Java实现图书管理系统
作者:~小明学编程
文章专栏:JavaSE基础
格言:目之所及皆为回忆,心之所想皆为过往
今天给大家带来的是用Java实现的图书管理系统。
目录
需求
图书类
创建图书类
创建书架
Operation
IOperation接口
添加图书AddOperation
借阅图书BorrowOperation
删除图书DelOperation
打印图书DisplayOperation
退出系统ExitOperation
查询书籍FindOperation
归还书籍ReturnOperation
user
User
NormalUser
AdminUser
Main
演示
需求
图书类
首先我们创建一个book包,在包里面放一个Book类和一个BookList类。
然后创建一个operation里面放的是我们的各种操作方法。
接着是我们的user类,里面分别放我们的管理员的类和普通成员的类。
最后就是我们的Main类,我们的程序从这里开始执行。
创建图书类
首先我们需要创建一个图书类,该类里面是我们的图书属性例如书名,作者名,价格等等。
public class Book {
//书名
private String name;
//作者名
private String author;
//价格
private int price;
//书的类型
private String type;
//是否借出
private boolean isBorrowed;
public Book(String name, String author, int price, String type) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public boolean isBorrowed() {
return isBorrowed;
}
public void setBorrowed(boolean borrowed) {
isBorrowed = borrowed;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
((isBorrowed==true)?",已借出":",未借出") +
'}';
}
}定义好我们的基本变量之后,然后给出set和get方法,方便之后对数据的修改,最后重写一下我们的toString()方法,便于直接打印。
创建书架
创建好我们书的类之后就是该创建书架了,所谓书架就是存放我们的书的,这里我们可以在里面给一个数组,用于存放不同的书。
然后就是给出我们书的数量,这里我们定义一个userSize用来记录我们图书的数量。
public class BookList {
private Book[] books = new Book[10];
private int userSize;
public BookList() {
books[0] = new Book("三体","刘慈欣",80,"科幻");
books[1] = new Book("平凡的世界","路遥",88,"文学");
books[2] = new Book("明朝那些事儿","当年明月",180,"历史");
this.userSize = 3;
}
public int getUserSize() {
return userSize;
}
public void setUserSize(int userSize) {
this.userSize = userSize;
}
//获取到pos位置的书
public Book getPos(int pos) {
return this.books[pos];
}
//设置pos位置下标的一本书
public void setBooks(int pos,Book book) {
this.books[pos] = book;
}
}然后就是set和get方法用于我们对userSize的调整,同时我们给出了调整我们书架里面书的方法。
这里我们给了一个构造方法,用于给我们的书架初始化放上三本书(小编我最爱看的对我影响最大的三本书哈哈),并且指定了书的个数userSize的大小为3。
Operation
该包里面装着我们的所有的对bookList的操作,还有一个接口IOperation,
IOperation接口
public interface IOperation {
void work(BookList bookList);
}添加图书AddOperation
public class AddOperation implements IOperation {
public void work(BookList bookList) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("添加图书操作");
System.out.println("请输入书名:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入作者:");
String Author = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入类型:");
String type = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入价格:");
int price = scanner.nextInt();
Book book = new Book(name,Author,price,type);
bookList.setBooks(bookList.getUserSize(),book);
bookList.setUserSize(bookList.getUserSize()+1);
}
}借阅图书BorrowOperation
public class BorrowOperation implements IOperation {
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("借书操作");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入想要借阅的书:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
for (int i = 0; i < bookList.getUserSize(); i++) {
if (name.equals(bookList.getPos(i).getName())==true) {
if(bookList.getPos(i).isBorrowed()==true) {//判断一下该书是否已经被借阅了
System.out.println("该书已经被借阅");
} else {
bookList.getPos(i).setBorrowed(true);
System.out.println("借阅成功!");
}
return;
}
}
System.out.println("您想要借阅的书不存在");
}
}删除图书DelOperation
public class DelOperation implements IOperation {
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("删除图书操作");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入想要删除图书的名称:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
//循环遍历所有图书
for (int i = 0; i < bookList.getUserSize(); i++) {
//找到书名后进行删除
if (name.equals(bookList.getPos(i).getName())==true) {
for (int j = i; j < bookList.getUserSize()-1; j++) {
bookList.setBooks(j,bookList.getPos(j+1));
}
bookList.setBooks(bookList.getUserSize(), null);//防止内存泄漏
bookList.setUserSize(bookList.getUserSize()-1);
System.out.println("删除完毕!");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("您要删除的图书不存在");
}
}打印图书DisplayOperation
public class DisplayOperation implements IOperation {
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("打印图书操作");
for (int i = 0; i < bookList.getUserSize(); i++) {
System.out.println(bookList.getPos(i));
