Python中进度条tqdm包使用方法及特性
1、引言
我们在使用python编写程序的时候,有的程序需要执行的时间很长,这时候我们希望能够为程序加上一个进度条,来实时显示程序的运行进度。众所周知,python中的tqdm包可以帮助我们为任何具有循环迭代过程的代码逻辑添加进度条,从而帮助我们感知代码运行的过程。
2、功能介绍
2.1 安装方法:
pip install tqdm
2.2 使用方法:
2.2.1 迭代对象处理
tqdm(list)方法可以传入任意一种list,比如数组
from tqdm import tqdm
for i in tqdm(range(1000)):
#do something
pass
或者string的数组
for char in tqdm(["a", "b", "c", "d"]):
#do something
pass
2.2.2 使用方法二: trange
trange(i) 是 tqdm(range(i)) 的简单写法
from tqdm import trange
for i in trange(100):
#do something
pass
2.2.3 手动方法
在for循环外部初始化tqdm,可以打印其他信息
bar = tqdm(["a", "b", "c", "d"])
for char in pbar:
pbar.set_description("Processing %s" % char)
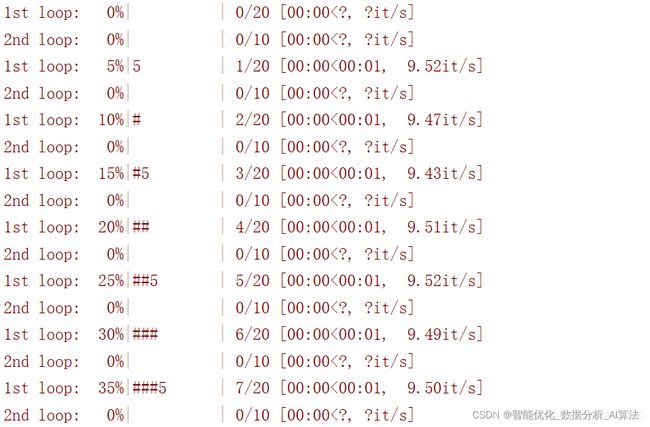
2.2.4 多循环进度条
通过tqdm也可以很简单的实现嵌套循环进度条的展示
from tqdm import tqdm
import time
for i in tqdm(range(20), ascii=True,desc="1st loop"):
for j in tqdm(range(10), ascii=True,desc="2nd loop"):
time.sleep(0.01)
2.2.5 多进程进度条
from time import sleep
from tqdm import trange, tqdm
from multiprocessing import Pool, freeze_support, RLock
L = list(range(9))
def progresser(n):
interval = 0.001 / (n + 2)
total = 5000
text = "#{}, est. {:<04.2}s".format(n, interval * total)
for i in trange(total, desc=text, position=n,ascii=True):
sleep(interval)
if __name__ == '__main__':
freeze_support() # for Windows support
p = Pool(len(L),
# again, for Windows support
initializer=tqdm.set_lock, initargs=(RLock(),))
p.map(progresser, L)
print("\n" * (len(L) - 2))
2.2.6 pandas中使用tqdm
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from tqdm import tqdm
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(0, 100, (100000, 6)))
tqdm.pandas(desc="my bar!")
df.progress_apply(lambda x: x**2)
2.2.7 递归使用进度条
from tqdm import tqdm
import os.path
def find_files_recursively(path, show_progress=True):
files = []
# total=1 assumes `path` is a file
t = tqdm(total=1, unit="file", disable=not show_progress)
if not os.path.exists(path):
raise IOError("Cannot find:" + path)
def append_found_file(f):
files.append(f)
t.update()
def list_found_dir(path):
"""returns os.listdir(path) assuming os.path.isdir(path)"""
try:
listing = os.listdir(path)
except:
return []
# subtract 1 since a "file" we found was actually this directory
t.total += len(listing) - 1
# fancy way to give info without forcing a refresh
t.set_postfix(dir=path[-10:], refresh=False)
t.update(0) # may trigger a refresh
return listing
def recursively_search(path):
if os.path.isdir(path):
for f in list_found_dir(path):
recursively_search(os.path.join(path, f))
else:
append_found_file(path)
recursively_search(path)
t.set_postfix(dir=path)
t.close()
return files
find_files_recursively("E:/")
3.特性介绍
3.1 autonotebook自动切换进度条风格
tqdm包是python中可以用于在终端或者jupyter notebook中显示进度条的第三方包。在终端中使用,我们可以通过from tqdm import tqdm,而在jupyter notebook中呢可以用rom tqdm.notebook import tqdm 来导入。
而tqdm最近几个版本中引入了实验性质的新特性,使得我们只需要统一通过from tqdm.autonotebook import tqdm导入tqdm,就可以自适应检测不同的运行环境从而自动控制显示.
