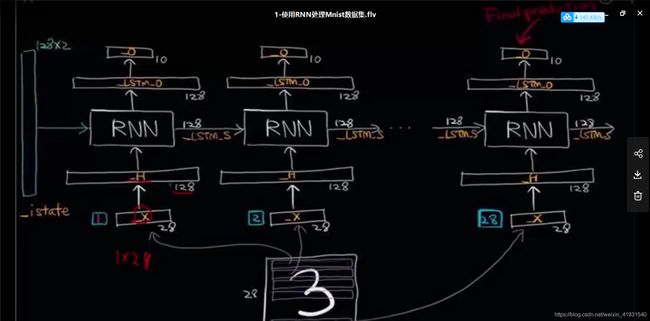
tensorflow搭建RNN模型
使用RNN处理MNIST手写数据集
一般来说CNN用来处理图像会更好一些,RNN一般用来处理语言或者情感方面的知识,这次就简单使用RNN来处理MNIST数据集
原理框图入下:
代码:
import tensorflow as tf
# 因为这个文件夹中有input_data.py文件,所以可以直接导入这个模块,否则需要输入完整的input_data
import input_data
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorflow.contrib import rnn
print ("Packages imported")
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("data/", one_hot=True)
trainimgs, trainlabels, testimgs, testlabels \
= mnist.train.images, mnist.train.labels, mnist.test.images, mnist.test.labels
ntrain, ntest, dim, nclasses \
= trainimgs.shape[0], testimgs.shape[0], trainimgs.shape[1], trainlabels.shape[1]
print ("MNIST loaded")
diminput = 28
dimhidden = 128
dimoutput = 10
nsteps = 28
weights = {
'hidden': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([diminput, dimhidden])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([dimhidden, dimoutput]))
}
biases = {
'hidden': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([dimhidden])),
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([dimoutput]))
}
# 对于mnsit数据集,如果是通过RNN来实现,那么我们首先就是要将28*28的图片格式改为28个1*28个数据
def _RNN(_X, _W, _b, _nsteps, _name):
# 1. Permute input from [batchsize, nsteps, diminput]
# => [nsteps, batchsize, diminput]
_X = tf.transpose(_X, [1, 0, 2])
# 2. Reshape input to [nsteps*batchsize, diminput]
_X = tf.reshape(_X, [-1, diminput])
# 3. Input layer => Hidden layer
_H = tf.matmul(_X, _W['hidden']) + _b['hidden']
print(_H)
# 4. Splite data to 'nsteps' chunks. An i-th chunck indicates i-th batch data
_Hsplit = tf.split(_H, _nsteps, 0)
print(_Hsplit)
# 5. Get LSTM's final output (_LSTM_O) and state (_LSTM_S)
# Both _LSTM_O and _LSTM_S consist of 'batchsize' elements
# Only _LSTM_O will be used to predict the output.
with tf.variable_scope(_name) as scope:
# scope.reuse_variables()
# tf封装好了完整的LSTM单元,forget_bias表示不遗忘信息
lstm_cell = rnn.BasicLSTMCell(dimhidden, forget_bias=1.0)
_LSTM_O, _LSTM_S = rnn.static_rnn(lstm_cell, _Hsplit,dtype=tf.float32)
# 6. Output
_O = tf.matmul(_LSTM_O[-1], _W['out']) + _b['out']
# Return!
return {
'X': _X, 'H': _H, 'Hsplit': _Hsplit,
'LSTM_O': _LSTM_O, 'LSTM_S': _LSTM_S, 'O': _O
}
print ("Network ready")
learning_rate = 0.001
x = tf.placeholder("float", [None, nsteps, diminput])
y = tf.placeholder("float", [None, dimoutput])
myrnn = _RNN(x, weights, biases, nsteps, 'basic')
pred = myrnn['O']
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=pred, labels=y))
optm = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost) # Adam Optimizer
accr = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1), tf.argmax(y,1)), tf.float32))
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
print ("Network Ready!")