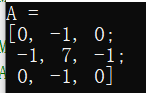
C++下OpenCV学习笔记----Mat类数据结构
C++下OpenCV学习笔记
----Mat类数据结构
文章目录
-
- C++下OpenCV学习笔记
-
-
-
- 一.简介
- 二.显式创建Mat类的七种方法
- 三.构造函数Mat::Mat
- 四.Mat类成员函数
-
-
一.简介
Mat不仅是非常有用的图像容器类,也是一个通用的矩阵类。
- attention
(1)不必再手动为Mat类开辟空间
(2)不必在不需要时立即释放空间 - 组成
(1)矩阵头:包含矩阵尺寸、存储方法、存储地址等信息
(2)一个指向存储所有像素值的矩阵的指针。其中,根据所选的存储方法的不同,矩阵可以是不同的维数。 - 矩阵复制
(1)浅拷贝:=和()
引用计数机制,即让每个Mat对象拥有不同的信息头,但共享同一矩阵。通过让矩阵指针指向同一地址实现。使用拷贝构造函数时只复制信息头和矩阵指针,而不复制矩阵。
1>代码实现
#include2>运行结果
3>attention
通过对任何一个对象作出改变也会影响其他对象。
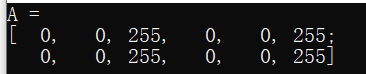
(2)创建只引用部分数据的信息头(以创建感兴趣区域ROI为例)
a.使用矩阵界定
1>代码实现
#include2>运行结果

b.用行和列界定
1>代码实现
#include2>运行结果

(3)深拷贝
a.完全深拷贝:clone()函数
1>代码实现
#include2>运行结果
3>attention
在内存中申请新的空间,与原独立。
b.copyTo()函数
是否申请新的内存空间,取决于现矩阵头中的大小信息是否与原来的一致,若一致则只深拷贝并不申请新的空间,否则先申请空间后再进行拷贝。
1>代码实现
#include#include2>运行结果

二.显式创建Mat类的七种方法
- 使用Mat()构造函数
Mat(int rows, int cols, int type, const Scalar& s);
第一个和第二个参数:表示行数和列数。
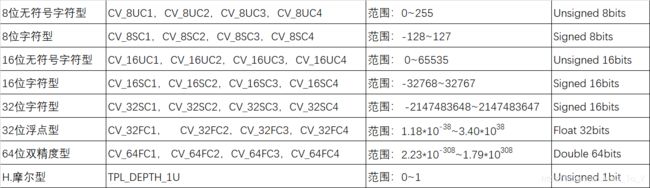
第三个参数:表示存储元素的数据类型以及每个矩阵点的通道数
CV_[The number of bits per item][Signed or Unsigned][Type prefix]C[The channel number]
即:CV_[位数][带符号与否][类型前缀]C[通道数]
第四个参数:表示使用指定的定制化值来初始化矩阵
1>代码实现
#includeScalar函数用法详见:Scalar函数用法
- 在C/C++中通过构造函数进行初始化
Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, const Scalar& s);
第一个参数:表示维度。
第二个参数:表示每个维度的尺寸。
第三和第四个参数:同1.
1>代码实现
#include 2>运行结果
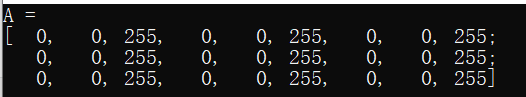
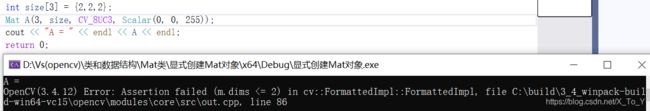
3>attention
第一个参数需要小于等于2。如果大于2,会报错:
- 为已存在的IplImage(IPLIMAGE)指针创建信息头
1>代码实现
#include- 利用create()函数
void Mat::create(int _rows, int _cols, int _type);
1>代码实现
#include 2>运行结果
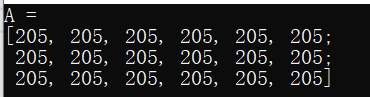
3>attention
此创建方法不能为矩阵设初值,只是在改变尺寸时重新为矩阵数据开辟内存而已。
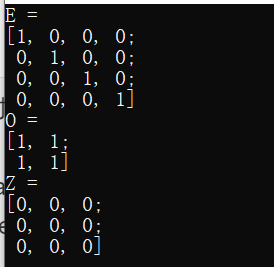
- 采用Matlab式的初始化方法
zeros(),ones(),eye()
1>代码实现
#include- 对小矩阵使用逗号分隔符式初始化函数
1>代码实现
#include- 为已存在的对象创建新信息头
clone(),copyTo()
1>代码实现
#include三.构造函数Mat::Mat
Mat共有24个构造函数,包括一个默认构造函数和23个重载的构造函数。函数列表如下:
//! default constructor
Mat();
//! constructs 2D matrix of the specified size and type
// (_type is CV_8UC1, CV_64FC3, CV_32SC(12) etc.)
Mat(int rows, int cols, int type);
Mat(Size size, int type);
//! constucts 2D matrix and fills it with the specified value _s.
Mat(int rows, int cols, int type, const Scalar& s);
Mat(Size size, int type, const Scalar& s);
//! constructs n-dimensional matrix
Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type);
Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, const Scalar& s);
//! copy constructor
Mat(const Mat& m);
//! constructor for matrix headers pointing to user-allocated data
Mat(int rows, int cols, int type, void* data, size_t step=AUTO_STEP);
Mat(Size size, int type, void* data, size_t step=AUTO_STEP);
Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, void* data, const size_t* steps=0);
//! creates a matrix header for a part of the bigger matrix
Mat(const Mat& m, const Range& rowRange, const Range& colRange=Range::all());
Mat(const Mat& m, const Rect& roi);
Mat(const Mat& m, const Range* ranges);
//! converts old-style CvMat to the new matrix; the data is not copied by default
Mat(const CvMat* m, bool copyData=false);
//! converts old-style CvMatND to the new matrix; the data is not copied by default
Mat(const CvMatND* m, bool copyData=false);
//! converts old-style IplImage to the new matrix; the data is not copied by default
Mat(const IplImage* img, bool copyData=false);
//! builds matrix from std::vector with or without copying the data
template explicit Mat(const vector<_Tp>& vec, bool copyData=false);
//! builds matrix from cv::Vec; the data is copied by default
template explicit Mat(const Vec<_Tp, n>& vec, bool copyData=true);
//! builds matrix from cv::Matx; the data is copied by default
template explicit Mat(const Matx<_Tp, m, n>& mtx, bool copyData=true);
//! builds matrix from a 2D point
template explicit Mat(const Point_<_Tp>& pt, bool copyData=true);
//! builds matrix from a 3D point
template explicit Mat(const Point3_<_Tp>& pt, bool copyData=true);
//! builds matrix from comma initializer
template explicit Mat(const MatCommaInitializer_<_Tp>& commaInitializer);
//! download data from GpuMat
explicit Mat(const gpu::GpuMat& m);
//! destructor - calls release()
~Mat();