Redis 项目实战 —— 抽奖大转盘
1. 项目介绍
这是一个基于Spring boot + Mybatis Plus + Redis 的简单案例。
主要是将活动内容、奖品信息、记录信息等缓存到Redis中,然后所有的抽奖过程全部从Redis中做数据的操作。
大致内容很简单,具体操作下面慢慢分析。
2. 项目演示
话不多说,首先上图看看项目效果,如果觉得还行的话咱们就来看看他具体是怎么实现的。
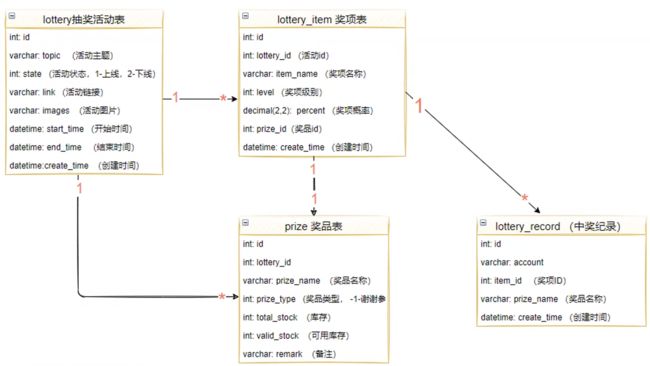
3. 表结构
该项目包含以下四张表,分别是活动表、奖项表、奖品表以及中奖记录表。具体的SQL会在文末给出。
4. 项目搭建
咱们首先先搭建一个标准的Spring boot 项目,直接IDEA创建,然后选择一些相关的依赖即可。
4.1 依赖
该项目主要用到了:Redis,thymeleaf,mybatis-plus等依赖。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidougroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>3.4.3version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidougroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-generatorartifactId>
<version>3.4.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>fastjsonartifactId>
<version>1.2.72version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.1.22version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commonsgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3artifactId>
<version>3.9version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.18.12version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commonsgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2artifactId>
<version>2.8.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstructgroupId>
<artifactId>mapstructartifactId>
<version>1.4.2.Finalversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstructgroupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-jdk8artifactId>
<version>1.4.2.Finalversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstructgroupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-processorartifactId>
<version>1.4.2.Finalversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-timegroupId>
<artifactId>joda-timeartifactId>
<version>2.10.6version>
dependency>
dependencies>
4.2 YML配置
依赖引入之后,我们需要进行相应的配置:数据库连接信息、Redis、mybatis-plus、线程池等。
server:
port: 8080
servlet:
context-path: /
spring:
datasource:
druid:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
initial-size: 30
max-active: 100
min-idle: 10
max-wait: 60000
time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000
min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000
validation-query: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
test-while-idle: true
test-on-borrow: false
test-on-return: false
filters: stat,wall
redis:
port: 6379
host: 127.0.0.1
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: -1
max-idle: 2000
max-wait: -1
min-idle: 1
time-between-eviction-runs: 5000
mvc:
view:
prefix: classpath:/templates/
suffix: .html
# mybatis-plus
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
auto-mapping-behavior: full
mapper-locations: classpath*:mapper/**/*Mapper.xml
# 线程池
async:
executor:
thread:
core-pool-size: 6
max-pool-size: 12
queue-capacity: 100000
name-prefix: lottery-service-
4.3 代码生成
这边我们可以直接使用mybatis-plus的代码生成器帮助我们生成一些基础的业务代码,避免这些重复的体力活。
这边贴出相关代码,直接修改数据库连接信息、相关包名模块名即可。
public class MybatisPlusGeneratorConfig {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 代码生成器
