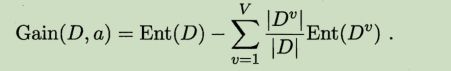机器学习实战(二)——python实现决策树
1.决策树介绍
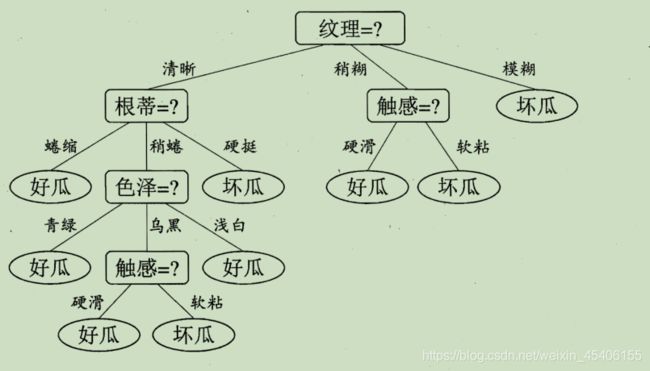
决策树是一种基本的分类和递归方法,决策树由节点和有向边组成
- 内部节点表示一个特征或者属性
- 叶子节点表示一种分类
- 有向边表示选择某种特征之后对数据集进行划分
2.决策树学习
决策树的生成包括三个步骤:特征选择、决策树生成、决策树剪枝
2.1 生成算法
- 将所有数据放在根节点
- 选择一个最优的特征,根据这个特征将训练数据分割成子集,使得各个子集在当前条件下有一个最好的分类
- 递归下去,直到所有数据子集都被基本正确分类、或者没有合适的特征为止
递归返回的三种情况:
-
当前节点包含的样本全部属于同一类别,无需进行划分
- 当前属性集为空,或者是所有样本在所有属性的取值均相同,无法划分。则将当前节点标记为叶节点,将类别设置为该叶节点所含有样本最多的类别
- 当前节点包含的样本为空,不能划分。则将当前节点标记为叶节点,类别设置为该节点父节点所含有样本最多的类别
2.2 特征选择
特征的选择依赖于信息增益或者信息增益比
2.2.1 信息增益
信息增益:选择某个特征对数据集划分,数据集纯度提升的多少为:g(D,A) = H(D) - H(D|A)
信息增益特点
- 信息增益大的特征具有更强的分类能力,如果某个特征的信息增益为0,则表示其没有什么分类能力
- 信息增益准则倾向于选择取值较多的特征问题,导致生成的决策树没有泛化能力 -> 使用信息增益比
2.2.2 信息增益率
2.3决策树剪枝
2.3.1 预剪枝
决策树在生成过程中,对每个节点在划分前进行估计,若当前节点的划分没有带来决策树泛化能力的提升,则停止划分,并将当前节点标记为叶节点。
特点
- 预剪枝降低了过拟合的风险,还显著减少了决策树的训练时间
- 有些划分虽然当前不能带来泛化能力的提升,但是在其基础上进行的后续划分,却有可能带来性能提高,因此,这种贪心的策略有欠拟合的风险
2.3.2 后剪枝
先生成一棵完整的决策树,然后自底向上对叶节点进行考察,若将该节点子树替换为叶节点能够带来泛化能力的提升,则将该节点退化为叶节点。
特点
- 后剪枝决策树通常比预剪枝决策树保留了更多的分支,且欠拟合的风险很小,泛化性能优于预剪枝决策树
- 训练时间开销相比预剪枝决策树大得多
3. python实现决策树
3.0 创建数据集
"""
函数说明:创建测试数据集
Parameters:
无
Returns:
dataSet - 数据集
labels - 特征标签
"""
def createDataSet():
dataSet = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'], #数据集
[0, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 'yes'],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 'no'],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 'no'],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'],
[2, 0, 1, 2, 'yes'],
[2, 0, 1, 1, 'yes'],
[2, 1, 0, 1, 'yes'],
[2, 1, 0, 2, 'yes'],
[2, 0, 0, 0, 'no']]
labels = ['年龄', '有工作', '有自己的房子', '信贷情况'] #特征标签
return dataSet, labels #返回数据集和分类属性3.1 特征选择
1. 计算香农熵 Ent(D)
"""
函数说明:计算给定数据集的经验熵(香农熵)
Parameters:
dataSet - 数据集
Returns:
shannonEnt - 经验熵(香农熵)
"""
def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
numEntires = len(dataSet) #返回数据集的行数
labelCounts = {} #保存每个标签(Label)出现次数的字典
for featVec in dataSet: #对每组特征向量进行统计
currentLabel = featVec[-1] #提取标签(Label)信息
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): #如果标签(Label)没有放入统计次数的字典,添加进去
labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1 #Label计数
shannonEnt = 0.0 #经验熵(香农熵)
for key in labelCounts: #计算香农熵
prob = float(labelCounts[key]) / numEntires #选择该标签(Label)的概率
shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob, 2) #利用公式计算
return shannonEnt #返回经验熵(香农熵)2. 选择最优特征
"""
函数说明:选择最优特征
Parameters:
dataSet - 数据集
Returns:
bestFeature - 信息增益最大的(最优)特征的索引值
"""
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 #特征数量
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) #计算数据集的香农熵
bestInfoGain = 0.0 #信息增益
bestFeature = -1 #最优特征的索引值
for i in range(numFeatures): #遍历所有特征
#获取dataSet的第i个所有特征
featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featList) #创建set集合{},元素不可重复
newEntropy = 0.0 #经验条件熵
for value in uniqueVals: #计算信息增益
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value) #subDataSet划分后的子集
prob = len(subDataSet) / float(len(dataSet)) #计算子集的概率
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet) #根据公式计算经验条件熵
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy #信息增益
# print("第%d个特征的增益为%.3f" % (i, infoGain)) #打印每个特征的信息增益
if (infoGain > bestInfoGain): #计算信息增益
