灰点检测系列1:利用灰点检测估计光源,求白平衡
论文:Revisiting Gray Pixel for Statistical Illumination Estimation
https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.08326
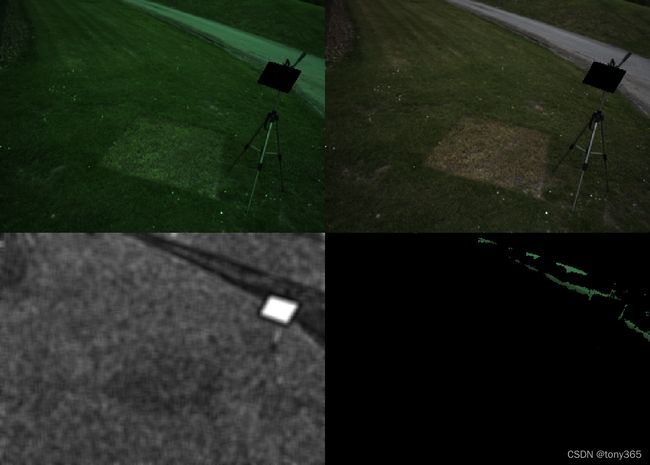
左上原图,右上白平衡后图(未经过gamma)
左下灰点可信度(越黑越可能是灰点),右下,筛选得到的灰点像素
python实现如下:
import os
import numpy as np
import scipy.io as scio
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import struct
from PIL import Image
from scipy import ndimage
import cv2
eps = 1e-9
def deriv_gauss(img, sigma):
Gaussoff = 0.000001
pw = np.array(range(50)).astype(np.int32)
ssq = sigma ** 2
width = np.sum(np.exp(-(pw * pw) / (2 * ssq)) > Gaussoff) - 1
xx = np.arange(2 * width + 1) - width
yy = np.arange(2 * width + 1) - width
x, y = np.meshgrid(xx, yy)
dg2d = -x * np.exp(-(x * x + y * y) / (2 * ssq)) / (np.pi * ssq)
dg2d = np.array(dg2d)
ax = ndimage.convolve(img, dg2d, mode='nearest')
ay = ndimage.convolve(img, dg2d.T, mode='nearest')
mag = np.sqrt(ax * ax + ay * ay)
return mag
def normr(data):
data1 = data / np.sqrt(np.sum(data * data, 1)).reshape(-1, 1)
return data1
def normc(data):
data1 = data / np.sqrt(np.sum(data * data, 0)).reshape(-1, 1)
return data1
def cal_angle(light, ref):
light = np.reshape(light, (-1, 3))
ref = np.reshape(ref, (-1, 3))
cos_angle = np.sum(light * ref, axis=1) / (
np.sqrt(np.sum(np.power(light, 2), 1)) * np.sqrt(np.sum(np.power(ref, 2), 1)))
angle = np.arccos(cos_angle)
angle = angle * 180 / np.pi
return angle
def cal_gray_index_with_angle(img, method, scale):
"""
:param img: input color-biased image
:param method: the method to calculate IIM, option = {'edge', 'std'}
:param scale: filter scale
:return: gray index map
"""
rr, cc, dd = img.shape
img[img == 0] = eps
data = []
t = np.ones([rr, cc])
if method == 'edge':
sigma = scale
for i in range(dd):
mm = deriv_gauss(np.log(img[:, :, i]), sigma)
data.append(mm.reshape(-1))
t = np.logical_and(t, mm < eps) # prevent low contrast region
else:
print('error method input !')