AutoGenerator mpg = new AutoGenerator();
// 全局配置
GlobalConfig gc = new GlobalConfig();
String projectPath = System.getProperty("user.dir");
gc.setOutputDir(projectPath + "/src/main/java");
gc.setAuthor("chen");
gc.setOpen(false);
//实体属性 Swagger2 注解
gc.setSwagger2(false);
mpg.setGlobalConfig(gc);
// 数据源配置
DataSourceConfig dsc = new DataSourceConfig();
dsc.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true");
dsc.setDriverName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dsc.setUsername("root");
dsc.setPassword("123456");
mpg.setDataSource(dsc);
// 包配置
PackageConfig pc = new PackageConfig();
// pc.setModuleName(scanner("模块名"));
pc.setParent("com.example.lottery");
pc.setEntity("dal.model");
pc.setMapper("dal.mapper");
pc.setService("service");
pc.setServiceImpl("service.impl");
mpg.setPackageInfo(pc);
// 配置模板
TemplateConfig templateConfig = new TemplateConfig();
templateConfig.setXml(null);
mpg.setTemplate(templateConfig);
// 策略配置
StrategyConfig strategy = new StrategyConfig();
strategy.setNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel);
strategy.setColumnNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel);
strategy.setSuperEntityClass("com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.activerecord.Model");
strategy.setEntityLombokModel(true);
strategy.setRestControllerStyle(true);
strategy.setEntityLombokModel(true);
// 公共父类
// strategy.setSuperControllerClass("com.baomidou.ant.common.BaseController");
// 写于父类中的公共字段
// strategy.setSuperEntityColumns("id");
strategy.setInclude(scanner("lottery,lottery_item,lottery_prize,lottery_record").split(","));
strategy.setControllerMappingHyphenStyle(true);
strategy.setTablePrefix(pc.getModuleName() + "_");
mpg.setStrategy(strategy);
mpg.setTemplateEngine(new FreemarkerTemplateEngine());
mpg.execute();
}
public static String scanner(String tip) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
StringBuilder help = new StringBuilder();
help.append("请输入" + tip + ":");
System.out.println(help.toString());
if (scanner.hasNext()) {
String ipt = scanner.next();
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(ipt)) {
return ipt;
}
}
throw new MybatisPlusException("请输入正确的" + tip + "!");
}
}
4.4 Redis 配置
我们如果在代码中使用 RedisTemplate 的话,需要添加相关配置,将其注入到Spring容器中。
@Configuration
public class RedisTemplateConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
// 使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerialize 替换默认序列化
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
objectMapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
objectMapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
SimpleModule simpleModule = new SimpleModule();
simpleModule.addSerializer(DateTime.class, new JodaDateTimeJsonSerializer());
simpleModule.addDeserializer(DateTime.class, new JodaDateTimeJsonDeserializer());
objectMapper.registerModule(simpleModule);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(objectMapper);
// 设置value的序列化规则和 key的序列化规则
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
