Matlab实现sift特征检测和两幅图像的特征点匹配(D. Lowe)
一、sift算法简介
尺度不变特征转换(Scale-invariant feature transform或SIFT)是一种电脑视觉的算法用来侦测与描述影像中的局部性特征,它在空间尺度中寻找极值点,并提取出其位置、尺度、旋转不变量,此算法由 David Lowe在1999年所发表,2004年完善总结。
其应用范围包含物体辨识、机器人地图感知与导航、影像缝合、3D模型建立、手势辨识、影像追踪和动作比对。
SIFT算法的特点有:
-
SIFT特征是图像的局部特征,其对旋转、尺度缩放、亮度变化保持不变性,对视角变化、仿射变换、噪声也保持一定程度的稳定性;
-
独特性(Distinctiveness)好,信息量丰富,适用于在海量特征数据库中进行快速、准确的匹配;
-
多量性,即使少数的几个物体也可以产生大量的SIFT特征向量;
-
高速性,经优化的SIFT匹配算法甚至可以达到实时的要求;
-
可扩展性,可以很方便的与其他形式的特征向量进行联合。
加拿大University of British Columbia 大学计算机科学系教授 David G. Lowe发表于2004年Int Journal of Computer Vision,2(60):91-110的那篇标题为“Distivtive Image Features from Scale -Invariant Keypoints" 的论文。作者在其学术网站上发表的Matlab程序代码(注意,这个程序代码的初始版本是 D. Alvaro and J.J. Guerrero, 来自Universidad de Zaragoza。)
上述代码可以很容易检索到:http://www.cs.ubc.ca/~lowe/keypoints/
二、sift算法的matlab实现
1.sift.m 检测特征点+构建特征点描述子
% [image, descriptors, locs] = sift(imageFile)
%
% This function reads an image and returns its SIFT keypoints.
% Input parameters:
% imageFile: the file name for the image.
%
% Returned:
% image: the image array in double format
% descriptors: a K-by-128 matrix, where each row gives an invariant
% descriptor for one of the K keypoints. The descriptor is a vector
% of 128 values normalized to unit length.
% locs: K-by-4 matrix, in which each row has the 4 values for a
% keypoint location (row, column, scale, orientation). The
% orientation is in the range [-PI, PI] radians.
%
% Credits: Thanks for initial version of this program to D. Alvaro and
% J.J. Guerrero, Universidad de Zaragoza (modified by D. Lowe)
function [image, descriptors, locs] = sift(imageFile)
% Load image
image = imread(imageFile);
% If you have the Image Processing Toolbox, you can uncomment the following
% lines to allow input of color images, which will be converted to grayscale.
% if isrgb(image)
% image = rgb2gray(image);
% end
[rows, cols] = size(image);
% Convert into PGM imagefile, readable by "keypoints" executable
f = fopen('tmp.pgm', 'w');
if f == -1
error('Could not create file tmp.pgm.');
end
fprintf(f, 'P5\n%d\n%d\n255\n', cols, rows);
fwrite(f, image', 'uint8');
fclose(f);
% Call keypoints executable
if isunix
command = '!./sift ';
else
command = '!siftWin32 ';
end
command = [command ' tmp.key' ];
eval(command);
% Open tmp.key and check its header
g = fopen('tmp.key', 'r');
if g == -1
error('Could not open file tmp.key.');
end
[header, count] = fscanf(g, '%d %d', [1 2]);
if count ~= 2
error('Invalid keypoint file beginning.');
end
num = header(1);
len = header(2);
if len ~= 128
error('Keypoint descriptor length invalid (should be 128).');
end
% Creates the two output matrices (use known size for efficiency)
locs = double(zeros(num, 4));
descriptors = double(zeros(num, 128));
% Parse tmp.key
for i = 1:num
[vector, count] = fscanf(g, '%f %f %f %f', [1 4]); %row col scale ori
if count ~= 4
error('Invalid keypoint file format');
end
locs(i, :) = vector(1, :);
[descrip, count] = fscanf(g, '%d', [1 len]);
if (count ~= 128)
error('Invalid keypoint file value.');
end
% Normalize each input vector to unit length
descrip = descrip / sqrt(sum(descrip.^2));
descriptors(i, :) = descrip(1, :);
end
fclose(g);
end
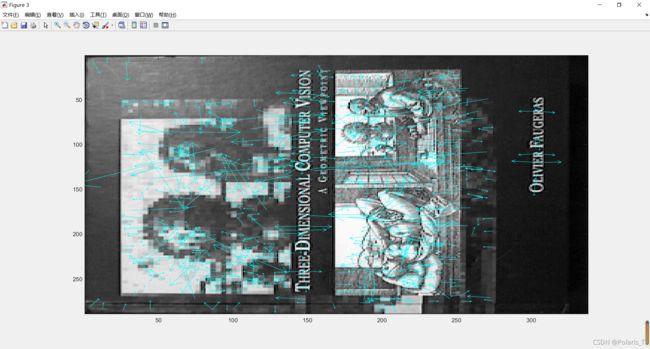
2.showkeys.m 绘制带有特征点的图像
% showkeys(image, locs)
%
% This function displays an image with SIFT keypoints overlayed.
