Ubuntu18.04 配置TensorRT加速YOLOv3-tiny实现实时高帧率检测
Ubuntu18.04 配置TensorRT加速
1.基本环境
CUDA=10.0
CUDNN=7.6
一. TensorRT的安装(tar安装)
1 .下载tar安装包
TensorRT=6.0.1.5
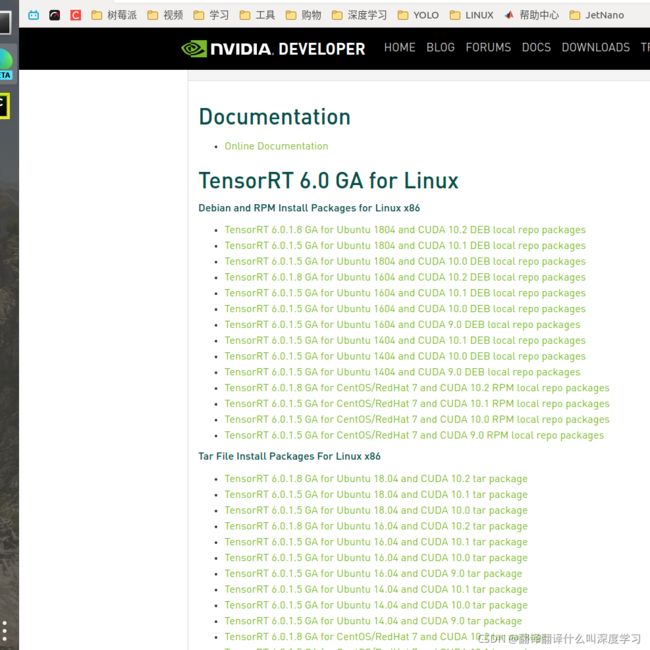
官方地址:https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt
由于NVIDIA下载文件需要登录,所以先登录下NVIDIA账号,然后点击:
GET STARTED->Download Now->TensorRT 6->勾选同意:
选择下边的Tar File 一栏,找到适用于Ubuntu18.04,CUDA10.0版本的安装包,点击链接即可下载。
https://developer.nvidia.com/compute/machine-learning/tensorrt/secure/6.0/GA_6.0.1.5/tars/TensorRT-6.0.1.5.Ubuntu-18.04.x86_64-gnu.cuda-10.0.cudnn7.6.tar.gz
2. 解压安装
2.1 添加环境变量
#解压安装包
tar xzvf 安装包
#添加环境变量
sudo gedit ~/.bashrc
#在最下边添加
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:解压路径/bin
2.2 安装TensorRT的python接口
cd TensorRT-6.x.x.x/python
sudo pip3 install tensorrt-6.x.x.x-cp3x-none-linux_x86_64.whl
2.3 安装UFF(TensorFlow所使用)
cd TensorRT-6.x.x.x/uff
sudo pip3 install uff-0.6.5-py2.py3-none-any.whl
2.4安装graphsurgeon
cd TensorRT-6.x.x.x/graphsurgeon
sudo pip3 install graphsurgeon-0.4.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl
3.安装TesorRT所需环境
3.1安装numpy、onnx、pycuda、Pillow、wget
sudo pip3 install numpy
#安装onnx所需依赖
sudo apt-get install protobuf-compiler libprotoc-dev cmake
#onnx
sudo pip3 install onnx==1.4.1
#安装pycuda可能会出现错误,
sudo pip3 install pycuda==2019.1.1
安装pycuda可能会出现cuda.h未找到错误,解决:
cuda.h这个文件的确找不到,只要添加cuda.h的搜索路径即可,
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/u011337602/article/details/81238164
1.未添加CUDA_INC_DIR到/etc/profile 在/etc/profile最后两行添加
export CUDA_INC_DIR=$CUDA_INC_DIR:/usr/local/cuda-x.x/include
保存并执行source /etc/profile
2.安装pycuda使用的是sudo pip3 install pycuda 这种情况下,执行的root权限,但由于pycuda安装时会使用nvcc,而nvcc是不具有root权限的,所以会导致安装失败。 因此需要去掉sudo,只在用户权限下执行pip3 install pycuda,即可安装成功。
sudo pip3 install Pillow==6.1.0
sudo pip3 install wget==3.2
至此依赖环境安装完成。
4. 下载项目
首先将trt-yolov3的github项目下载下来,地址:https://github.com/yqlbu/TRT-yolov3
- 点击进入该文件夹,进入yolov3_onnx文件夹,把下载好的yolov3-tiny.weights以及yolov3-tiny.cfg文件放入该文件夹。
- 修改download.sh文件,该文件原本包含下载yolov3-tiny.weights以及yolov3-tiny.cfg文件,但是太慢了,于是手动导入yolov3-tiny.weights文件之后对其进行修改,替换为:
#!/bin/bash
set -e
echo
echo "Creating YOLOv3-Tiny-288 and YOLOv3-Tiny-416 configs..."
cat yolov3-tiny.cfg | sed -e '8s/width=416/width=288/' | sed -e '9s/height=416/height=288/' > yolov3-tiny-288.cfg
echo >> yolov3-tiny-288.cfg
ln -sf yolov3-tiny.weights yolov3-tiny-288.weights
cp yolov3-tiny.cfg yolov3-tiny-416.cfg
echo >> yolov3-tiny-416.cfg
ln -sf yolov3-tiny.weights yolov3-tiny-416.weights
echo
echo "Done."
