[论文速读]:CVPR 2020 在傅里叶域自适应实现语义分割 Fourier Domain Adaptation
FDA: Fourier Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation
[PAPER] [GITHUB]
Abstract
We describe a simple method for unsupervised domain adaptation, whereby the discrepancy between the source and target distributions is reduced by swapping the low-frequency spectrum of one with the other. We illustrate the method in semantic segmentation, where densely annotated images are aplenty in one domain (e.g., synthetic data), but difficult to obtain in another (e.g., real images). Current state-of-the-art methods are complex, some requiring adversarial optimization to render the backbone of a neural network invariant to the discrete domain selection variable. Our method does not require any training to perform the domain alignment, just a simple Fourier Transform and its inverse. Despite its simplicity, it achieves state-of-the-art performance in the current benchmarks, when integrated into a relatively standard semantic segmentation model. Our results indicate that even simple procedures can discount nuisance variability in the data that more sophisticated methods struggle to learn away.
本文提出了一种简单的无监督域适应方法,通过交换源域和目标域的低频频谱来减少二者分布之间的差异。
该方法用在语义分割中,语义分割的特点是,在一个源域(如合成数据)有大量注释的图像,但在目标域(如真实图像)很难获得注释的图像。
目前的语义分割方法需要对抗优化,以使神经网络的骨干不变的离散域选择变量。
本文的方法不需要任何训练来执行域的对齐,只需要一个简单的傅里叶变换及其反变换。
尽管很简单,当集成到一个相对标准的语义分割模型中时,它在当前的基准测试中获得了最先进的性能。研究结果表明,即使是简单的程序也可以消除数据中的可变性,而复杂的方法也很难学到这些。
Fourier Domain Adaptation (FDA)
定义:
source dataset: ![]() ; target dataset:
; target dataset:![]()
color image: ![]() ; semantic map:
; semantic map:![]()
目标:
Fourier Domain Adaptation (FDA) :reduce the domain gap between the two datasets.
方法:
amplitude and phase components of the Fourier transform(傅里叶变换的振幅和相位分量):![]()
inverse Fourier transform that maps spectral signals (phase and amplitude) back to image space(反傅里叶变换,光谱信号(相位和振幅)映射到图像空间):![]()
mask:![]()
Fourier Domain Adaptation:
![]()
Figure 1. Spectral Transfer: Mapping a source image to a target “style” without altering semantic content. A randomly sampled target image provides the style by swapping the low-frequency component of the spectrum of the source image with its own. The outcome “source image in target style” shows a smaller domain gap perceptually and improves transfer learning for semantic segmentation as measured in the benchmarks in Sect. 3
Choice of β:
图2说明了 β 的效果。当细胞密度增大到1.0时,图像 x_{s→t} 接近目标图像 x_t,但也显示出可见伪影,如图2中放大区域所示。我们设置 β ≤ 0.15.。然而,在表1中,展示了不同的选择的效果以及得到的模型的平均值,类似于一个简单的多尺度池化方法。
Figure 2. Effect of the size of the domain β, shown in Fig. 1, where the spectrum is swapped: increasing β will decrease the domain gap but introduce artifacts (see zoomed insets). We tune β until artifacts in the transformed images become obvious and use a single value for some experiments. In other experiments, we maintain multiple values simultaneously in a multi-scale setting (Table 1).
FDA for Semantic Segmentation
定义两种 Loss :
1. cross-entropy loss:
![]() :semantic segmentation network
:semantic segmentation network
![]() 源域 到 目标域 的变换;该损失函数的涵义是,来自 源域 的图像变换到 目标域,然后其估计的 语义分割 应与源域的 GT 语义分割图 的交叉熵最小。
源域 到 目标域 的变换;该损失函数的涵义是,来自 源域 的图像变换到 目标域,然后其估计的 语义分割 应与源域的 GT 语义分割图 的交叉熵最小。
2. robust weighting function for entropy minimization:
![]() is the Charbonnier penalty function [ Towards ultimate motion estimation: Combining highest accuracy with real-time performance. In Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV’05) ]
is the Charbonnier penalty function [ Towards ultimate motion estimation: Combining highest accuracy with real-time performance. In Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV’05) ]
Figure 3. Charbonnier penalty used for robust entropy minimization, visualized for different values of the parameter η.
overall loss to train the semantic segmentation network φ w from scratch
![]()
Self-Supervised training
mean prediction for a certain target image ![]() can be obtained by:
can be obtained by:
we directly train multiple models ![]() with different β ′ s in the FDA process, with no need to explicitly force model divergence. We instantiate M=3 segmentation networks
with different β ′ s in the FDA process, with no need to explicitly force model divergence. We instantiate M=3 segmentation networks ![]() , m = 1, 2, 3,
, m = 1, 2, 3,
self-supervised training loss:
【本文的核心思想在于 Fourier Domain Adaptation 的定义,故而 for Semantic Segmentation 这节写的笔记简略(本人不是做这块的,后面这部分真心看不懂 T_T)】
![[论文速读]:CVPR 2020 在傅里叶域自适应实现语义分割 Fourier Domain Adaptation_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/f70fe1e3b2fb4591a928525dd96ebfc1.jpg)
![[论文速读]:CVPR 2020 在傅里叶域自适应实现语义分割 Fourier Domain Adaptation_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/8735437bd29e40fdbf95910f24db0ca4.jpg)
![[论文速读]:CVPR 2020 在傅里叶域自适应实现语义分割 Fourier Domain Adaptation_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/a4c2260c787343dcab34a9f770646807.jpg)
![[论文速读]:CVPR 2020 在傅里叶域自适应实现语义分割 Fourier Domain Adaptation_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/ae46ba9524d74132ac52a2fca976c7ee.jpg)

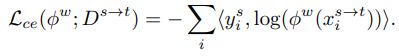
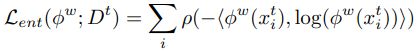
![[论文速读]:CVPR 2020 在傅里叶域自适应实现语义分割 Fourier Domain Adaptation_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/e9c990983c5a4427ac90a13edf3a8a57.jpg)

