openvino推理yolov5,onnx和IR和pytorch对比
本文使用openvino对onnx和IR进行推理并比较推理速度
环境要求和参考链接
环境安装好
onnx==1.9.0
onnxruntime==1.8.0
protobuf==3.19.4
openvino-dev==2022.1.0
参考
文件夹结构
giihub上下载YOLOv5的官方project,以及YOLOv5s.pt权重文件
使用export.py可导出onnx和IR文件
导出onnx文件命令
python export.py --weights yolov5s.pt --include onnx
导出IR文件命令
python export.py --weights yolov5s.pt --include openvino
具体代码内容
在yolov5文件夹下新建py文件
1、导入需要的库
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
from PIL import Image
from openvino.runtime import Core
from utils.augmentations import letterbox
from utils.general import scale_coords, non_max_suppression
from draw_box_utils import draw_objs
import time
from models.experimental import attempt_load
2、一些路径
coco80_names = ['person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light',
'fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee',
'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard',
'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple',
'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch',
'potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard',
'cell phone', 'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase',
'scissors', 'teddy bear', 'hair drier', 'toothbrush']
weights = './yolov5s.pt'
onnx_path = './yolov5s.onnx'
img_path = "./data/street.jpg"
ir_path = './yolov5s_openvino_model/yolov5s.xml'
num_images = 20
3、图像预处理函数
# 图像预处理
def preprocess():
img_size = (640, 640) # h, w
origin_img = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread(img_path), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
reshape_img, ratio, pad = letterbox(origin_img/255, img_size, auto=False)
processed_img = np.expand_dims(np.transpose(reshape_img, [2, 0, 1]), 0).astype(np.float32)
return processed_img,reshape_img,origin_img,ratio,pad
4、预测结果后处理函数
# 后处理
def post_process(result,reshape_img,origin_img,ratio,pad,save_name):
result = non_max_suppression(torch.Tensor(result))[0]
boxes = result[:, :4].numpy() # 坐标
scores = result[:, 4].numpy() # 置信度
cls = result[:, 5].numpy().astype(int)
boxes = scale_coords(reshape_img.shape, boxes, origin_img.shape, (ratio, pad))
draw_img = draw_objs(Image.fromarray(origin_img),
boxes,
cls,
scores,
category_index=dict([(str(i), v) for i, v in enumerate(coco80_names)]))
draw_img.save(save_name)
5、使用onnx进行推理
# onnx模型推理
def onnx_infer(input_img):
ie = Core()
compiled_model_onnx = ie.compile_model(model=onnx_path, device_name='CPU')
output_layer_onnx = compiled_model_onnx.output(0)
# Run inference on the input image
res_onnx = compiled_model_onnx([input_img])[output_layer_onnx]
return res_onnx,compiled_model_onnx
# onnx推理20张图所用时间
def onnx_20(input_img,compiled_model_onnx):
start = time.perf_counter()
for _ in range(num_images):
compiled_model_onnx([input_img])
end = time.perf_counter()
time_onnx = end - start
print(
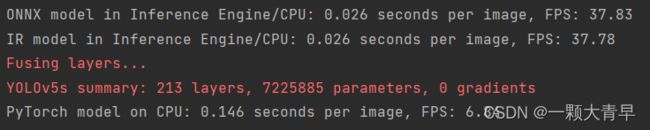
f"ONNX model in Inference Engine/CPU: {time_onnx / num_images:.3f} "
f"seconds per image, FPS: {num_images / time_onnx:.2f}"
)```
#### 6、使用IR进行推理
```python
# 用IR模型推理
def IR_infer(input_img):
ie = Core()
model_ir = ie.read_model(model=ir_path)
compiled_model_ir = ie.compile_model(model=model_ir, device_name="CPU")
# Get input and output layers
output_layer_ir = compiled_model_ir.output(0)
# Run inference on the input image
res_ir = compiled_model_ir([input_img])[output_layer_ir]
return res_ir,compiled_model_ir
# IR推理20张图所用时间
def IR_20(input_img,compiled_model_ir):
start = time.perf_counter()
for _ in range(num_images):
compiled_model_ir([input_img])
end = time.perf_counter()
time_ir = end - start
print(
f"IR model in Inference Engine/CPU: {time_ir / num_images:.3f} "
f"seconds per image, FPS: {num_images / time_ir:.2f}"
)
7、使用pytorch模型推理时间
#使用pytorch模型推理
def pytorch_20(input_img):
model = attempt_load(weights, device='cpu', inplace=True, fuse=True)
with torch.no_grad():
start = time.perf_counter()
for _ in range(num_images):
model(torch.as_tensor(input_img).float())
end = time.perf_counter()
time_torch = end - start
print(
f"PyTorch model on CPU: {time_torch / num_images:.3f} seconds per image, "
f"FPS: {num_images / time_torch:.2f}"
)
8、主函数
if __name__ == '__main__':
input_img,reshape_img,origin_img,ratio,pad = preprocess()
res_onnx, compiled_model_onnx = onnx_infer(input_img)
res_ir,compiled_model_ir = IR_infer(input_img)
onnx_20(input_img, compiled_model_onnx)
IR_20(input_img,compiled_model_ir)
pytorch_20(input_img)
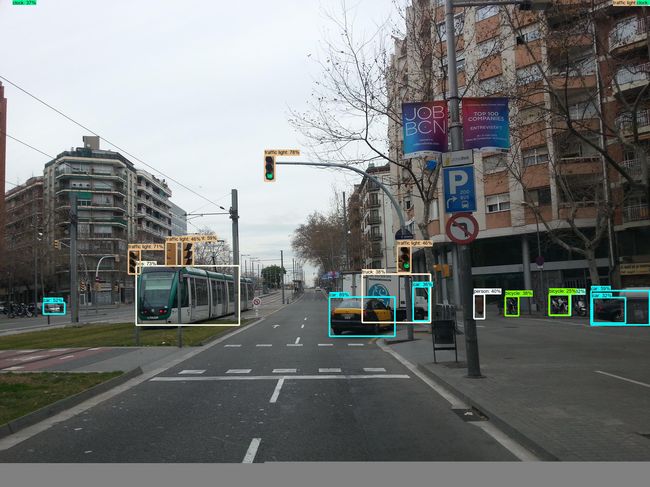
post_process(res_onnx,reshape_img,origin_img,ratio,pad,'predict_onnx.jpg')
post_process(res_ir, reshape_img, origin_img, ratio, pad, 'predict_ir.jpg')