bestInfoGain = infoGain #更新信息增益,找到最大的信息增益
bestFeature = i #记录信息增益最大的特征的索引值
return bestFeature #返回信息增益最大的特征的索引值3.2 . 根据特征划分数据集
"""
函数说明:按照给定特征划分数据集
Parameters:
dataSet - 待划分的数据集
axis - 划分数据集的特征
value - 需要返回的特征的值
Returns:
划分后的数据集
"""
def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value):
retDataSet = [] #创建返回的数据集列表
for featVec in dataSet: #遍历数据集
if featVec[axis] == value:
reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis] #去掉axis特征
reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:]) #将符合条件的添加到返回的数据集
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
return retDataSet #返回划分后的数据集3.3 递归生成决策树
递归返回的三种情况:
-
当前节点包含的样本全部属于同一类别,无需进行划分
- 当前属性集为空,或者是所有样本在所有属性的取值均相同,无法划分。则将当前节点标记为叶节点,将类别设置为该叶节点所含有样本最多的类别
- 当前节点包含的样本为空,不能划分。则将当前节点标记为叶节点,类别设置为该节点父节点所含有样本最多的类别
"""
函数说明:统计classList中出现此处最多的元素(类标签)
Parameters:
classList - 类标签列表
Returns:
sortedClassCount[0][0] - 出现此处最多的元素(类标签)
"""
def majorityCnt(classList):
classCount = {}
for vote in classList: #统计classList中每个元素出现的次数
if vote not in classCount.keys():classCount[vote] = 0
classCount[vote] += 1
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key = operator.itemgetter(1), reverse = True) #根据字典的值降序排序
return sortedClassCount[0][0] #返回classList中出现次数最多的元素
"""
函数说明:创建决策树
Parameters:
dataSet - 训练数据集
labels - 分类属性标签
featLabels - 存储选择的最优特征标签
Returns:
myTree - 决策树
"""
def createTree(dataSet, labels, featLabels):
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet] #取分类标签(是否放贷:yes or no)
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): #如果类别完全相同则停止继续划分
return classList[0]
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1 or len(labels) == 0: #遍历完所有特征时返回出现次数最多的类标签
return majorityCnt(classList)
bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet) #选择最优特征
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat] #最优特征的标签
featLabels.append(bestFeatLabel)
myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}} #根据最优特征的标签生成树
del(labels[bestFeat]) #删除已经使用特征标签
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet] #得到训练集中所有最优特征的属性值
uniqueVals = set(featValues) #去掉重复的属性值
for value in uniqueVals: #遍历特征,创建决策树。
myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value), labels, featLabels)
return myTree3.4 对给定的测试数据进行分类
"""
函数说明:使用决策树分类
Parameters:
inputTree - 已经生成的决策树
featLabels - 存储选择的最优特征标签
testVec - 测试数据列表,顺序对应最优特征标签
Returns:
classLabel - 分类结果
"""
def classify(inputTree, featLabels, testVec):
firstStr = next(iter(inputTree)) #获取决策树结点
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr] #下一个字典
featIndex = featLabels.index(firstStr)
for key in secondDict.keys():
if testVec[featIndex] == key:
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
classLabel = classify(secondDict[key], featLabels, testVec)
else: classLabel = secondDict[key]
return classLabel
3.5 测试
if __name__ == '__main__':
dataSet, labels = createDataSet()
featLabels = []
myTree = createTree(dataSet, labels, featLabels)
testVec = [0,1] #测试数据
result = classify(myTree, featLabels, testVec)
if result == 'yes':
print('放贷')
if result == 'no':
print('不放贷')4.参考文献
https://cuijiahua.com/blog/2017/11/ml_3_decision_tree_2.html