data = np.array(data).T # n * 3
data[data == 0] = eps
data_normed = normr(data)
gt = normr(np.ones_like(data_normed))
cos_ang = np.clip(np.sum(data_normed*gt, axis=1), 0, 0.9999)
angular_error = np.arccos(cos_ang)
Greyidx_angular = np.reshape(angular_error, (rr, cc))
Greyidx = Greyidx_angular / (np.max(Greyidx_angular) + eps)
Greyidx_angular[t] = np.max(Greyidx_angular)
Greyidx[t] = np.max(Greyidx)
# filter
siz = 7
hh = np.ones([siz, siz]) / (siz*siz)
Greyidx = ndimage.convolve(Greyidx, hh, mode='nearest')
Greyidx_angular = ndimage.convolve(Greyidx_angular, hh, mode='nearest')
return Greyidx, Greyidx_angular
def gray_detect_angle_meanshift(img, numGPs, mask, K, kernel, is_angular_ranking):
return
def detect_gray_with_angle(im, mask, gt):
Npre = 1
bandwidth = 0.1
h, w, n = im.shape
numGPs = int(np.floor(h*w*Npre // 100))
'''
mask saturated and dark pixels
'''
mask[np.max(im, axis=2) >= 0.95] = 1
mask[np.sum(im, axis=2) <= 8/255.0] = 1
scale = 0.5
gray_idx_norm, gray_idx_angle = cal_gray_index_with_angle(im, 'edge', scale)
# sel
gray_idx_angle[mask] = np.max(gray_idx_angle)
# cal angle
angle_sorted = np.sort(gray_idx_angle.copy().reshape(-1))
angle_thr = angle_sorted[numGPs]
mask_sel = gray_idx_angle < angle_thr
print('dd :', numGPs, angle_thr, gray_idx_angle.min,gray_idx_angle.max, mask_sel.shape, np.sum(mask_sel))
im_selected = im[mask_sel]
ill = np.sum(im_selected, axis=0).reshape(-1, n)
ill = ill / np.sqrt(np.sum(ill * ill, 1)).reshape(-1, 1)
im_choose = im * mask_sel[..., None]
ill2 = np.sum(im_choose, axis=(0, 1)).reshape(-1, n)
ill2 = ill2 / np.sqrt(np.sum(ill2 * ill2, 1)).reshape(-1, 1)
print(numGPs, angle_thr, im_selected.shape, 'est ill: ', ill, ill2)
an1 = cal_angle(ill, gt)
an2 = cal_angle(ill2, gt)
show_fig = 0
if show_fig:
gray_idx_norm_3ch = np.tile(gray_idx_norm[..., None], (1, 1, 3))
im_choose_BGR = im_choose[:, :, ::-1]
second_row = np.hstack((gray_idx_norm_3ch, im_choose_BGR))
im_BGR = im[:, :, ::-1]
# im_mask = im_BGR * mask[..., None]
wb_gain = np.max(ill2) / ill2
im_wb = im * wb_gain
im_BGR_wb = im_wb[:, :, ::-1]
res1 = np.hstack((im_BGR, im_BGR_wb))
res = np.vstack((res1, second_row))
cv2.namedWindow('im', 0)
cv2.imshow('im', res)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
return ill2, an2
if __name__ == "__main__":
# single pic
filename = r'G:\ffcc-master_20201108\ffcc-master\data\shi_gehler\preprocessed\GehlerShi\000129.png'
imbgr = cv2.imread(filename)
im = imbgr[:, :, ::-1]
im = im / 255
gt_file = filename[:-4] + '.txt'
ill_gt = np.loadtxt(gt_file)
h, w, n = im.shape
mask = np.zeros((h, w)).astype(bool)
ill, angle = detect_gray_with_angle(im, mask, ill_gt)
ill = ill.reshape(-1)
print(ill, angle)
print(ill[1] / ill)
# dir
ills = []
angles = []
dir = r'G:\ffcc-master_20201108\ffcc-master\data\shi_gehler\preprocessed\GehlerShi'
filesets = os.listdir(dir)
for file in filesets:
if file.endswith('.png'):
filename = os.path.join(dir, file)
im = cv2.imread(filename)
im = im[:, :, ::-1] / 255
file_gt = filename[:-4] + '.txt'
gt = np.loadtxt(file_gt)
print(filename)
mask = np.zeros((h, w)).astype(bool)
ill, angle = detect_gray_with_angle(im, mask, gt)
ills.append(ill)
angles.append(angle)
print(ill, gt, angle)
angles = np.array(angles)
np.savetxt('wb_detect_gray_with_angle.txt', angles, delimiter=' ', fmt='%.7f')
print(angles, np.mean(angles))