}
class JodaDateTimeJsonSerializer extends JsonSerializer<DateTime> {
@Override
public void serialize(DateTime dateTime, JsonGenerator jsonGenerator, SerializerProvider serializerProvider) throws IOException {
jsonGenerator.writeString(dateTime.toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
}
}
class JodaDateTimeJsonDeserializer extends JsonDeserializer<DateTime> {
@Override
public DateTime deserialize(JsonParser jsonParser, DeserializationContext deserializationContext) throws IOException, JsonProcessingException {
String dateString = jsonParser.readValueAs(String.class);
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormat.forPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
return dateTimeFormatter.parseDateTime(dateString);
}
}
4.5 常量管理
由于代码中会用到一些共有的常量,我们应该将其抽离出来。
public class LotteryConstants {
/**
* 表示正在抽奖的用户标记
*/
public final static String DRAWING = "DRAWING";
/**
* 活动标记 LOTTERY:lotteryID
*/
public final static String LOTTERY = "LOTTERY";
/**
* 奖品数据 LOTTERY_PRIZE:lotteryID:PrizeId
*/
public final static String LOTTERY_PRIZE = "LOTTERY_PRIZE";
/**
* 默认奖品数据 DEFAULT_LOTTERY_PRIZE:lotteryID
*/
public final static String DEFAULT_LOTTERY_PRIZE = "DEFAULT_LOTTERY_PRIZE";
public enum PrizeTypeEnum {
THANK(-1), NORMAL(1), UNIQUE(2);
private int value;
private PrizeTypeEnum(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return this.value;
}
}
/**
* 奖项缓存:LOTTERY_ITEM:LOTTERY_ID
*/
public final static String LOTTERY_ITEM = "LOTTERY_ITEM";
/**
* 默认奖项: DEFAULT_LOTTERY_ITEM:LOTTERY_ID
*/
public final static String DEFAULT_LOTTERY_ITEM = "DEFAULT_LOTTERY_ITEM";
}
public enum ReturnCodeEnum {
SUCCESS("0000", "成功"),
LOTTER_NOT_EXIST("9001", "指定抽奖活动不存在"),
LOTTER_FINISH("9002", "活动已结束"),
LOTTER_REPO_NOT_ENOUGHT("9003", "当前奖品库存不足"),
LOTTER_ITEM_NOT_INITIAL("9004", "奖项数据未初始化"),
LOTTER_DRAWING("9005", "上一次抽奖还未结束"),
REQUEST_PARAM_NOT_VALID("9998", "请求参数不正确"),
SYSTEM_ERROR("9999", "系统繁忙,请稍后重试");
private String code;
private String msg;
private ReturnCodeEnum(String code, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public String getCodeString() {
return getCode() + "";
}
}
对Redis中的key进行统一的管理。
public class RedisKeyManager {
/**
* 正在抽奖的key
*
* @param accountIp
* @return
*/
public static String getDrawingRedisKey(String accountIp) {
return new StringBuilder(LotteryConstants.DRAWING).append(":").append(accountIp).toString();
}
/**
* 获取抽奖活动的key
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
public static String getLotteryRedisKey(Integer id) {
return new StringBuilder(LotteryConstants.LOTTERY).append(":").append(id).toString();
}
/**
* 获取指定活动下的所有奖品数据
*
* @param lotteryId
* @return
*/
public static String getLotteryPrizeRedisKey(Integer lotteryId) {
return new StringBuilder(LotteryConstants.LOTTERY_PRIZE).append(":").append(lotteryId).toString();
}
public static String getLotteryPrizeRedisKey(Integer lotteryId, Integer prizeId) {
return new StringBuilder(LotteryConstants.LOTTERY_PRIZE).append(":").append(lotteryId).append(":").append(prizeId).toString();
