基于python的简易神经网络算法
BP神经网络:
BP(Back-propagation,反向传播)神经网络是最传统的神经网络。也就是使用了Back-propagation算法的神经网络。
BP神经网络通过反向传播的误差,在模拟过程中收集系统所产生的误差,并且返回这些误差到输出值,之后用这些误差来调整神经元的权重,这样生成一个可以模拟出原始问题的人工神经网络系统。
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data_x = pd.read_csv("X_data.csv", header=None)
data_x.insert(loc=0, column=-1, value=1)
data_x = np.array(data_x)
data_y = pd.read_csv("y_label.csv", header=None).values
data_y = data_y.reshape(data_y.shape[0])
theta1 = np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=(401, 25))
theta2 = np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=(26, 10))
# theta1 = np.zeros((401, 25))
# theta2 = np.zeros((26, 10))
thetas = [theta1, theta2]
def guiyihua(x):
return (x - np.min(x)) / (np.max(x) - np.min(x))
def sigmoid(x, w):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-np.dot(x, w)))
def sigmoid_grad(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(x)) * (1 - 1 / (1 + np.exp(x)))
# 计算梯度函数
def grad(x, y, w):
return -np.dot(x.T, y - sigmoid(x, w))
# 前向传播
def forword(x, ws, l):
a = []
z = []
for i in range(0, l):
if i == 0:
a.append(x)
else:
a.append(np.insert(sigmoid(a[i - 1], ws[i - 1]), 0, 1, axis=1))
z.append(np.dot(a[i], ws[i]))
z[l - 1] = (np.dot(a[l - 1], ws[l - 1]))
a.append(sigmoid(a[l - 1], ws[l - 1]))
return a, z
# 后向传播,返回各theta梯度
def back(a, z, y, l):
gamas = []
y = pd.get_dummies(y)
gamas.append(a[l] - y)
for i in range(1, l):
gama = (np.dot(gamas[i - 1], thetas[1][1:, :].T)) * sigmoid_grad(z[i - 1])
gamas.append(gama)
# 数组重新排序
newgamas = []
for i in range(len(gamas) - 1, -1, -1):
newgamas.append(gamas[i])
# 计算梯度
grads = []
for i in range(len(thetas)):
grad = np.dot(a[i].T, newgamas[i])
grads.append(grad)
return grads
def pre(x, ws, l):
a, z = forword(x, ws, l)
pred = np.argmax(a[l], axis=1) + 1
print(pred)
print('准确率:', np.sum(pred == data_y) / len(data_y) * 100, '%')
def train(x, y, l):
echops = 50000 # 训练次数
alpha = 1e-3 # 学习率
acc = 1 # 退出精度
for echop in range(echops):
a, z = forword(x, thetas, l)
grads = back(a, z, y, l)
# print("梯度最大值:", maxoflist(grads)) # 查看所有层梯度的最大值
if maxoflist(grads) <= acc:
break
for i in range(len(thetas)):
thetas[i] -= alpha * grads[i]
print("训练次数:", echop)
def maxoflist(list):
max_ = np.max(np.abs(list[0]))
for i in range(len(list)):
if np.max(np.abs(list[i])) > max_:
max_ = np.max(np.abs(list[i]))
return max_
theta1 = guiyihua(theta1)
theta2 = guiyihua(theta2)
l = 2
train(data_x, data_y, l)
pre(data_x, thetas, l)
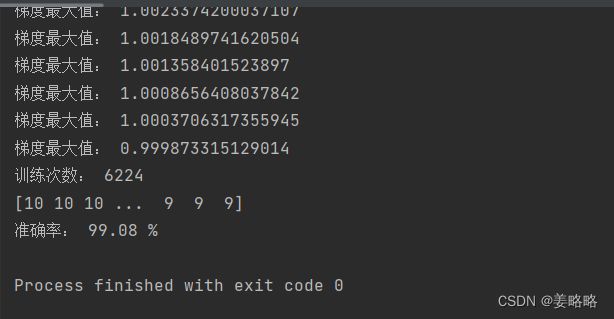
结果:
可以看到训练后的拥有两层神经网络的预测准确率已经达到了99.08%