作业8:RNN - 简单循环网络
目录
- 神经网络与深度学习作业8:RNN - 简单循环网络
-
- 1. 使用Numpy实现SRN
- 2. 在1的基础上,增加激活函数tanh
- 3. 分别使用nn.RNNCell、nn.RNN实现SRN
- 4. 分析“二进制加法” 源代码
- 5. 实现“Character-Level Language Models”源代码
- 7. “编码器-解码器”的简单实现
神经网络与深度学习作业8:RNN - 简单循环网络
简单循环网络 ( Simple Recurrent Network , SRN) 只有一个隐藏层的神经网络 .
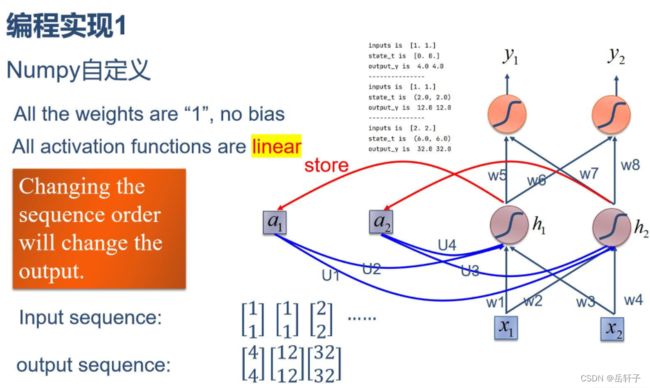
1. 使用Numpy实现SRN
import numpy as np
inputs = np.array([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.],
[2., 2.]]) # 初始化输入序列
print('inputs is ', inputs)
state_t = np.zeros(2, ) # 初始化存储器
print('state_t is ', state_t)
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.
U1, U2, U3, U4 = 1., 1., 1., 1.
print('--------------------------------------')
for input_t in inputs:
print('inputs is ', input_t)
print('state_t is ', state_t)
in_h1 = np.dot([w1, w3], input_t) + np.dot([U2, U4], state_t)
in_h2 = np.dot([w2, w4], input_t) + np.dot([U1, U3], state_t)
state_t = in_h1, in_h2
output_y1 = np.dot([w5, w7], [in_h1, in_h2])
output_y2 = np.dot([w6, w8], [in_h1, in_h2])
print('output_y is ', output_y1, output_y2)
print('---------------')
运行结果:
inputs is [[1. 1.]
[1. 1.]
[2. 2.]]
state_t is [0. 0.]
--------------------------------------
inputs is [1. 1.]
state_t is [0. 0.]
output_y is 4.0 4.0
---------------
inputs is [1. 1.]
state_t is (2.0, 2.0)
output_y is 12.0 12.0
---------------
inputs is [2. 2.]
state_t is (6.0, 6.0)
output_y is 32.0 32.0
---------------
2. 在1的基础上,增加激活函数tanh
import numpy as np
inputs = np.array([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.],
[2., 2.]]) # 初始化输入序列
print('inputs is ', inputs)
state_t = np.zeros(2, ) # 初始化存储器
print('state_t is ', state_t)
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.
U1, U2, U3, U4 = 1., 1., 1., 1.
print('--------------------------------------')
for input_t in inputs:
print('inputs is ', input_t)
print('state_t is ', state_t)
in_h1 = np.tanh(np.dot([w1, w3], input_t) + np.dot([U2, U4], state_t))
in_h2 = np.tanh(np.dot([w2, w4], input_t) + np.dot([U1, U3], state_t))
state_t = in_h1, in_h2
output_y1 = np.dot([w5, w7], [in_h1, in_h2])
output_y2 = np.dot([w6, w8], [in_h1, in_h2])
print('output_y is ', output_y1, output_y2)
print('---------------')
运行结果:
inputs is [[1. 1.]
[1. 1.]
[2. 2.]]
state_t is [0. 0.]
--------------------------------------
inputs is [1. 1.]
state_t is [0. 0.]
output_y is 1.9280551601516338 1.9280551601516338
---------------
inputs is [1. 1.]
state_t is (0.9640275800758169, 0.9640275800758169)
output_y is 1.9984510891336251 1.9984510891336251
---------------
inputs is [2. 2.]