}
public static String getDefaultLotteryPrizeRedisKey(Integer lotteryId) {
return new StringBuilder(LotteryConstants.DEFAULT_LOTTERY_PRIZE).append(":").append(lotteryId).toString();
}
public static String getLotteryItemRedisKey(Integer lotteryId) {
return new StringBuilder(LotteryConstants.LOTTERY_ITEM).append(":").append(lotteryId).toString();
}
public static String getDefaultLotteryItemRedisKey(Integer lotteryId) {
return new StringBuilder(LotteryConstants.DEFAULT_LOTTERY_ITEM).append(":").append(lotteryId).toString();
}
}
4.6 业务代码
4.6.1 抽奖接口
我们首先编写抽奖接口,根据前台传的参数查询到具体的活动,然后进行相应的操作。(当然,前端直接是写死的/lottery/1)
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public ResultResp<LotteryItemVo> doDraw(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, HttpServletRequest request) {
String accountIp = CusAccessObjectUtil.getIpAddress(request);
log.info("begin LotteryController.doDraw,access user {}, lotteryId,{}:", accountIp, id);
ResultResp<LotteryItemVo> resultResp = new ResultResp<>();
try {
//判断当前用户上一次抽奖是否结束
checkDrawParams(id, accountIp);
//抽奖
DoDrawDto dto = new DoDrawDto();
dto.setAccountIp(accountIp);
dto.setLotteryId(id);
lotteryService.doDraw(dto);
//返回结果设置
resultResp.setCode(ReturnCodeEnum.SUCCESS.getCode());
resultResp.setMsg(ReturnCodeEnum.SUCCESS.getMsg());
//对象转换
resultResp.setResult(lotteryConverter.dto2LotteryItemVo(dto));
} catch (Exception e) {
return ExceptionUtil.handlerException4biz(resultResp, e);
} finally {
//清除占位标记
redisTemplate.delete(RedisKeyManager.getDrawingRedisKey(accountIp));
}
return resultResp;
}
private void checkDrawParams(Integer id, String accountIp) {
if (null == id) {
throw new RewardException(ReturnCodeEnum.REQUEST_PARAM_NOT_VALID.getCode(), ReturnCodeEnum.REQUEST_PARAM_NOT_VALID.getMsg());
}
//采用setNx命令,判断当前用户上一次抽奖是否结束
Boolean result = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(RedisKeyManager.getDrawingRedisKey(accountIp), "1", 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//如果为false,说明上一次抽奖还未结束
if (!result) {
throw new RewardException(ReturnCodeEnum.LOTTER_DRAWING.getCode(), ReturnCodeEnum.LOTTER_DRAWING.getMsg());
}
}
为了避免用户重复点击抽奖,所以我们通过Redis来避免这种问题,用户每次抽奖的时候,通过setNx给用户排队并设置过期时间;如果用户点击多次抽奖,Redis设置值的时候发现该用户上次抽奖还未结束则抛出异常。
最后用户抽奖成功的话,记得清除该标记,从而用户能够继续抽奖。
4.6.2 初始化数据
从抽奖入口进来,校验成功以后则开始业务操作。
@Override
public void doDraw(DoDrawDto drawDto) throws Exception {
RewardContext context = new RewardContext();
LotteryItem lotteryItem = null;
try {
//JUC工具 需要等待线程结束之后才能运行
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
//判断活动有效性
Lottery lottery = checkLottery(drawDto);
//发布事件,用来加载指定活动的奖品信息
applicationContext.publishEvent(new InitPrizeToRedisEvent(this, lottery.getId(), countDownLatch));
//开始抽奖
lotteryItem = doPlay(lottery);
//记录奖品并扣减库存
countDownLatch.await(); //等待奖品初始化完成
String key = RedisKeyManager.getLotteryPrizeRedisKey(lottery.getId(), lotteryItem.getPrizeId());
int prizeType = Integer.parseInt(redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(key, "prizeType").toString());