并执行: sudo ./download.sh
3. 修改yolo_to_onnx.py文件否则可能报错,为下:
from __future__ import print_function
import sys
import hashlib
import argparse
from collections import OrderedDict
import onnx
from onnx import helper
from onnx import TensorProto
import numpy as np
class DarkNetParser(object):
"""Definition of a parser for DarkNet-based YOLOv3."""
def __init__(self, supported_layers):
"""Initializes a DarkNetParser object.
Keyword argument:
supported_layers -- a string list of supported layers in DarkNet naming convention,
parameters are only added to the class dictionary if a parsed layer is included.
"""
# A list of YOLOv3 layers containing dictionaries with all layer
# parameters:
self.layer_configs = OrderedDict()
self.supported_layers = supported_layers
self.layer_counter = 0
def parse_cfg_file(self, cfg_file_path):
"""Takes the yolov3.cfg file and parses it layer by layer,
appending each layer's parameters as a dictionary to layer_configs.
Keyword argument:
cfg_file_path -- path to the yolov3.cfg file as string
"""
with open(cfg_file_path, 'r') as cfg_file:
remainder = cfg_file.read()
while remainder is not None:
layer_dict, layer_name, remainder = self._next_layer(remainder)
if layer_dict is not None:
self.layer_configs[layer_name] = layer_dict
return self.layer_configs
def _next_layer(self, remainder):
"""Takes in a string and segments it by looking for DarkNet delimiters.
Returns the layer parameters and the remaining string after the last delimiter.
Example for the first Conv layer in yolo.cfg ...
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=32
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
... becomes the following layer_dict return value:
{'activation': 'leaky', 'stride': 1, 'pad': 1, 'filters': 32,
'batch_normalize': 1, 'type': 'convolutional', 'size': 3}.
'001_convolutional' is returned as layer_name, and all lines that follow in yolo.cfg
are returned as the next remainder.
Keyword argument:
remainder -- a string with all raw text after the previously parsed layer
"""
remainder = remainder.split('[', 1)
if len(remainder) == 2:
remainder = remainder[1]
else:
return None, None, None
remainder = remainder.split(']', 1)
if len(remainder) == 2:
layer_type, remainder = remainder
else:
return None, None, None
if remainder.replace(' ', '')[0] == '#':
remainder = remainder.split('\n', 1)[1]
layer_param_block, remainder = remainder.split('\n\n', 1)
layer_param_lines = layer_param_block.split('\n')[1:]
layer_name = str(self.layer_counter).zfill(3) + '_' + layer_type
layer_dict = dict(type=layer_type)
if layer_type in self.supported_layers:
for param_line in layer_param_lines:
if param_line[0] == '#':
continue
param_type, param_value = self._parse_params(param_line)
layer_dict[param_type] = param_value
self.layer_counter += 1
return layer_dict, layer_name, remainder
def _parse_params(self, param_line):
"""Identifies the parameters contained in one of the cfg file and returns
them in the required format for each parameter type, e.g. as a list, an int or a float.
Keyword argument:
param_line -- one parsed line within a layer block
"""
param_line = param_line.replace(' ', '')
param_type, param_value_raw = param_line.split('=')
param_value = None
if param_type == 'layers':
layer_indexes = list()
for index in param_value_raw.split(','):
layer_indexes.append(int(index))
param_value = layer_indexes
elif isinstance(param_value_raw, str) and not param_value_raw.isalpha():
condition_param_value_positive = param_value_raw.isdigit()
condition_param_value_negative = param_value_raw[0] == '-' and \
param_value_raw[1:].isdigit()
if condition_param_value_positive or condition_param_value_negative:
param_value = int(param_value_raw)
else:
param_value = float(param_value_raw)
else:
param_value = str(param_value_raw)
return param_type, param_value
class MajorNodeSpecs(object):
"""Helper class used to store the names of ONNX output names,
corresponding to the output of a DarkNet layer and its output channels.
Some DarkNet layers are not created and there is no corresponding ONNX node,
but we still need to track them in order to set up skip connections.
"""
def __init__(self, name, channels):
""" Initialize a MajorNodeSpecs object.
Keyword arguments:
name -- name of the ONNX node
channels -- number of output channels of this node
"""
self.name = name
self.channels = channels
self.created_onnx_node = False
if name is not None and isinstance(channels, int) and channels > 0:
self.created_onnx_node = True
class ConvParams(object):
"""Helper class to store the hyper parameters of a Conv layer,
including its prefix name in the ONNX graph and the expected dimensions
of weights for convolution, bias, and batch normalization.