state_t is (0.9992255445668126, 0.9992255445668126)
output_y is 1.9999753470497836 1.9999753470497836
---------------
3. 分别使用nn.RNNCell、nn.RNN实现SRN
import torch
batch_size = 1
seq_len = 3 # 序列长度
input_size = 2 # 输入序列维度
hidden_size = 2 # 隐藏层维度
output_size = 2 # 输出层维度
# RNNCell
cell = torch.nn.RNNCell(input_size=input_size, hidden_size=hidden_size)
# 初始化参数 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/342012463
for name, param in cell.named_parameters():
if name.startswith("weight"):
torch.nn.init.ones_(param)
else:
torch.nn.init.zeros_(param)
# 线性层
liner = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
liner.weight.data = torch.Tensor([[1, 1], [1, 1]])
liner.bias.data = torch.Tensor([0.0])
seq = torch.Tensor([[[1, 1]],
[[1, 1]],
[[2, 2]]])
hidden = torch.zeros(batch_size, hidden_size)
output = torch.zeros(batch_size, output_size)
for idx, input in enumerate(seq):
print('=' * 20, idx, '=' * 20)
print('Input :', input)
print('hidden :', hidden)
hidden = cell(input, hidden)
output = liner(hidden)
print('output :', output)
运行结果:
==================== 0 ====================
Input : tensor([[1., 1.]])
hidden : tensor([[0., 0.]])
output : tensor([[1.9281, 1.9281]], grad_fn=)
==================== 1 ====================
Input : tensor([[1., 1.]])
hidden : tensor([[0.9640, 0.9640]], grad_fn=)
output : tensor([[1.9985, 1.9985]], grad_fn=)
==================== 2 ====================
Input : tensor([[2., 2.]])
hidden : tensor([[0.9992, 0.9992]], grad_fn=)
output : tensor([[2.0000, 2.0000]], grad_fn=)
使用torch.nn.RNN:
import torch
batch_size = 1
seq_len = 3
input_size = 2
hidden_size = 2
num_layers = 1
output_size = 2
cell = torch.nn.RNN(input_size=input_size, hidden_size=hidden_size, num_layers=num_layers)
for name, param in cell.named_parameters(): # 初始化参数
if name.startswith("weight"):
torch.nn.init.ones_(param)
else:
torch.nn.init.zeros_(param)
# 线性层
liner = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
liner.weight.data = torch.Tensor([[1, 1], [1, 1]])
liner.bias.data = torch.Tensor([0.0])
inputs = torch.Tensor([[[1, 1]],
[[1, 1]],
[[2, 2]]])
hidden = torch.zeros(num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size)
out, hidden = cell(inputs, hidden)
print('Input :', inputs[0])
print('hidden:', 0, 0)
print('Output:', liner(out[0]))
print('--------------------------------------')
print('Input :', inputs[1])
print('hidden:', out[0])
print('Output:', liner(out[1]))
print('--------------------------------------')
print('Input :', inputs[2])
print('hidden:', out[1])
print('Output:', liner(out[2]))
运行结果:
Input : tensor([[1., 1.]])
hidden: 0 0
Output: tensor([[1.9281, 1.9281]], grad_fn=)
--------------------------------------
Input : tensor([[1., 1.]])
hidden: tensor([[0.9640, 0.9640]], grad_fn=)
Output: tensor([[1.9985, 1.9985]], grad_fn=)
--------------------------------------
Input : tensor([[2., 2.]])
hidden: tensor([[0.9992, 0.9992]], grad_fn=)
Output: tensor([[2.0000, 2.0000]], grad_fn=)
4. 分析“二进制加法” 源代码
import copy, numpy as np
np.random.seed(0)
#定义sigmoid函数
def sigmoid(x):
output = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
return output
#定义sigmoid导数
def sigmoid_output_to_derivative(output):
return output * (1 - output)
#训练数据的产生
int2binary = {}
binary_dim = 8 #定义二进制位的长度
largest_number = pow(2, binary_dim)#定义数据的最大值
binary = np.unpackbits(
np.array([range(largest_number)], dtype=np.uint8).T, axis=1)#函数产生包装所有符合的二进制序列
for i in range(largest_number):#遍历从0-256的值
int2binary[i] = binary[i]#对于每个整型值赋值二进制序列
# print(int2binary)
# 产生输入变量
alpha = 0.1 #设置更新速度(学习率)
input_dim = 2 #输入维度大小
hidden_dim = 16 #隐藏层维度大小