context.setLottery(lottery);
context.setLotteryItem(lotteryItem);
context.setAccountIp(drawDto.getAccountIp());
context.setKey(key);
//调整库存及记录中奖信息
AbstractRewardProcessor.rewardProcessorMap.get(prizeType).doReward(context);
} catch (UnRewardException u) { //表示因为某些问题未中奖,返回一个默认奖项
context.setKey(RedisKeyManager.getDefaultLotteryPrizeRedisKey(lotteryItem.getLotteryId()));
lotteryItem = (LotteryItem) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(RedisKeyManager.getDefaultLotteryItemRedisKey(lotteryItem.getLotteryId()));
context.setLotteryItem(lotteryItem);
AbstractRewardProcessor.rewardProcessorMap.get(LotteryConstants.PrizeTypeEnum.THANK.getValue()).doReward(context);
}
//拼接返回数据
drawDto.setLevel(lotteryItem.getLevel());
drawDto.setPrizeName(context.getPrizeName());
drawDto.setPrizeId(context.getPrizeId());
}
首先我们通过CountDownLatch来保证商品初始化的顺序,关于CountDownLatch可以查看 JUC工具 该文章。
然后我们需要检验一下活动的有效性,确保活动未结束。
检验活动通过后则通过ApplicationEvent 事件实现奖品数据的加载,将其存入Redis中。或者通过ApplicationRunner在程序启动时获取相关数据。我们这使用的是事件机制。ApplicationRunner 的相关代码在下文我也顺便贴出。
事件机制
public class InitPrizeToRedisEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private Integer lotteryId;
private CountDownLatch countDownLatch;
public InitPrizeToRedisEvent(Object source, Integer lotteryId, CountDownLatch countDownLatch) {
super(source);
this.lotteryId = lotteryId;
this.countDownLatch = countDownLatch;
}
public Integer getLotteryId() {
return lotteryId;
}
public void setLotteryId(Integer lotteryId) {
this.lotteryId = lotteryId;
}
public CountDownLatch getCountDownLatch() {
return countDownLatch;
}
public void setCountDownLatch(CountDownLatch countDownLatch) {
this.countDownLatch = countDownLatch;
}
}
有了事件机制,我们还需要一个监听事件,用来初始化相关数据信息。具体业务逻辑大家可以参考下代码,有相关的注释信息,主要就是将数据库中的数据添加进redis中,需要注意的是,我们为了保证原子性,是通过HASH来存储数据的,这样之后库存扣减的时候就可以通过opsForHash来保证其原子性。
当初始化奖品信息之后,则通过countDown()方法表名执行完成,业务代码中线程阻塞的地方可以继续执行了。
@Slf4j
@Component
public class InitPrizeToRedisListener implements ApplicationListener<InitPrizeToRedisEvent> {
@Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
LotteryPrizeMapper lotteryPrizeMapper;
@Autowired
LotteryItemMapper lotteryItemMapper;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(InitPrizeToRedisEvent initPrizeToRedisEvent) {
log.info("begin InitPrizeToRedisListener," + initPrizeToRedisEvent);
Boolean result = redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(RedisKeyManager.getLotteryPrizeRedisKey(initPrizeToRedisEvent.getLotteryId()), "1");
//已经初始化到缓存中了,不需要再次缓存
if (!result) {
log.info("already initial");
initPrizeToRedisEvent.getCountDownLatch().countDown();
return;
}
QueryWrapper<LotteryItem> lotteryItemQueryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
lotteryItemQueryWrapper.eq("lottery_id", initPrizeToRedisEvent.getLotteryId());
List<LotteryItem> lotteryItems = lotteryItemMapper.selectList(lotteryItemQueryWrapper);
//如果指定的奖品没有了,会生成一个默认的奖项
LotteryItem defaultLotteryItem = lotteryItems.parallelStream().filter(o -> o.getDefaultItem().intValue() == 1).findFirst().orElse(null);