Additionally acts as a wrapper for generating safe names for all
weights, checking on feasible combinations.
"""
def __init__(self, node_name, batch_normalize, conv_weight_dims):
"""Constructor based on the base node name (e.g. 101_convolutional), the batch
normalization setting, and the convolutional weights shape.
Keyword arguments:
node_name -- base name of this YOLO convolutional layer
batch_normalize -- bool value if batch normalization is used
conv_weight_dims -- the dimensions of this layer's convolutional weights
"""
self.node_name = node_name
self.batch_normalize = batch_normalize
assert len(conv_weight_dims) == 4
self.conv_weight_dims = conv_weight_dims
def generate_param_name(self, param_category, suffix):
"""Generates a name based on two string inputs,
and checks if the combination is valid."""
assert suffix
assert param_category in ['bn', 'conv']
assert(suffix in ['scale', 'mean', 'var', 'weights', 'bias'])
if param_category == 'bn':
assert self.batch_normalize
assert suffix in ['scale', 'bias', 'mean', 'var']
elif param_category == 'conv':
assert suffix in ['weights', 'bias']
if suffix == 'bias':
assert not self.batch_normalize
param_name = self.node_name + '_' + param_category + '_' + suffix
return param_name
class UpsampleParams(object):
#Helper class to store the scale parameter for an Upsample node.
def __init__(self, node_name, value):
"""Constructor based on the base node name (e.g. 86_Upsample),
and the value of the scale input tensor.
Keyword arguments:
node_name -- base name of this YOLO Upsample layer
value -- the value of the scale input to the Upsample layer as a numpy array
"""
self.node_name = node_name
self.value = value
def generate_param_name(self):
"""Generates the scale parameter name for the Upsample node."""
param_name = self.node_name + '_' + 'scale'
return param_name
class WeightLoader(object):
"""Helper class used for loading the serialized weights of a binary file stream
and returning the initializers and the input tensors required for populating
the ONNX graph with weights.
"""
def __init__(self, weights_file_path):
"""Initialized with a path to the YOLOv3 .weights file.
Keyword argument:
weights_file_path -- path to the weights file.
"""
self.weights_file = self._open_weights_file(weights_file_path)
def load_upsample_scales(self, upsample_params):
"""Returns the initializers with the value of the scale input
tensor given by upsample_params.
Keyword argument:
upsample_params -- a UpsampleParams object
"""
initializer = list()
inputs = list()
name = upsample_params.generate_param_name()
shape = upsample_params.value.shape
data = upsample_params.value
scale_init = helper.make_tensor(
name, TensorProto.FLOAT, shape, data)
scale_input = helper.make_tensor_value_info(
name, TensorProto.FLOAT, shape)
initializer.append(scale_init)
inputs.append(scale_input)
return initializer, inputs
def load_conv_weights(self, conv_params):
"""Returns the initializers with weights from the weights file and
the input tensors of a convolutional layer for all corresponding ONNX nodes.
Keyword argument:
conv_params -- a ConvParams object
"""
initializer = list()
inputs = list()
if conv_params.batch_normalize:
bias_init, bias_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'bn', 'bias')
bn_scale_init, bn_scale_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'bn', 'scale')
bn_mean_init, bn_mean_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'bn', 'mean')
bn_var_init, bn_var_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'bn', 'var')
initializer.extend(
[bn_scale_init, bias_init, bn_mean_init, bn_var_init])
inputs.extend([bn_scale_input, bias_input,
bn_mean_input, bn_var_input])
else:
bias_init, bias_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'conv', 'bias')
initializer.append(bias_init)
inputs.append(bias_input)
conv_init, conv_input = self._create_param_tensors(
conv_params, 'conv', 'weights')
initializer.append(conv_init)
inputs.append(conv_input)
return initializer, inputs
def _open_weights_file(self, weights_file_path):
"""Opens a YOLOv3 DarkNet file stream and skips the header.
Keyword argument:
weights_file_path -- path to the weights file.
"""
weights_file = open(weights_file_path, 'rb')
length_header = 5
np.ndarray(
shape=(length_header, ), dtype='int32', buffer=weights_file.read(
length_header * 4))
return weights_file
def _create_param_tensors(self, conv_params, param_category, suffix):
"""Creates the initializers with weights from the weights file together with
the input tensors.
Keyword arguments:
conv_params -- a ConvParams object
param_category -- the category of parameters to be created ('bn' or 'conv')
suffix -- a string determining the sub-type of above param_category (e.g.,
'weights' or 'bias')
"""
param_name, param_data, param_data_shape = self._load_one_param_type(
conv_params, param_category, suffix)
initializer_tensor = helper.make_tensor(
param_name, TensorProto.FLOAT, param_data_shape, param_data)
input_tensor = helper.make_tensor_value_info(
param_name, TensorProto.FLOAT, param_data_shape)
return initializer_tensor, input_tensor
def _load_one_param_type(self, conv_params, param_category, suffix):
"""Deserializes the weights from a file stream in the DarkNet order.