output_dim = 1 #输出维度大小
# 随机产生网络权重
synapse_0 = 2 * np.random.random((input_dim, hidden_dim)) - 1
synapse_1 = 2 * np.random.random((hidden_dim, output_dim)) - 1
synapse_h = 2 * np.random.random((hidden_dim, hidden_dim)) - 1
#梯度初始值设置为0
synapse_0_update = np.zeros_like(synapse_0)
synapse_1_update = np.zeros_like(synapse_1)
synapse_h_update = np.zeros_like(synapse_h)
#训练逻辑
for j in range(10000):
# 产生一个简单的加法问题
a_int = np.random.randint(largest_number / 2) # 产生一个加法操作数
a = int2binary[a_int] # 找到二进制序列编码
b_int = np.random.randint(largest_number / 2) # 产生另一个加法操作数
b = int2binary[b_int] # 找到二进制序列编码
# 计算正确值(标签值)
c_int = a_int + b_int
c = int2binary[c_int] # 得到正确的结果序列
# 设置存储器,存储中间值(记忆功能)
d = np.zeros_like(c)
overallError = 0 #设置误差
layer_2_deltas = list()
layer_1_values = list()
layer_1_values.append(np.zeros(hidden_dim))
# moving along the positions in the binary encoding
for position in range(binary_dim):
# 产生输入和输出
X = np.array([[a[binary_dim - position - 1], b[binary_dim - position - 1]]])
y = np.array([[c[binary_dim - position - 1]]]).T
# 隐藏层计算
layer_1 = sigmoid(np.dot(X, synapse_0) + np.dot(layer_1_values[-1], synapse_h))
# 输出层
layer_2 = sigmoid(np.dot(layer_1, synapse_1))
# 计算差别
layer_2_error = y - layer_2
#计算每个梯度
layer_2_deltas.append((layer_2_error) * sigmoid_output_to_derivative(layer_2))
#计算所有损失
overallError += np.abs(layer_2_error[0])
# 编码记忆的中间值
d[binary_dim - position - 1] = np.round(layer_2[0][0])
# 拷贝副本
layer_1_values.append(copy.deepcopy(layer_1))
future_layer_1_delta = np.zeros(hidden_dim)
for position in range(binary_dim):
X = np.array([[a[position], b[position]]])
layer_1 = layer_1_values[-position - 1]
prev_layer_1 = layer_1_values[-position - 2]
# 输出层误差
layer_2_delta = layer_2_deltas[-position - 1]
# 隐藏层误差
layer_1_delta = (future_layer_1_delta.dot(synapse_h.T) + layer_2_delta.dot(
synapse_1.T)) * sigmoid_output_to_derivative(layer_1)
# 计算梯度
synapse_1_update += np.atleast_2d(layer_1).T.dot(layer_2_delta)
synapse_h_update += np.atleast_2d(prev_layer_1).T.dot(layer_1_delta)
synapse_0_update += X.T.dot(layer_1_delta)
future_layer_1_delta = layer_1_delta
#梯度下降
synapse_0 += synapse_0_update * alpha
synapse_1 += synapse_1_update * alpha
synapse_h += synapse_h_update * alpha
#重新初始化
synapse_0_update *= 0
synapse_1_update *= 0
synapse_h_update *= 0
# 打印训练过程
if (j % 1000 == 0):
print("Error:" + str(overallError))
print("Pred:" + str(d))
print("True:" + str(c))
out = 0
for index, x in enumerate(reversed(d)):
out += x * pow(2, index)
print(str(a_int) + " + " + str(b_int) + " = " + str(out))
print("------------")
运行结果:
------------
Error:[3.72191702]
Pred:[1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1]
True:[0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1]
4 + 73 = 223
------------
Error:[3.5852713]
Pred:[0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0]
True:[0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0]
71 + 11 = 8
------------
Error:[2.53352328]
Pred:[1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0]
True:[1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0]
81 + 113 = 162
------------
Error:[0.57691441]
Pred:[0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1]
True:[0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1]
81 + 0 = 81
------------
Error:[1.42589952]
Pred:[1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1]
True:[1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1]
4 + 125 = 129
------------
Error:[0.47477457]
Pred:[0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0]
True:[0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0]