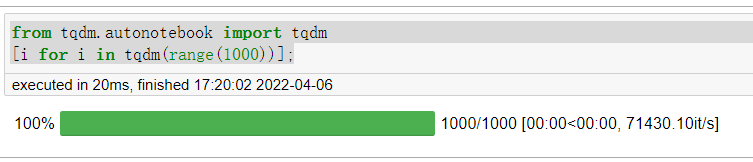
from tqdm.autonotebook import tqdm
[i for i in tqdm(range(1000))];
3.2 延迟渲染进度条
有时候我们希望当循环过程很快就执行完时,可以不打印进度条,毕竟进度条的主要目的是监控长时间运行过程,这时我们就可以给tqdm()添加参数delay来设置延时的秒数,当循环过程实际运行时长低于delay则无需打印多余的迭代过程:

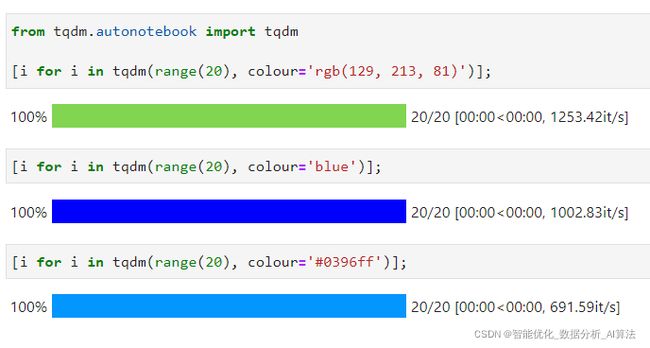
3.3 自定义进度条色彩
通过为tqdm()设置参数colour,可以传入多种常见色彩格式值,这在jupyter类编辑器中效果尤为明显:
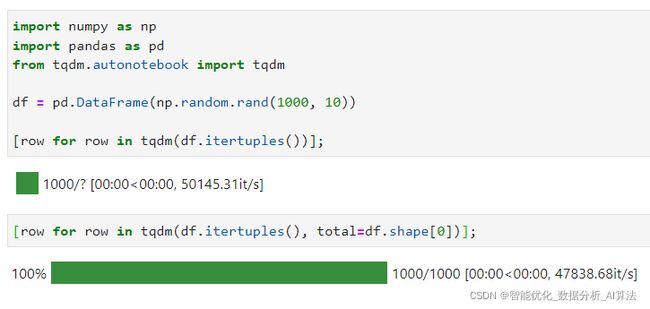
3.4 自主控制的进度上限
有些情况下,我们传入tqdm()的对象在迭代过程中是无法预先计算得到进度上限轮次的,典型如pandas中数据框的itertuples(),这种时候我们就可以利用total参数自行预设上限:
3.5 针对enumerate、zip和map的替代
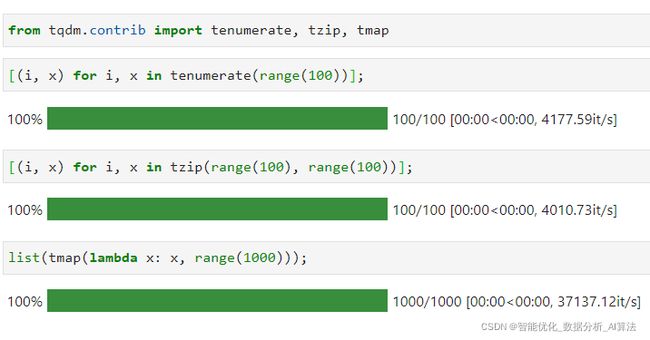
Python中除了常规的循环过程以外,还有几种内置函数也具有迭代循环的属性,而tqdm为了方便我们对这些非典型的循环过程添加进度条,也单独开发了tenumerate、tzip以及tmap这三个API,用于替代enumerate、zip和map:
3.6 设置进度条“用完即逝”
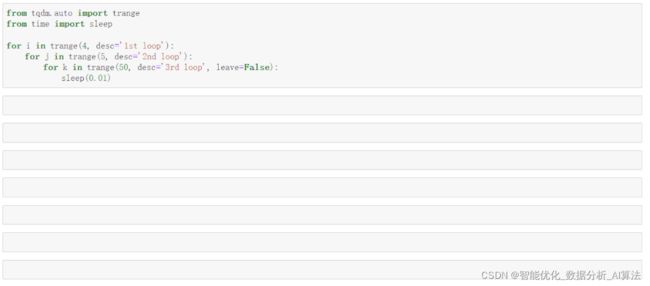
当我们希望为多层循环过程添加进度条监视时,常规的为每一层都直接使用tqdm(),会导致打印出过多的进度条,反而不利于我们观察进度过程。
而通过使用tqdm.auto中的trange(),我们可以通过设置参数leave=False,来让我们对应的进度条加载到头就自动消失掉,譬如下面动图中所展示的例子:
参考:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/u3-HCKQutfSJ9dPS_caYyQ