一、单张绘制
1.1 代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rc('font',family='Times New Roman', size=15)
def sigmoid(x):
return 1. / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def tanh(x):
return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
def relu(x):
return np.where(x < 0, 0, x)
def prelu(x):
return np.where(x<0, x * 0.5, x)
def plot_sigmoid():
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.1)
y = sigmoid(x)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.plot(x, y,color="black", lw=3)
plt.xticks(fontsize=15)
plt.yticks(fontsize=15)
plt.xlim([-10.05, 10.05])
plt.ylim([-0.02, 1.02])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
def plot_tanh():
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.1)
y = tanh(x)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.plot(x, y, color="black", lw=3)
plt.xticks(fontsize=15)
plt.yticks(fontsize=15)
plt.xlim([-10.05, 10.05])
plt.ylim([-0.02, 1.02])
ax.set_yticks([-1.0, -0.5, 0.5, 1.0])
ax.set_xticks([-10, -5, 5, 10])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
def plot_relu():
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.1)
y = relu(x)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.plot(x, y, color="black", lw=3)
plt.xticks(fontsize=15)
plt.yticks(fontsize=15)
plt.xlim([-10.05, 10.05])
plt.ylim([-0.02, 1.02])
ax.set_yticks([2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
def plot_prelu():
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.1)
y = prelu(x)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.plot(x, y, color="black", lw=3)
plt.xticks(fontsize=15)
plt.yticks(fontsize=15)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
plot_sigmoid()
plot_tanh()
plot_relu()
plot_prelu()
1.2 绘制结果
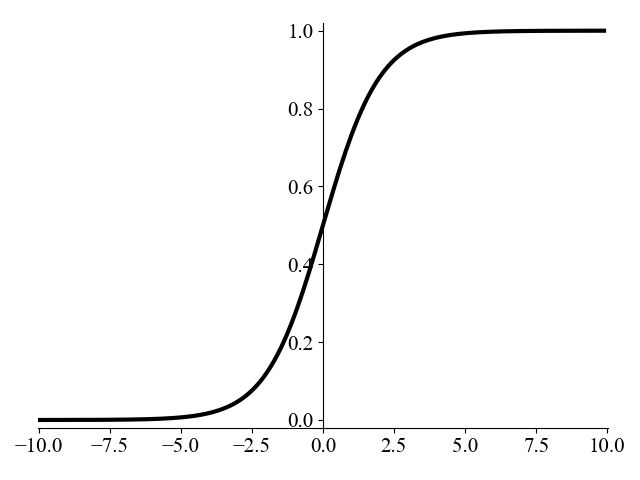
(1)Sigmoid
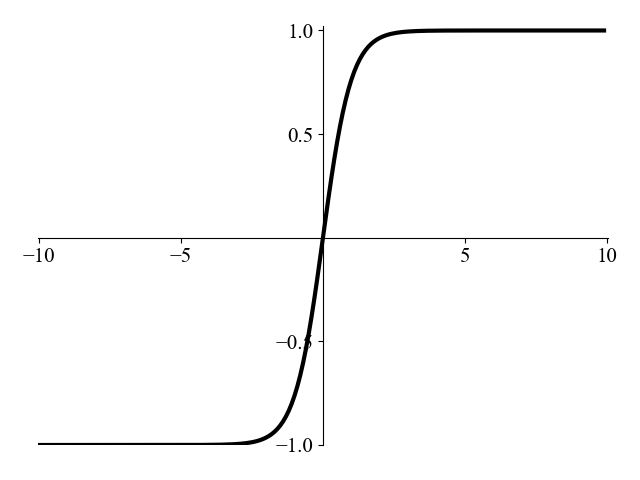
(2)Tanh
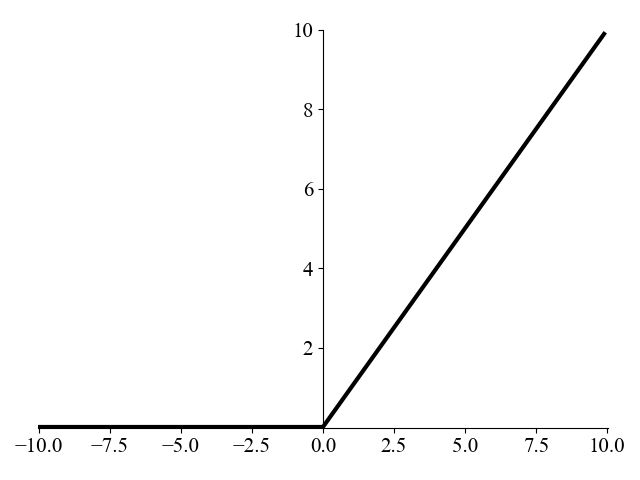
(3)ReLU
(4)PReLU
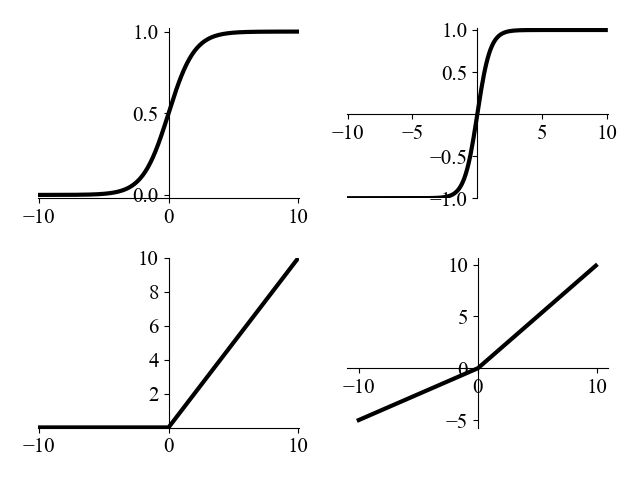
二、4张图绘制成1张图
2.1 代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rc('font',family='Times New Roman', size=15)
def sigmoid(x):
return 1. / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def tanh(x):
return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
def relu(x):
return np.where(x < 0, 0, x)
def prelu(x):
return np.where(x<0, x * 0.5, x)
def plot_sigmoid(fig):
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.1)
y = sigmoid(x)
ax = fig.add_subplot(221)
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.plot(x, y,color="black", lw=3)
plt.xticks(fontsize=15)
plt.yticks(fontsize=15)
plt.xlim([-10.05, 10.05])
plt.ylim([-0.02, 1.02])
plt.tight_layout()
def plot_tanh(fig):
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.1)
y = tanh(x)
ax = fig.add_subplot(222)
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.plot(x, y, color="black", lw=3)
plt.xticks(fontsize=15)
plt.yticks(fontsize=15)
plt.xlim([-10.05, 10.05])
plt.ylim([-0.02, 1.02])
ax.set_yticks([-1.0, -0.5, 0.5, 1.0])
ax.set_xticks([-10, -5, 5, 10])
plt.tight_layout()
def plot_relu(fig):
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.1)
y = relu(x)
ax = fig.add_subplot(223)
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.plot(x, y, color="black", lw=3)
plt.xticks(fontsize=15)
plt.yticks(fontsize=15)
plt.xlim([-10.05, 10.05])
plt.ylim([-0.02, 1.02])
ax.set_yticks([2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
plt.tight_layout()
def plot_prelu(fig):
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.1)
y = prelu(x)
ax = fig.add_subplot(224)
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
ax.plot(x, y, color="black", lw=3)
plt.xticks(fontsize=15)
plt.yticks(fontsize=15)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
fig = plt.figure()
plot_sigmoid(fig)
plot_tanh(fig)
plot_relu(fig)
plot_prelu(fig)
2.2 绘制结果