39 + 17 = 56
------------
Error:[0.21595037]
Pred:[0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0]
True:[0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0]
11 + 3 = 14
------------
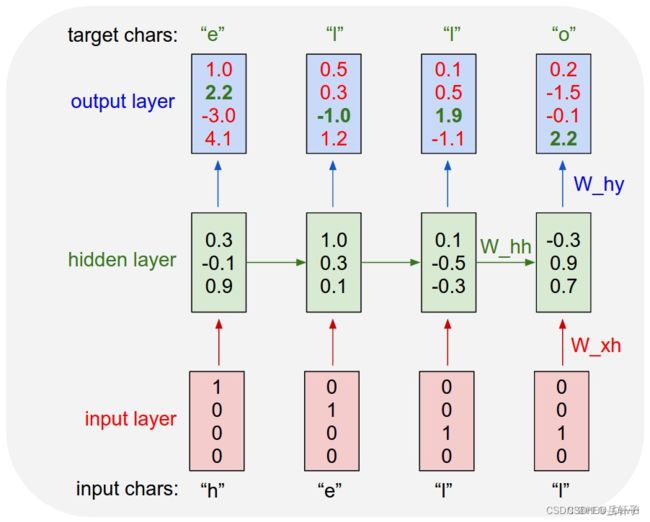
5. 实现“Character-Level Language Models”源代码
import torch
# 使用RNN 有嵌入层和线性层
num_class = 4 # 4个类别
input_size = 4 # 输入维度是4
hidden_size = 8 # 隐层是8个维度
embedding_size = 10 # 嵌入到10维空间
batch_size = 1
num_layers = 2 # 两层的RNN
seq_len = 5 # 序列长度是5
# 准备数据
idx2char = ['e','h','l','o'] # 字典
x_data = [[1,0,2,2,3]] # hello 维度(batch,seqlen)
y_data = [3,1,2,3,2] # ohlol 维度 (batch*seqlen)
inputs = torch.LongTensor(x_data)
labels = torch.LongTensor(y_data)
# 构造模型
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.emb = torch.nn.Embedding(input_size,embedding_size)
self.rnn = torch.nn.RNN(input_size=embedding_size,hidden_size=hidden_size,num_layers=num_layers,batch_first=True)
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size,num_class)
def forward(self,x):
hidden = torch.zeros(num_layers,x.size(0),hidden_size)
x = self.emb(x) # (batch,seqlen,embeddingsize)
x,_ = self.rnn(x,hidden)
x = self.fc(x)
return x.view(-1,num_class) # 转变维2维矩阵,seq*batchsize*numclass -》((seq*batchsize),numclass)
model = Model()
# 损失函数和优化器
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr=0.05) # lr = 0.01学习的太慢
# 训练
for epoch in range(15):
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(inputs) # inputs是(seq,Batchsize,Inputsize) outputs是(seq,Batchsize,Hiddensize)
loss = criterion(outputs,labels) # labels是(seq,batchsize,1)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
_,idx = outputs.max(dim=1)
idx = idx.data.numpy()
print("Epoch {}/15 loss={:.3f}".format(epoch+1,loss.item()))
运行结果:
Epoch 1/15 loss=1.354
Epoch 2/15 loss=1.042
Epoch 3/15 loss=0.808
Epoch 4/15 loss=0.574
Epoch 5/15 loss=0.377
Epoch 6/15 loss=0.236
Epoch 7/15 loss=0.147
Epoch 8/15 loss=0.095
Epoch 9/15 loss=0.062
Epoch 10/15 loss=0.041
Epoch 11/15 loss=0.027
Epoch 12/15 loss=0.019
Epoch 13/15 loss=0.013
Epoch 14/15 loss=0.010
Epoch 15/15 loss=0.007
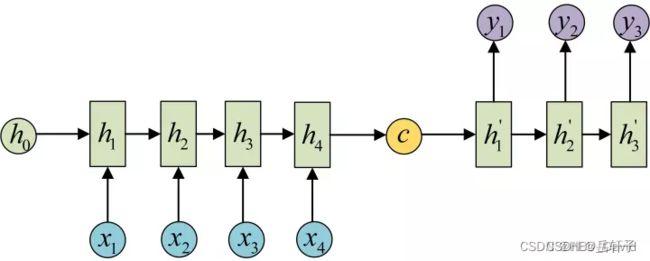
7. “编码器-解码器”的简单实现
import torch
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.data as Data
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
letter = [c for c in 'SE?abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz']
letter2idx = {n: i for i, n in enumerate(letter)}
seq_data = [['man', 'women'], ['black', 'white'], ['king', 'queen'], ['girl', 'boy'], ['up', 'down'], ['high', 'low']]
# Seq2Seq Parameter
n_step = max([max(len(i), len(j)) for i, j in seq_data]) # max_len(=5)
n_hidden = 128
n_class = len(letter2idx) # classfication problem
batch_size = 3
def make_data(seq_data):
enc_input_all, dec_input_all, dec_output_all = [], [], []
for seq in seq_data:
for i in range(2):
seq[i] = seq[i] + '?' * (n_step - len(seq[i])) # 'man??', 'women'
enc_input = [letter2idx[n] for n in (seq[0] + 'E')] # ['m', 'a', 'n', '?', '?', 'E']
dec_input = [letter2idx[n] for n in ('S' + seq[1])] # ['S', 'w', 'o', 'm', 'e', 'n']
dec_output = [letter2idx[n] for n in (seq[1] + 'E')] # ['w', 'o', 'm', 'e', 'n', 'E']
enc_input_all.append(np.eye(n_class)[enc_input])
dec_input_all.append(np.eye(n_class)[dec_input])
dec_output_all.append(dec_output) # not one-hot
# make tensor
return torch.Tensor(enc_input_all), torch.Tensor(dec_input_all), torch.LongTensor(dec_output_all)
enc_input_all, dec_input_all, dec_output_all = make_data(seq_data)
class TranslateDataSet(Data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, enc_input_all, dec_input_all, dec_output_all):