Keyword arguments:
conv_params -- a ConvParams object
param_category -- the category of parameters to be created ('bn' or 'conv')
suffix -- a string determining the sub-type of above param_category (e.g.,
'weights' or 'bias')
"""
param_name = conv_params.generate_param_name(param_category, suffix)
channels_out, channels_in, filter_h, filter_w = conv_params.conv_weight_dims
if param_category == 'bn':
param_shape = [channels_out]
elif param_category == 'conv':
if suffix == 'weights':
param_shape = [channels_out, channels_in, filter_h, filter_w]
elif suffix == 'bias':
param_shape = [channels_out]
param_size = np.product(np.array(param_shape))
param_data = np.ndarray(
shape=param_shape,
dtype='float32',
buffer=self.weights_file.read(param_size * 4))
param_data = param_data.flatten().astype(float)
return param_name, param_data, param_shape
class GraphBuilderONNX(object):
"""Class for creating an ONNX graph from a previously generated list of layer dictionaries."""
def __init__(self, model_name, output_tensors):
"""Initialize with all DarkNet default parameters used creating YOLOv3,
and specify the output tensors as an OrderedDict for their output dimensions
with their names as keys.
Keyword argument:
output_tensors -- the output tensors as an OrderedDict containing the keys'
output dimensions
"""
self.model_name = model_name
self.output_tensors = output_tensors
self._nodes = list()
self.graph_def = None
self.input_tensor = None
self.epsilon_bn = 1e-5
self.momentum_bn = 0.99
self.alpha_lrelu = 0.1
self.param_dict = OrderedDict()
self.major_node_specs = list()
self.batch_size = 1
def build_onnx_graph(
self,
layer_configs,
weights_file_path,
verbose=True):
"""Iterate over all layer configs (parsed from the DarkNet representation
of YOLOv3-608), create an ONNX graph, populate it with weights from the weights
file and return the graph definition.
Keyword arguments:
layer_configs -- an OrderedDict object with all parsed layers' configurations
weights_file_path -- location of the weights file
verbose -- toggles if the graph is printed after creation (default: True)
"""
for layer_name in layer_configs.keys():
layer_dict = layer_configs[layer_name]
major_node_specs = self._make_onnx_node(layer_name, layer_dict)
if major_node_specs.name is not None:
self.major_node_specs.append(major_node_specs)
outputs = list()
for tensor_name in self.output_tensors.keys():
output_dims = [self.batch_size, ] + \
self.output_tensors[tensor_name]
output_tensor = helper.make_tensor_value_info(
tensor_name, TensorProto.FLOAT, output_dims)
outputs.append(output_tensor)
inputs = [self.input_tensor]
weight_loader = WeightLoader(weights_file_path)
initializer = list()
# If a layer has parameters, add them to the initializer and input lists.
for layer_name in self.param_dict.keys():
_, layer_type = layer_name.split('_', 1)
params = self.param_dict[layer_name]
if layer_type == 'convolutional':
initializer_layer, inputs_layer = weight_loader.load_conv_weights(
params)
initializer.extend(initializer_layer)
inputs.extend(inputs_layer)
elif layer_type == 'upsample':
initializer_layer, inputs_layer = weight_loader.load_upsample_scales(
params)
initializer.extend(initializer_layer)
inputs.extend(inputs_layer)
del weight_loader
self.graph_def = helper.make_graph(
nodes=self._nodes,
name=self.model_name,
inputs=inputs,
outputs=outputs,
initializer=initializer
)
if verbose:
print(helper.printable_graph(self.graph_def))
model_def = helper.make_model(self.graph_def,
producer_name='NVIDIA TensorRT sample')
return model_def
def _make_onnx_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""Take in a layer parameter dictionary, choose the correct function for
creating an ONNX node and store the information important to graph creation
as a MajorNodeSpec object.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- the layer's name (also the corresponding key in layer_configs)
layer_dict -- a layer parameter dictionary (one element of layer_configs)
"""
layer_type = layer_dict['type']
if self.input_tensor is None:
if layer_type == 'net':
major_node_output_name, major_node_output_channels = self._make_input_tensor(
layer_name, layer_dict)
major_node_specs = MajorNodeSpecs(major_node_output_name,
major_node_output_channels)
else:
raise ValueError('The first node has to be of type "net".')