Map<String, Object> lotteryItemMap = new HashMap<>(16);
lotteryItemMap.put(RedisKeyManager.getLotteryItemRedisKey(initPrizeToRedisEvent.getLotteryId()), lotteryItems);
lotteryItemMap.put(RedisKeyManager.getDefaultLotteryItemRedisKey(initPrizeToRedisEvent.getLotteryId()), defaultLotteryItem);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().multiSet(lotteryItemMap);
QueryWrapper queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper();
queryWrapper.eq("lottery_id", initPrizeToRedisEvent.getLotteryId());
List<LotteryPrize> lotteryPrizes = lotteryPrizeMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
//保存一个默认奖项
AtomicReference<LotteryPrize> defaultPrize = new AtomicReference<>();
lotteryPrizes.stream().forEach(lotteryPrize -> {
if (lotteryPrize.getId().equals(defaultLotteryItem.getPrizeId())) {
defaultPrize.set(lotteryPrize);
}
String key = RedisKeyManager.getLotteryPrizeRedisKey(initPrizeToRedisEvent.getLotteryId(), lotteryPrize.getId());
setLotteryPrizeToRedis(key, lotteryPrize);
});
String key = RedisKeyManager.getDefaultLotteryPrizeRedisKey(initPrizeToRedisEvent.getLotteryId());
setLotteryPrizeToRedis(key, defaultPrize.get());
initPrizeToRedisEvent.getCountDownLatch().countDown(); //表示初始化完成
log.info("finish InitPrizeToRedisListener," + initPrizeToRedisEvent);
}
private void setLotteryPrizeToRedis(String key, LotteryPrize lotteryPrize) {
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class));
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, "id", lotteryPrize.getId());
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, "lotteryId", lotteryPrize.getLotteryId());
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, "prizeName", lotteryPrize.getPrizeName());
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, "prizeType", lotteryPrize.getPrizeType());
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, "totalStock", lotteryPrize.getTotalStock());
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, "validStock", lotteryPrize.getValidStock());
}
}
上面部分是通过事件的方法来初始化数据,下面我们说下ApplicationRunner的方式:
这种方式很简单,在项目启动的时候将数据加载进去即可。
我们只需要实现ApplicationRunner接口即可,然后在run方法中从数据库读取数据加载到Redis中。
@Slf4j
@Component
public class LoadDataApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
LotteryMapper lotteryMapper;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
log.info("=========begin load lottery data to Redis===========");
//加载当前抽奖活动信息
Lottery lottery = lotteryMapper.selectById(1);
log.info("=========finish load lottery data to Redis===========");
}
}
4.6.3 抽奖
我们在使用事件进行数据初始化的时候,可以同时进行抽奖操作,但是注意的是这个时候需要使用countDownLatch.await();来阻塞当前线程,等待数据初始化完成。
在抽奖的过程中,我们首先尝试从Redis中获取相关数据,如果Redis中没有则从数据库中加载数据,如果数据库中也没查询到相关数据,则表明相关的数据没有配置完成。
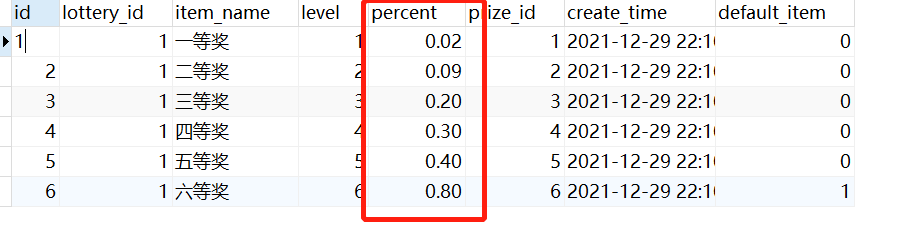
获取数据之后,我们就该开始抽奖了。抽奖的核心在于随机性以及概率性,咱们总不能随便抽抽都能抽到一等奖吧?所以我们需要在表中设置每个奖项的概率性。如下所示:
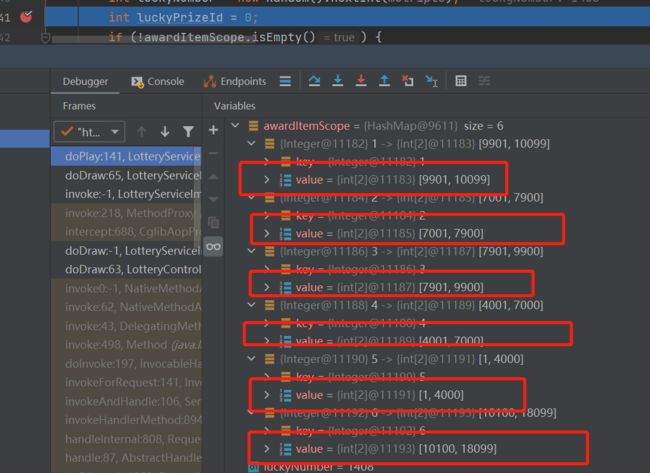
在我们抽奖的时候需要根据概率划分处相关区间。我们可以通过Debug的方式来查看一下具体怎么划分的:
奖项的概率越大,区间越大;大家看到的顺序是不同的,由于我们在上面通过Collections.shuffle(lotteryItems);将集合打乱了,所以这里看到的不是顺序展示的。