self.enc_input_all = enc_input_all
self.dec_input_all = dec_input_all
self.dec_output_all = dec_output_all
def __len__(self): # return dataset size
return len(self.enc_input_all)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return self.enc_input_all[idx], self.dec_input_all[idx], self.dec_output_all[idx]
loader = Data.DataLoader(TranslateDataSet(enc_input_all, dec_input_all, dec_output_all), batch_size, True)
# Model
class Seq2Seq(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Seq2Seq, self).__init__()
self.encoder = nn.RNN(input_size=n_class, hidden_size=n_hidden, dropout=0.5) # encoder
self.decoder = nn.RNN(input_size=n_class, hidden_size=n_hidden, dropout=0.5) # decoder
self.fc = nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_class)
def forward(self, enc_input, enc_hidden, dec_input):
enc_input = enc_input.transpose(0, 1) # enc_input: [n_step+1, batch_size, n_class]
dec_input = dec_input.transpose(0, 1) # dec_input: [n_step+1, batch_size, n_class]
# h_t : [num_layers(=1) * num_directions(=1), batch_size, n_hidden]
_, h_t = self.encoder(enc_input, enc_hidden)
# outputs : [n_step+1, batch_size, num_directions(=1) * n_hidden(=128)]
outputs, _ = self.decoder(dec_input, h_t)
model = self.fc(outputs) # model : [n_step+1, batch_size, n_class]
return model
model = Seq2Seq().to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
for epoch in range(5000):
for enc_input_batch, dec_input_batch, dec_output_batch in loader:
# make hidden shape [num_layers * num_directions, batch_size, n_hidden]
h_0 = torch.zeros(1, batch_size, n_hidden).to(device)
(enc_input_batch, dec_intput_batch, dec_output_batch) = (
enc_input_batch.to(device), dec_input_batch.to(device), dec_output_batch.to(device))
# enc_input_batch : [batch_size, n_step+1, n_class]
# dec_intput_batch : [batch_size, n_step+1, n_class]
# dec_output_batch : [batch_size, n_step+1], not one-hot
pred = model(enc_input_batch, h_0, dec_intput_batch)
# pred : [n_step+1, batch_size, n_class]
pred = pred.transpose(0, 1) # [batch_size, n_step+1(=6), n_class]
loss = 0
for i in range(len(dec_output_batch)):
# pred[i] : [n_step+1, n_class]
# dec_output_batch[i] : [n_step+1]
loss += criterion(pred[i], dec_output_batch[i])
if (epoch + 1) % 1000 == 0:
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =', '{:.6f}'.format(loss))
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# Test
def translate(word):
enc_input, dec_input, _ = make_data([[word, '?' * n_step]])
enc_input, dec_input = enc_input.to(device), dec_input.to(device)
# make hidden shape [num_layers * num_directions, batch_size, n_hidden]
hidden = torch.zeros(1, 1, n_hidden).to(device)
output = model(enc_input, hidden, dec_input)
# output : [n_step+1, batch_size, n_class]
predict = output.data.max(2, keepdim=True)[1] # select n_class dimension
decoded = [letter[i] for i in predict]
translated = ''.join(decoded[:decoded.index('E')])
return translated.replace('?', '')
print('test')
print('man ->', translate('man'))
print('mans ->', translate('mans'))
print('king ->', translate('king'))
print('black ->', translate('black'))
print('up ->', translate('up'))
print('old ->', translate('old'))
print('high ->', translate('high'))
运行结果:
Epoch: 1000 cost = 0.002239
Epoch: 1000 cost = 0.002386
Epoch: 2000 cost = 0.000498
Epoch: 2000 cost = 0.000489
Epoch: 3000 cost = 0.000148
Epoch: 3000 cost = 0.000156
Epoch: 4000 cost = 0.000053
Epoch: 4000 cost = 0.000050
Epoch: 5000 cost = 0.000018
Epoch: 5000 cost = 0.000018
test
man -> women
mans -> women
king -> queen
black -> white
up -> down
old -> white
high -> low