证流程,我们先得认识与之相关的三个基本组件:AuthenticationManager、ProviderManager、AuthenticationProvider,同时还要去了解接入认证器的过滤器AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter,这四个类搞清楚了,基本上认证流程也清楚了。
AuthenticationManager
从名称上看AuthenticationManager是一个认证管理器,它定义了Spring Security过滤器要如何执行认证操作。AuthenticationManager在认证成功后会返回一个Authentication对象,这个Authenticaiton会被设置到SecurityContextHolder中。
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;
}从AuthenticationManager的源码中可以看到AuthenticationManager接受一个Authentication对象进行身份认证,此时传入的Authentication对象只包含简单的用户名和密码等简单的属性,如果认证成功之后返回的Authentication的属性会得到填充,包含用户具备的角色信息。
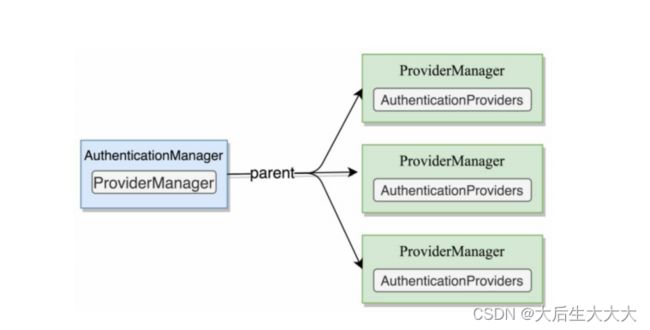
AuthenticationManager是一个接口,它有诸多的实现类,开发者可以自定义AuthenticationManager的实现类。不过在实际开发中,我们使用的最多的是providerManager。在Spring Security框架中默认也是使用ProviderManager。
AuthenticationProvider
Spring Security支持多种不同的认证方式,不同的认证方式对应不同的身份类型,AuthenticationProvider是针对不同的身份类型执行具体的身份认证。例如常见的DaoAuthenticationProvider用来支持用户名/密码登录认证。其源码如下:
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class authentication);
}-
authenticate方法用来执行具体的认证方式
-
supports方法用来判断当前的AuthenticationProvider是否支持对应的身份认证
ProviderManager
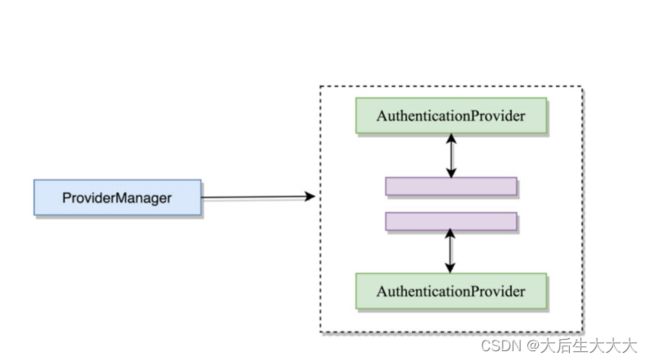
ProviderManager是AuthenticationManager的一个重要实现类,在前面学习的章节中有提到。下面这幅图可以清楚的反应ProviderManager和AuthenticationProvider的关系:
在Spring Security中,由于系统中可能会同时支持多种不同的认证方式,例如:用户名/密码、验证码、手机号码动态验证。而不同的认证方式对应了不同的AuthenticaitonProvider,所以一个完整的认证流程可能由多个AuthenticationProvider来提供。
多个AuthenticationProvider将组成一个列表,这个列表将由ProviderManager来代理。换句话说,在ProviderManager中遍历列表中的每一个AuthenticationProvider去身份认证,最终得到一个认证结果。
我们重点看一下ProviderManager的authenticate方法:
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
Class toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
AuthenticationException parentException = null;
Authentication result = null;
Authentication parentResult = null;
int currentPosition = 0;
int size = this.providers.size();
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Authenticating request with %s (%d/%d)",
provider.getClass().getSimpleName(), ++currentPosition, size));
}
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException | InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
prepareException(ex, authentication);
// SEC-546: Avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to
// invalid account status
throw ex;
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
lastException = ex;
}
}
if (result == null && this.parent != null) {
// Allow the parent to try.