在生成对应区间后,我们通过生成随机数,看随机数落在那个区间中,然后将对应的奖项返回。这就实现了我们的抽奖过程。
private LotteryItem doPlay(Lottery lottery) {
LotteryItem lotteryItem = null;
QueryWrapper<LotteryItem> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq("lottery_id", lottery.getId());
Object lotteryItemsObj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(RedisKeyManager.getLotteryItemRedisKey(lottery.getId()));
List<LotteryItem> lotteryItems;
//说明还未加载到缓存中,同步从数据库加载,并且异步将数据缓存
if (lotteryItemsObj == null) {
lotteryItems = lotteryItemMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
} else {
lotteryItems = (List<LotteryItem>) lotteryItemsObj;
}
//奖项数据未配置
if (lotteryItems.isEmpty()) {
throw new BizException(ReturnCodeEnum.LOTTER_ITEM_NOT_INITIAL.getCode(), ReturnCodeEnum.LOTTER_ITEM_NOT_INITIAL.getMsg());
}
int lastScope = 0;
Collections.shuffle(lotteryItems);
Map<Integer, int[]> awardItemScope = new HashMap<>();
//item.getPercent=0.05 = 5%
for (LotteryItem item : lotteryItems) {
int currentScope = lastScope + new BigDecimal(item.getPercent().floatValue()).multiply(new BigDecimal(mulriple)).intValue();
awardItemScope.put(item.getId(), new int[]{lastScope + 1, currentScope});
lastScope = currentScope;
}
int luckyNumber = new Random().nextInt(mulriple);
int luckyPrizeId = 0;
if (!awardItemScope.isEmpty()) {
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, int[]>> set = awardItemScope.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, int[]> entry : set) {
if (luckyNumber >= entry.getValue()[0] && luckyNumber <= entry.getValue()[1]) {
luckyPrizeId = entry.getKey();
break;
}
}
}
for (LotteryItem item : lotteryItems) {
if (item.getId().intValue() == luckyPrizeId) {
lotteryItem = item;
break;
}
}
return lotteryItem;
}
4.6.4 调整库存及记录
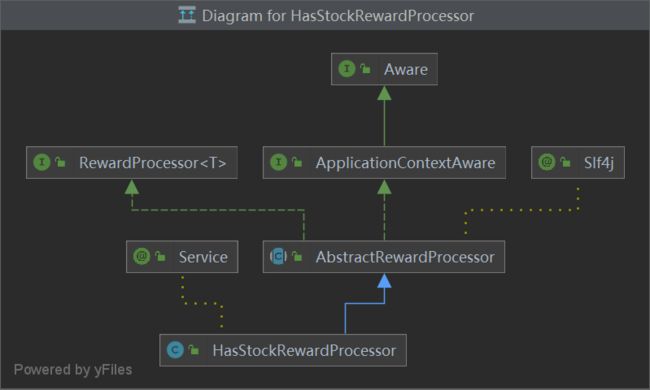
在调整库存的时候,我们需要考虑到每个奖品类型的不同,根据不同类型的奖品采取不同的措施。比如如果是一些价值高昂的奖品,我们需要通过分布式锁来确保安全性;或者比如有些商品我们需要发送相应的短信;所以我们需要采取一种具有扩展性的实现机制。
具体的实现机制可以看下方的类图,我首先定义一个奖品方法的接口(RewardProcessor),然后定义一个抽象类(AbstractRewardProcessor),抽象类中定义了模板方法,然后我们就可以根据不同的类型创建不同的处理器即可,这大大加强了我们的扩展性。
比如我们这边就创建了库存充足处理器及库存不足处理器。
接口:
public interface RewardProcessor<T> {
void doReward(RewardContext context);
}
抽象类:
@Slf4j
public abstract class AbstractRewardProcessor implements RewardProcessor<RewardContext>, ApplicationContextAware {
public static Map<Integer, RewardProcessor> rewardProcessorMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, RewardProcessor>();
@Autowired
protected RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private void beforeProcessor(RewardContext context) {
}
@Override
public void doReward(RewardContext context) {
beforeProcessor(context);
processor(context);
afterProcessor(context);
}
protected abstract void afterProcessor(RewardContext context);
/**
* 发放对应的奖品
*
* @param context
*/
protected abstract void processor(RewardContext context);
/**
* 返回当前奖品类型
*
* @return
*/
protected abstract int getAwardType();
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
rewardProcessorMap.put(LotteryConstants.PrizeTypeEnum.THANK.getValue(), (RewardProcessor) applicationContext.getBean(NoneStockRewardProcessor.class));