else:
node_creators = dict()
node_creators['convolutional'] = self._make_conv_node
node_creators['maxpool'] = self._make_maxpool_node
node_creators['shortcut'] = self._make_shortcut_node
node_creators['route'] = self._make_route_node
node_creators['upsample'] = self._make_upsample_node
if layer_type in node_creators.keys():
major_node_output_name, major_node_output_channels = \
node_creators[layer_type](layer_name, layer_dict)
major_node_specs = MajorNodeSpecs(major_node_output_name,
major_node_output_channels)
else:
print(
'Layer of type %s not supported, skipping ONNX node generation.' %
layer_type)
major_node_specs = MajorNodeSpecs(layer_name,
None)
return major_node_specs
def _make_input_tensor(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""Create an ONNX input tensor from a 'net' layer and store the batch size.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- the layer's name (also the corresponding key in layer_configs)
layer_dict -- a layer parameter dictionary (one element of layer_configs)
"""
batch_size = layer_dict['batch']
channels = layer_dict['channels']
height = layer_dict['height']
width = layer_dict['width']
self.batch_size = batch_size
input_tensor = helper.make_tensor_value_info(
str(layer_name), TensorProto.FLOAT, [
batch_size, channels, height, width])
self.input_tensor = input_tensor
return layer_name, channels
def _get_previous_node_specs(self, target_index=-1):
"""Get a previously generated ONNX node (skip those that were not generated).
Target index can be passed for jumping to a specific index.
Keyword arguments:
target_index -- optional for jumping to a specific index (default: -1 for jumping
to previous element)
"""
previous_node = None
for node in self.major_node_specs[target_index::-1]:
if node.created_onnx_node:
previous_node = node
break
assert previous_node is not None
return previous_node
def _make_conv_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""Create an ONNX Conv node with optional batch normalization and
activation nodes.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- the layer's name (also the corresponding key in layer_configs)
layer_dict -- a layer parameter dictionary (one element of layer_configs)
"""
previous_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs()
inputs = [previous_node_specs.name]
previous_channels = previous_node_specs.channels
kernel_size = layer_dict['size']
stride = layer_dict['stride']
filters = layer_dict['filters']
batch_normalize = False
if 'batch_normalize' in layer_dict.keys(
) and layer_dict['batch_normalize'] == 1:
batch_normalize = True
kernel_shape = [kernel_size, kernel_size]
weights_shape = [filters, previous_channels] + kernel_shape
conv_params = ConvParams(layer_name, batch_normalize, weights_shape)
strides = [stride, stride]
dilations = [1, 1]
weights_name = conv_params.generate_param_name('conv', 'weights')
inputs.append(weights_name)
if not batch_normalize:
bias_name = conv_params.generate_param_name('conv', 'bias')
inputs.append(bias_name)
conv_node = helper.make_node(
'Conv',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name],
kernel_shape=kernel_shape,
strides=strides,
auto_pad='SAME_LOWER',
dilations=dilations,
name=layer_name
)
self._nodes.append(conv_node)
inputs = [layer_name]
layer_name_output = layer_name
if batch_normalize:
layer_name_bn = layer_name + '_bn'
bn_param_suffixes = ['scale', 'bias', 'mean', 'var']
for suffix in bn_param_suffixes:
bn_param_name = conv_params.generate_param_name('bn', suffix)
inputs.append(bn_param_name)
batchnorm_node = helper.make_node(
'BatchNormalization',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name_bn],
epsilon=self.epsilon_bn,
momentum=self.momentum_bn,
name=layer_name_bn
)
self._nodes.append(batchnorm_node)
inputs = [layer_name_bn]
layer_name_output = layer_name_bn
if layer_dict['activation'] == 'leaky':
layer_name_lrelu = layer_name + '_lrelu'
lrelu_node = helper.make_node(
'LeakyRelu',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name_lrelu],
name=layer_name_lrelu,
alpha=self.alpha_lrelu
)
self._nodes.append(lrelu_node)
inputs = [layer_name_lrelu]
layer_name_output = layer_name_lrelu
elif layer_dict['activation'] == 'linear':
pass
else:
print('Activation not supported.')
self.param_dict[layer_name] = conv_params
return layer_name_output, filters
def _make_shortcut_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""Create an ONNX Add node with the shortcut properties from
the DarkNet-based graph.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- the layer's name (also the corresponding key in layer_configs)
layer_dict -- a layer parameter dictionary (one element of layer_configs)
"""
shortcut_index = layer_dict['from']
activation = layer_dict['activation']
assert activation == 'linear'
first_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs()
second_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs(
target_index=shortcut_index)
assert first_node_specs.channels == second_node_specs.channels
channels = first_node_specs.channels
inputs = [first_node_specs.name, second_node_specs.name]
shortcut_node = helper.make_node(
'Add',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name],
name=layer_name,
)
self._nodes.append(shortcut_node)
return layer_name, channels
def _make_route_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""If the 'layers' parameter from the DarkNet configuration is only one index, continue
node creation at the indicated (negative) index. Otherwise, create an ONNX Concat node
with the route properties from the DarkNet-based graph.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- the layer's name (also the corresponding key in layer_configs)
layer_dict -- a layer parameter dictionary (one element of layer_configs)
"""
route_node_indexes = layer_dict['layers']
if len(route_node_indexes) == 1:
split_index = route_node_indexes[0]
assert split_index < 0
# Increment by one because we skipped the YOLO layer:
split_index += 1
self.major_node_specs = self.major_node_specs[:split_index]
layer_name = None
channels = None
else:
inputs = list()
channels = 0
for index in route_node_indexes:
if index > 0:
# Increment by one because we count the input as a node (DarkNet
# does not)
index += 1
route_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs(
target_index=index)
inputs.append(route_node_specs.name)
channels += route_node_specs.channels
assert inputs
assert channels > 0
route_node = helper.make_node(
'Concat',
axis=1,
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name],
name=layer_name,
)
self._nodes.append(route_node)
return layer_name, channels
def _make_upsample_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""Create an ONNX Upsample node with the properties from
the DarkNet-based graph.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- the layer's name (also the corresponding key in layer_configs)
layer_dict -- a layer parameter dictionary (one element of layer_configs)
"""
upsample_factor = float(layer_dict['stride'])
# Create the scales array with node parameters
scales=np.array([1.0, 1.0, upsample_factor, upsample_factor]).astype(np.float)
previous_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs()
inputs = [previous_node_specs.name]
channels = previous_node_specs.channels
assert channels > 0
upsample_params = UpsampleParams(layer_name, scales)
scales_name = upsample_params.generate_param_name()