}
}
}退出系统ExitOperation
public class ExitOperation implements IOperation {
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("退出操作");
System.exit(0);
}
}查询书籍FindOperation
public class FindOperation implements IOperation {
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("查询操作");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入查找的书名:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
for (int i = 0; i < bookList.getUserSize(); i++) {
if (name.equals(bookList.getPos(i).getName())==true) {
System.out.println("信息如下");
System.out.println(bookList.getPos(i));
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有找到该书!");
}
}归还书籍ReturnOperation
public class ReturnOperation implements IOperation {
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("返回操作");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入想要归还的书:");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
for (int i = 0; i < bookList.getUserSize(); i++) {
if (name.equals(bookList.getPos(i).getName())==true) {
if(bookList.getPos(i).isBorrowed()==false) {//判断一下该书是否已经被借阅了
System.out.println("该书已经归还");
} else {
bookList.getPos(i).setBorrowed(false);
System.out.println("归还成功!");
}
return;
}
}
System.out.println("您想要归还的书不存在");
}
}以上就是我们对BookList的操作部分。
user
我们的user这个部分是我们的分部管理,因为我们登录的时候会提醒我们是普通用户登录还是管理员登录,所以我们至少需要创建两个类,但是这两个类肯定会有很多相似的方法和成员,所以这个时候我们就再创建一个User的抽象类,然后让我们AdminUser管理员的类和我们的NormalUser普通类分别继承我们的User
User
public abstract class User {
protected String name; //用户姓名
protected IOperation[] iOperation; //定义接口类型的数组每个元素指向实现接口的对象
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//此时的menu为后续的动态绑定做准备
public abstract int menu();
public void doWork(int choice, BookList bookList) {
iOperation[choice].work(bookList);
}
}这里我们的抽象类有name成员,还有IOperation类型的数组,这里也解释了为什么我们刚刚要创建接口,因为有了接口我们后面可以向接口里面放我们的操作方法,因为其它的类都实现了我们的接口并且重写了接口里面的work()方法。
NormalUser
public class NormalUser extends User{
public NormalUser(String name) {
super(name);
this.iOperation = new IOperation[]{
new ExitOperation(),
new FindOperation(),
new BorrowOperation(),
new ReturnOperation(),
};
}
public int menu() {
System.out.println("********管理员菜单********");
System.out.println(" 欢迎"+this.name+"进入菜单");
System.out.println("1.查找图书");
System.out.println("2.借阅图书");
System.out.println("3.归还图书");
System.out.println("0.退出系统");
System.out.println("************************");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
return choice;
}
}这里首先是我们的构造方向,先帮父类构造,然后将IOperation进行初始化里面放着是我们普通用户所能进行的一系列操作,再下面就是我们的菜单方法,因为我们的普通用户和管理员所能进行的操作是不一样的,同时选择我们需要的操作。
AdminUser
public class AdminUser extends User{
public AdminUser(String name) {
super(name);
this.iOperation = new IOperation[]{
new ExitOperation(),
new FindOperation(),
new AddOperation(),
new DelOperation(),
new DisplayOperation(),
};
}
public int menu() {
System.out.println("********管理员菜单********");
System.out.println(" 欢迎"+this.name+"进入菜单");
System.out.println("1.查找图书");
System.out.println("2.新增图书");
System.out.println("3.删除图书");
System.out.println("4.显示图书");
System.out.println("0.退出系统");
System.out.println("************************");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
return choice;
}
}
管理员类就是菜单里面的方法和IOperation数组与前面有一点区别。
Main
public class Main {
public static User login() {
System.out.println("请输入你的姓名:");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入你的身份:1->管理员 0->普通用户");
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
//根据选择直接返回我们的对象。
if (choice==1) {
return new AdminUser(name);
} else {
return new NormalUser(name);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BookList bookList = new BookList();
//发生向上转型
User user = login();
//此时将发生动态绑定
while (true) {
int choice = user.menu();
user.doWork(choice, bookList);
}
}
}首先看我们的主函数,我么new了一个BookList也就是我们的书架,然后开始登录操作输入身份之后最后返回一个用户的对象,此时我们拥有了两个对象,一个是书架bookList,还有就是我们的用户对象,然后我们的用户就可以对我们的书架进行一系列的操作了。
首先就是打印我们的菜单,顺便返回我们的操作,接着拿着我们的操作choice和我们的书架bookList去执行,user.doWork(),拿着我们的choice找到我们IOperation找到对应的操作最后完成指定的功能。
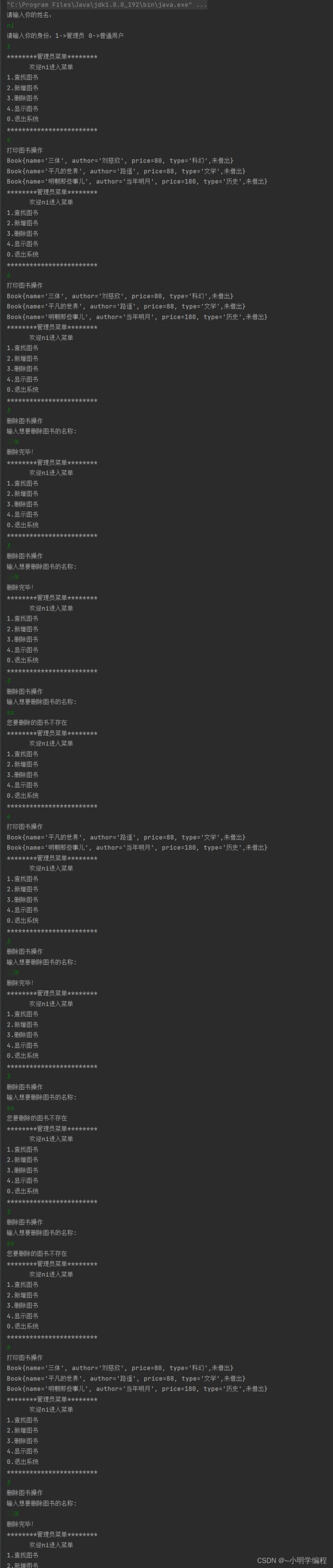
演示