% Input parameters:
% image: the file name for the image (grayscale)
% locs: matrix in which each row gives a keypoint location (row,
% column, scale, orientation)
function showkeys(image, locs)
disp('Drawing SIFT keypoints ...');
% Draw image with keypoints
figure('Position', [50 50 size(image,2) size(image,1)]);
colormap('gray');
imagesc(image);
hold on;
imsize = size(image);
for i = 1: size(locs,1)
% Draw an arrow, each line transformed according to keypoint parameters.
TransformLine(imsize, locs(i,:), 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
TransformLine(imsize, locs(i,:), 0.85, 0.1, 1.0, 0.0);
TransformLine(imsize, locs(i,:), 0.85, -0.1, 1.0, 0.0);
end
hold off;
% ------ Subroutine: TransformLine -------
% Draw the given line in the image, but first translate, rotate, and
% scale according to the keypoint parameters.
%
% Parameters:
% Arrays:
% imsize = [rows columns] of image
% keypoint = [subpixel_row subpixel_column scale orientation]
%
% Scalars:
% x1, y1; begining of vector
% x2, y2; ending of vector
end
function TransformLine(imsize, keypoint, x1, y1, x2, y2)
% The scaling of the unit length arrow is set to approximately the radius
% of the region used to compute the keypoint descriptor.
len = 6 * keypoint(3);
% Rotate the keypoints by 'ori' = keypoint(4)
s = sin(keypoint(4));
c = cos(keypoint(4));
% Apply transform
r1 = keypoint(1) - len * (c * y1 + s * x1);
c1 = keypoint(2) + len * (- s * y1 + c * x1);
r2 = keypoint(1) - len * (c * y2 + s * x2);
c2 = keypoint(2) + len * (- s * y2 + c * x2);
line([c1 c2], [r1 r2], 'Color', 'c');
end
3.appendimages.m 绘制两幅图像经过特征匹配后的一幅图像
% im = appendimages(image1, image2)
%
% Return a new image that appends the two images side-by-side.
function im = appendimages(image1, image2)
% Select the image with the fewest rows and fill in enough empty rows
% to make it the same height as the other image.
rows1 = size(image1,1);
rows2 = size(image2,1);
if (rows1 < rows2)
image1(rows2,1) = 0;
else
image2(rows1,1) = 0;
end
% Now append both images side-by-side.
im = [image1 image2];
end
4.match.m 读取两幅图像,分别提取它们的关键点并进行匹配
% num = match(image1, image2)
%
% This function reads two images, finds their SIFT features, and
% displays lines connecting the matched keypoints. A match is accepted
% only if its distance is less than distRatio times the distance to the
% second closest match.
% It returns the number of matches displayed.
%
% Example: match('scene.pgm','book.pgm');
function num = match(image1, image2)
% Find SIFT keypoints for each image
[im1, des1, loc1] = sift(image1);
[im2, des2, loc2] = sift(image2);
% For efficiency in Matlab, it is cheaper to compute dot products between
% unit vectors rather than Euclidean distances. Note that the ratio of
% angles (acos of dot products of unit vectors) is a close approximation
% to the ratio of Euclidean distances for small angles.