# For ONNX opset >= 9, the Upsample node takes the scales array as an input.
inputs.append(scales_name)
upsample_node = helper.make_node(
'Upsample',
mode='nearest',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name],
name=layer_name,
)
self._nodes.append(upsample_node)
self.param_dict[layer_name] = upsample_params
return layer_name, channels
def _make_maxpool_node(self, layer_name, layer_dict):
"""Create an ONNX Maxpool node with the properties from
the DarkNet-based graph.
Keyword arguments:
layer_name -- the layer's name (also the corresponding key in layer_configs)
layer_dict -- a layer parameter dictionary (one element of layer_configs)
"""
stride = layer_dict['stride']
kernel_size = layer_dict['size']
previous_node_specs = self._get_previous_node_specs()
inputs = [previous_node_specs.name]
channels = previous_node_specs.channels
kernel_shape = [kernel_size, kernel_size]
strides = [stride, stride]
assert channels > 0
maxpool_node = helper.make_node(
'MaxPool',
inputs=inputs,
outputs=[layer_name],
kernel_shape=kernel_shape,
strides=strides,
auto_pad='SAME_UPPER',
name=layer_name,
)
self._nodes.append(maxpool_node)
return layer_name, channels
def generate_md5_checksum(local_path):
"""Returns the MD5 checksum of a local file.
Keyword argument:
local_path -- path of the file whose checksum shall be generated
"""
with open(local_path, 'rb') as local_file:
data = local_file.read()
return hashlib.md5(data).hexdigest()
def main():
"""Run the DarkNet-to-ONNX conversion for YOLOv3."""
if sys.version_info[0] < 3:
raise Exception('This modified version of yolov3_to_onnx.py script is only compatible with python3...')
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--model', type=str, default='yolov3-416',
choices=['yolov3-288', 'yolov3-416', 'yolov3-608',
'yolov3-tiny-288', 'yolov3-tiny-416'])
args = parser.parse_args()
cfg_file_path = '%s.cfg' % args.model
weights_file_path = '%s.weights' % args.model
output_file_path = '%s.onnx' % args.model
yolo_dim = int(args.model.split('-')[-1]) # 288, 416 or 608
# These are the only layers DarkNetParser will extract parameters from. The three layers of
# type 'yolo' are not parsed in detail because they are included in the post-processing later:
supported_layers = ['net', 'convolutional', 'maxpool',
'shortcut', 'route', 'upsample']
# Create a DarkNetParser object, and the use it to generate an OrderedDict with all
# layer's configs from the cfg file:
parser = DarkNetParser(supported_layers)
layer_configs = parser.parse_cfg_file(cfg_file_path)
# We do not need the parser anymore after we got layer_configs:
del parser
# In above layer_config, there are three outputs that we need to know the output
# shape of (in CHW format):
output_tensor_dims = OrderedDict()
d = yolo_dim
if 'tiny' in args.model:
output_tensor_dims['016_convolutional'] = [255, d // 32, d // 32]
output_tensor_dims['023_convolutional'] = [255, d // 16, d // 16]
else:
output_tensor_dims['082_convolutional'] = [255, d // 32, d // 32]
output_tensor_dims['094_convolutional'] = [255, d // 16, d // 16]
output_tensor_dims['106_convolutional'] = [255, d // 8, d // 8]
# Create a GraphBuilderONNX object with the known output tensor dimensions:
builder = GraphBuilderONNX(args.model, output_tensor_dims)
# Now generate an ONNX graph with weights from the previously parsed layer configurations
# and the weights file:
yolov3_model_def = builder.build_onnx_graph(
layer_configs=layer_configs,
weights_file_path=weights_file_path,
verbose=True)
# Once we have the model definition, we do not need the builder anymore:
del builder
# Perform a sanity check on the ONNX model definition:
onnx.checker.check_model(yolov3_model_def)
# Serialize the generated ONNX graph to this file:
onnx.save(yolov3_model_def, output_file_path)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
- 修改onnx_to_trt.py文件为下:
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import argparse
import tensorrt as trt
EXPLICIT_BATCH = []
if trt.__version__[0] >= '7':
EXPLICIT_BATCH.append(
1 << (int)(trt.NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag.EXPLICIT_BATCH))
def build_engine(onnx_file_path, engine_file_path, verbose=False):
"""Takes an ONNX file and creates a TensorRT engine."""