try {
parentResult = this.parent.authenticate(authentication);
result = parentResult;
}
catch (ProviderNotFoundException ex) {
// ignore as we will throw below if no other exception occurred prior to
// calling parent and the parent
// may throw ProviderNotFound even though a provider in the child already
// handled the request
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
parentException = ex;
lastException = ex;
}
}
if (result != null) {
if (this.eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication && (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
// Authentication is complete. Remove credentials and other secret data
// from authentication
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
}
// If the parent AuthenticationManager was attempted and successful then it
// will publish an AuthenticationSuccessEvent
// This check prevents a duplicate AuthenticationSuccessEvent if the parent
// AuthenticationManager already published it
if (parentResult == null) {
this.eventPublisher.publishAuthenticationSuccess(result);
}
return result;
}
// Parent was null, or didn't authenticate (or throw an exception).
if (lastException == null) {
lastException = new ProviderNotFoundException(this.messages.getMessage("ProviderManager.providerNotFound",
new Object[] { toTest.getName() }, "No AuthenticationProvider found for {0}"));
}
// If the parent AuthenticationManager was attempted and failed then it will
// publish an AbstractAuthenticationFailureEvent
// This check prevents a duplicate AbstractAuthenticationFailureEvent if the
// parent AuthenticationManager already published it
if (parentException == null) {
prepareException(lastException, authentication);
}
throw lastException;
}这段源码也比较简单,逻辑也比较清晰:
- 首先获取Authentication对象的类型
- getProviders方法获取当前ProviderManager代理的所有的AuthenticationProvider的对象,挨个的调用AuthenticationProvider的supports方法判断是否支持当前的Authentication对象,要是不支持就调用下一个AuthenticationProvider,如果支持的话就调用当前的AuthenticationProvider的authenticate方法进行认证
- 调用AuthenticationProvider对象的authenticate如果认证成功,则返回Authentication对象,同时调用copyDetails方法给Authentication对象的details属性赋值
- 接下来就是异常处理相关的事情
小伙伴现在大致已经熟悉Authentication、AuthenticationManager、ProviderManager以及AuthenticationProvider的工作原理了。接下我们学习下这些组件是如何跟登录联系起来的。这里就要设计我们下面学习的一个重要的过滤器 ------> AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter。
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
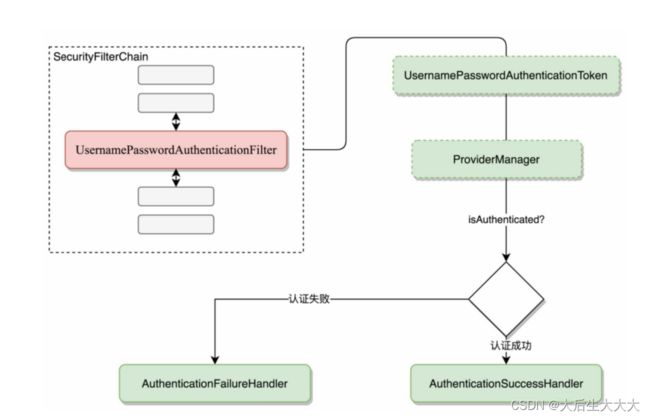
作为Spring Security过滤器中的一环AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter可以用来处理任何交给它的身份认证。下图描述了AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter的工作原理:
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter作为一个抽象类,如果使用用户名/密码登录,那么它对应的实现类是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter,构造出来Authenticaiton的对象则是UsernamePasswordAuthenticaitonToken。至于AuthenticationManager前面学习过,一般情况下她的实现类是ProviderManager,这里在ProviderManager中认证。认证成功会进入成功的回调,否则进入失败的回调。因此对于上面的流程可以再详细一点:
所以认证的基本流程是这样:
- 当用户提交登录请求时,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter会从当前请求的HttpServletRequest中提取出用户名、密码,然后创建一个UsernamePasswrodToken对象
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken对象作为一个Authenticaiton对象传入ProvoderManager中进行具体的认证
- 如果认证失败,则会进行登录信息存储、Session处理、登录成功事件发布以及登录成功方法回调等操作
- 如果登录失败,则SecurityContextHolder中相关信息将被清除,登录失败回调也会被调用