%
% distRatio: Only keep matches in which the ratio of vector angles from the
% nearest to second nearest neighbor is less than distRatio.
distRatio = 0.6;
% For each descriptor in the first image, select its match to second image.
des2t = des2'; % Precompute matrix transpose
for i = 1 : size(des1,1)
dotprods = des1(i,:) * des2t; % Computes vector of dot products
[vals,indx] = sort(acos(dotprods)); % Take inverse cosine and sort results
% Check if nearest neighbor has angle less than distRatio times 2nd.
if (vals(1) < distRatio * vals(2))
match(i) = indx(1);
else
match(i) = 0;
end
end
% Create a new image showing the two images side by side.
im3 = appendimages(im1,im2);
% Show a figure with lines joining the accepted matches.
figure('Position', [100 100 size(im3,2) size(im3,1)]);
colormap('gray');
imagesc(im3);
hold on;
cols1 = size(im1,2);
for i = 1: size(des1,1)
if (match(i) > 0)
line([loc1(i,2) loc2(match(i),2)+cols1], ...
[loc1(i,1) loc2(match(i),1)], 'Color', 'c');
end
end
hold off;
num = sum(match > 0);
fprintf('Found %d matches.\n', num);
end
四、说明
1 match.m
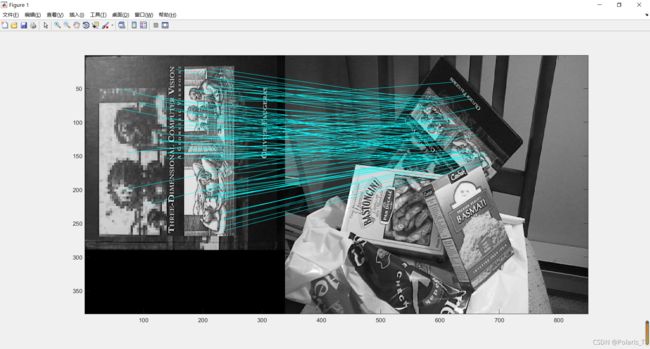
功能:该函数读入两幅(灰度)图像,找出各自的 SIFT 特征, 并显示两连接两幅图像中被匹配的特征点(关键特征点(the matched keypoints)直线(将对应特征点进行连接)。判断匹配的准则是匹配距离小于distRatio倍于下一个最近匹配的距离( A match is accepted only if its distance is less than distRatio times the distance to the second closest match.
该程序返回显示的匹配对的数量。( It returns the number of matches displayed.)
调用实例: match(‘desk.jpg’,‘book.jpg’);
( 测试一个含有一本书的桌面的图像和一本书的图像之间特征匹配)
注意:
(1)图像为灰度图像,如果是彩色图像,应该在调用前利用rgb2gray转换为灰度图像。
(2)参数distRatio 为控制匹配点数量的系数,这里取 0.6,该参数决定了匹配点的数量,在Match.m文件中调整该参数,获得最合适的匹配点数量。
2.sift.m:SIFT算法的核心
具体原理详见David G. Lowe发表于2004年Int Journal of Computer Vision,2(60):91-110的那篇标题为“Distivtive Image Features from Scale -Invariant Keypoints" 的论文
功能:该函数读入灰度图像,返回SIFT 特征关键点( SIFT keypoints.)
调用方式:[image, descriptors, locs] = sift(imageFile)
输入参数:imageFile: 图像文件名
返回参数:image: 是具有double format格式的图像矩阵,descriptors: 一个 K-by-128的矩阵x, 其中每行是针对找到的K个关键特征点(the K keypoints)的不变量描述子,这个描述子(descriptor)是一个拥有128个数值并归一化为单位长度向量;locs: 是K-by-4 矩阵, 其中的每一行具有四个数值,表示关键点位置信息 (在图像中的行坐标,列坐标(row, column) ,注意,一般图像的左上角为坐标原点);尺度scale,高斯尺度空间的参数,其中该参数也决定了frame(结构)确定的图像disk的大小;最后一个参数是方向orientation),方向参数的范围是[-PI, PI] 单位为弧度。
3.appendimages.m
该函数创建一个新的图像分别包含两个匹配的图像和他们之间的匹配对的连接直线。
4.其余详细解释可参考博文https://www.cnblogs.com/xfzhang/articles/1878089.html