TRT_LOGGER = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.VERBOSE) if verbose else trt.Logger()
with trt.Builder(TRT_LOGGER) as builder, builder.create_network(*EXPLICIT_BATCH) as network, trt.OnnxParser(network, TRT_LOGGER) as parser:
builder.max_workspace_size = 1 << 28
builder.max_batch_size = 1
builder.fp16_mode = True
#builder.strict_type_constraints = True
# Parse model file
if not os.path.exists(onnx_file_path):
print('ONNX file {} not found, please run yolov3_to_onnx.py first to generate it.'.format(onnx_file_path))
exit(0)
print('Loading ONNX file from path {}...'.format(onnx_file_path))
with open(onnx_file_path, 'rb') as model:
print('Beginning ONNX file parsing')
if not parser.parse(model.read()):
print('ERROR: Failed to parse the ONNX file.')
for error in range(parser.num_errors):
print(parser.get_error(error))
return None
if trt.__version__[0] >= '7':
# The actual yolov3.onnx is generated with batch size 64.
# Reshape input to batch size 1
shape = list(network.get_input(0).shape)
shape[0] = 1
network.get_input(0).shape = shape
print('Completed parsing of ONNX file')
print('Building an engine; this may take a while...')
engine = builder.build_cuda_engine(network)
print('Completed creating engine')
with open(engine_file_path, 'wb') as f:
f.write(engine.serialize())
return engine
def main():
"""Create a TensorRT engine for ONNX-based YOLOv3."""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('-v', '--verbose', action='store_true',
help='enable verbose output (for debugging)')
parser.add_argument('--model', type=str, default='yolov3-416',
choices=['yolov3-288', 'yolov3-416', 'yolov3-608',
'yolov3-tiny-288', 'yolov3-tiny-416'])
args = parser.parse_args()
onnx_file_path = '%s.onnx' % args.model
engine_file_path = '%s.trt' % args.model
_ = build_engine(onnx_file_path, engine_file_path, args.verbose)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
- 将weights模型转化为onnx模型:
终端:
python3 yolov3_tiny_to_onnx.py --model yolov3-416
yolov3-416由原来download.sh文件生成,
6. 将onnx模型转化为trt模型:
python3 onnx_to_tensorrt.py --model yolov3-416
运行完5 6两步之后文件夹中便会有.onnx以及.trt两个文件。
创建trt-yolov3-detector-camera.py文件(链接中的相机未更改)放置于.trt文件目录相同的路径下:
"""detector.py
This script demonstrates how to do real-time object detection with
TensorRT optimized Single-Shot Multibox Detector (SSD) engine.
"""
import sys
import argparse
import cv2
import pycuda.autoinit # This is needed for initializing CUDA driver
sys.path.append('/home/nano/Developer/TRT-yolov3') #这里改一下
import numpy as np
from utils.yolo_classes import get_cls_dict
from utils.yolov3 import TrtYOLOv3
#from camera import add_camera_args, Camera
from utils.visualization import open_window, show_fps, record_time, show_runtime
from utils.engine import BBoxVisualization
WINDOW_NAME = 'TensorRT YOLOv3 Detector'
INPUT_HW = (300, 300)
SUPPORTED_MODELS = [
'ssd_mobilenet_v2_coco'
]
def parse_args():
"""Parse input arguments."""