rewardProcessorMap.put(LotteryConstants.PrizeTypeEnum.NORMAL.getValue(), (RewardProcessor) applicationContext.getBean(HasStockRewardProcessor.class));
}
}
我们可以从抽象类中的doReward方法处开始查看,比如我们这边先查看库存充足处理器中的代码:
库存处理器执行的时候首相将Redis中对应的奖项库存减1,这时候是不需要加锁的,因为这个操作是原子性的。
当扣减后,我们根据返回的值判断商品库存是否充足,这个时候库存不足则提示未中奖或者返回一个默认商品。
最后我们还需要记得更新下数据库中的相关数据。
@Override
protected void processor(RewardContext context) {
//扣减库存(redis的更新)
Long result = redisTemplate.opsForHash().increment(context.getKey(), "validStock", -1);
//当前奖品库存不足,提示未中奖,或者返回一个兜底的奖品
if (result.intValue() < 0) {
throw new UnRewardException(ReturnCodeEnum.LOTTER_REPO_NOT_ENOUGHT.getCode(), ReturnCodeEnum.LOTTER_REPO_NOT_ENOUGHT.getMsg());
}
List<Object> propertys = Arrays.asList("id", "prizeName");
List<Object> prizes = redisTemplate.opsForHash().multiGet(context.getKey(), propertys);
context.setPrizeId(Integer.parseInt(prizes.get(0).toString()));
context.setPrizeName(prizes.get(1).toString());
//更新库存(数据库的更新)
lotteryPrizeMapper.updateValidStock(context.getPrizeId());
}
方法执行完成之后,我们需要执行afterProcessor方法:
这个地方我们是通过异步任务异步存入抽奖记录信息。
@Override
protected void afterProcessor(RewardContext context) {
asyncLotteryRecordTask.saveLotteryRecord(context.getAccountIp(), context.getLotteryItem(), context.getPrizeName());
}
在这边我们可以发现是通过Async注解,指定一个线程池,开启一个异步执行的方法。
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AsyncLotteryRecordTask {
@Autowired
LotteryRecordMapper lotteryRecordMapper;
@Async("lotteryServiceExecutor")
public void saveLotteryRecord(String accountIp, LotteryItem lotteryItem, String prizeName) {
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---saveLotteryRecord");
//存储中奖信息
LotteryRecord record = new LotteryRecord();
record.setAccountIp(accountIp);
record.setItemId(lotteryItem.getId());
record.setPrizeName(prizeName);
record.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
lotteryRecordMapper.insert(record);
}
}
创建一个线程池:相关的配置信息是我们定义在YML文件中的数据。
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ThreadPoolExecutorProperties.class)
public class ThreadPoolExecutorConfig {
@Bean(name = "lotteryServiceExecutor")
public Executor lotteryServiceExecutor(ThreadPoolExecutorProperties poolExecutorProperties) {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(poolExecutorProperties.getCorePoolSize());
executor.setMaxPoolSize(poolExecutorProperties.getMaxPoolSize());
executor.setQueueCapacity(poolExecutorProperties.getQueueCapacity());
executor.setThreadNamePrefix(poolExecutorProperties.getNamePrefix());
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
return executor;
}
}
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "async.executor.thread")
public class ThreadPoolExecutorProperties {
private int corePoolSize;
private int maxPoolSize;
private int queueCapacity;
private String namePrefix;
}
4.7 总结
以上便是整个项目的搭建,关于前端界面无非就是向后端发起请求,根据返回的奖品信息,将指针落在对应的转盘位置处,具体代码可以前往项目地址查看。希望大家可以动个小手点点赞,嘻嘻。
5. 项目地址
如果直接使用项目的话,记得修改数据库中活动的结束时间。
Redis
具体的实战项目在lottery工程中。