desc = ('Capture and display live camera video, while doing '
'real-time object detection with TensorRT optimized '
'YOLOv3 model on Jetson Family')
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=desc)
parser = add_camera_args(parser)
parser.add_argument('--model', type=str, default='yolov3-416',
choices=['yolov3-288', 'yolov3-416', 'yolov3-608',
'yolov3-tiny-288', 'yolov3-tiny-416'])
parser.add_argument('--runtime', action='store_true',
help='display detailed runtime')
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
def loop_and_detect(img, runtime, trt_yolov3, conf_th, vis):
timer = cv2.getTickCount()
if img is not None:
if runtime:
boxes, confs, clss, _preprocess_time, _postprocess_time,_network_time = trt_yolov3.detect(img, conf_th)
img, _visualize_time = vis.draw_bboxes(img, boxes, confs, clss)
time_stamp = record_time(_preprocess_time, _postprocess_time, _network_time, _visualize_time)
#show_runtime(time_stamp)
else:
boxes, confs, clss, _, _, _ = trt_yolov3.detect(img, conf_th)
img, _ = vis.draw_bboxes(img, boxes, confs, clss)
fps = cv2.getTickFrequency() / (cv2.getTickCount() - timer)
img = show_fps(img, fps)
cv2.imshow(WINDOW_NAME, img)
def gstreamer_pipeline(
capture_width=1280,
capture_height=720,
display_width=1280,
display_height=720,
framerate=60,
flip_method=0,
):
return (
"nvarguscamerasrc ! "
"video/x-raw(memory:NVMM), "
"width=(int)%d, height=(int)%d, "
"format=(string)NV12, framerate=(fraction)%d/1 ! "
"nvvidconv flip-method=%d ! "
"video/x-raw, width=(int)%d, height=(int)%d, format=(string)BGRx ! "
"videoconvert ! "
"video/x-raw, format=(string)BGR ! appsink"
% (
capture_width,
capture_height,
framerate,
flip_method,
display_width,
display_height,
)
)
def main():
cls_dict = get_cls_dict('coco')
yolo_dim = 416 # 416 or 608
trt_yolov3 = TrtYOLOv3('yolov3-tiny-416', (yolo_dim, yolo_dim))
print('[INFO] Camera: starting')
#cap = cv2.VideoCapture(gstreamer_pipeline(flip_method=0), cv2.CAP_GSTREAMER)
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
open_window(WINDOW_NAME, 1280, 720,'TensorRT YOLOv3 Detector')
vis = BBoxVisualization(cls_dict)
if cap.isOpened():
#window_handle = cv2.namedWindow("CSI Camera", cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)
while True:
ret_val, img = cap.read()
img=cv2.flip(img,1)
loop_and_detect(img, 20, trt_yolov3, conf_th=0.3, vis=vis)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
运行该文件:
python3 trt-yolov3-detector-camera.py
即可利用摄像头进行视频的实时检测。
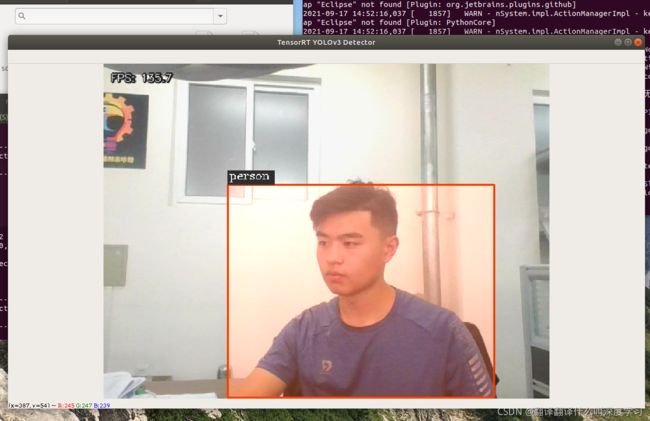
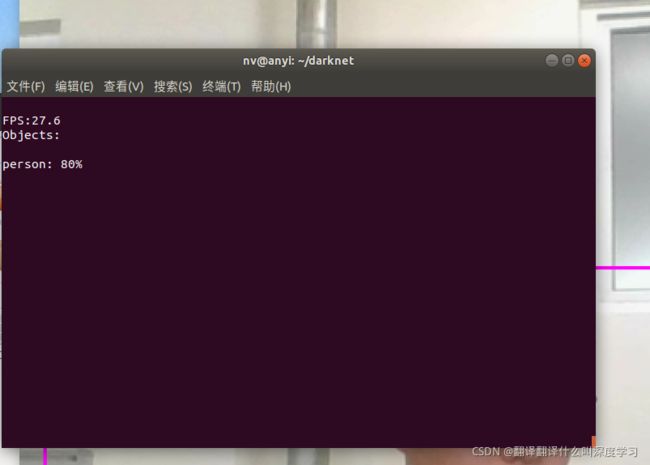
视频检测可以提升到120~140帧左右(GTX1650),相比较于只是使用darknet进行yolov3-tiny检测(30帧),提升了近4倍。
之前在jetson nano 4G上运行yolov3-tiny,darknet在5帧左右(不知道是不是配置出了问题),TensorRT加速之后能够达到15帧左右。在识别精度方面未进行实验验证,会下降多少。
BUG解决
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘cv2’ 问题,若是之前安装过opencvx.xx版本,可以尝试下运行:
python
import cv2
试试,若没有出现上述错误,再运行python3 import cv2,一般都是由于安装的opencv版本低导致的,将opencv版本提升一下(最好在4.1之前)就可解决.
Opecv官方文档:
https://docs.opencv.org/master/d7/d9f/tutorial_linux_install.html#tutorial_linux_install_quick_start
参考文献
1.Jetson Nano 使用yolov3-tiny及TensorRT加速,达到接近实时目标检测与识别_云逸的博客-CSDN博客
2.Jetson Nano使用TensorRT加速yolov3-tiny目标识别
3.Jetson Nano 使用yolov3-tiny及TensorRT加速,达到接近实时目标检测与识别
4.trt-yolov3:Jetson Nano上的yolov3-tiny识别(已完结)