构建神经网络- 手写字体识别案例
神经网络构建:
Multilayer_Perceptron.py:
import numpy as np
from utils.features import prepare_for_training#做归一化
from utils.hypothesis import sigmoid, sigmoid_gradient#sigmoid函数 极其导数
class MultilayerPerceptron:
#定义初始化函数
def __init__(self,data,labels,layers,normalize_data =False):
#数据预处理函数调用
data_processed = prepare_for_training(data,normalize_data = normalize_data)[0]
#初始化赋值操作
self.data= data_processed
self.labels= labels
self.layers= layers #784 25 10
self.normalize_data= normalize_data
self.thetas = MultilayerPerceptron.thetas_init(layers)#权重参数初始化
#第一层是输入层,输入像素点个数:28*28*1(长 宽 颜色通道)--不可改
#第二层:隐层神经元个数 25个(把784特征转化为25维向量) --可改
#第三层:分类层,10分类任务
def predict(self,data):
data_processed = prepare_for_training(data,normalize_data = self.normalize_data)[0]
num_examples = data_processed.shape[0]
predictions = MultilayerPerceptron.feedforward_propagation(data_processed,self.thetas,self.layers)
return np.argmax(predictions,axis=1).reshape((num_examples,1))#返回最大概率值
#定义训练模块对参数进行更新,神经网络也是用优化算法去做的(要传入最大迭代次数max_iterations 和学习率alpha)
def train(self,max_iterations=1000,alpha=0.1):
#为了方便权重矩阵参数进行更新,把矩阵拉成一个向量,(后面再还原成矩阵)
unrolled_theta = MultilayerPerceptron.thetas_unroll(self.thetas)
#调用梯度下降函数对参数进行更新
(optimized_theta,cost_history) = MultilayerPerceptron.gradient_descent(self.data,self.labels,unrolled_theta,self.layers,max_iterations,alpha)
#还原成矩阵thetas_roll
self.thetas = MultilayerPerceptron.thetas_roll(optimized_theta,self.layers)
return self.thetas,cost_history
#定义权重矩阵初始化函数(传入要更新权重的层数)
@staticmethod
def thetas_init(layers):
num_layers = len(layers)#layer是list结构
thetas = {}#定义一个字典 每一层权重参数写里面
#用for循环对每层权重参数进行赋值
#在此案例中只有3层784 25 10 需要赋值的只有两层
#循环执行两次得到25*785和10*26两组矩阵(785 26加上了权重偏置)
for layer_index in range(num_layers - 1):
"""
会执行两次,得到两组参数矩阵:25*785 , 10*26
"""
in_count = layers[layer_index]
out_count = layers[layer_index+1]
# 这里需要考虑到偏置项,记住一点偏置的个数跟输出的结果是一致的
thetas[layer_index] = np.random.rand(out_count,in_count+1)*0.05 #随机进行初始化操作,值尽量小一点
return thetas
#把矩阵合并向量
@staticmethod
def thetas_unroll(thetas):
num_theta_layers = len(thetas)
unrolled_theta = np.array([])
for theta_layer_index in range(num_theta_layers):
unrolled_theta = np.hstack((unrolled_theta,thetas[theta_layer_index].flatten()))
#flatten只能适用于numpy对象,即array或者mat,普通的list列表不适用 a.flatten():a是个数组(矩阵),a.flatten()就是把a降到一维,默认是按行的方向降
return unrolled_theta
#定义梯度下降函数:梯度下降求的是前向和反向传播的参数更新
#step:计算loss值 由loss计算梯度值 梯度值更新 return优化完的theta
@staticmethod
def gradient_descent(data,labels,unrolled_theta,layers,max_iterations,alpha):
optimized_theta = unrolled_theta
cost_history = []
for _ in range(max_iterations):
cost = MultilayerPerceptron.cost_function(data,labels,MultilayerPerceptron.thetas_roll(optimized_theta,layers),layers)
cost_history.append(cost)
theta_gradient = MultilayerPerceptron.gradient_step(data,labels,optimized_theta,layers)#计算theta梯度
optimized_theta = optimized_theta - alpha* theta_gradient#对theta进行更新
return optimized_theta,cost_history
#计算theta梯度函数:
@staticmethod
def gradient_step(data,labels,optimized_theta,layers):
theta = MultilayerPerceptron.thetas_roll(optimized_theta,layers)#把向量还原为矩阵
thetas_rolled_gradients = MultilayerPerceptron.back_propagation(data,labels,theta,layers)#调用反向传播函数
thetas_unrolled_gradients = MultilayerPerceptron.thetas_unroll(thetas_rolled_gradients)
return thetas_unrolled_gradients
#定义反向传播函数:
@staticmethod
def back_propagation(data,labels,thetas,layers):
num_layers = len(layers)
(num_examples,num_features) = data.shape#(1700 875)
num_label_types = layers[-1]
deltas = {}
#初始化操作
for layer_index in range(num_layers -1 ):
in_count = layers[layer_index]
out_count = layers[layer_index+1]
deltas[layer_index] = np.zeros((out_count,in_count+1)) #25*785 10*26
for example_index in range(num_examples):
layers_inputs = {}
layers_activations = {}
layers_activation = data[example_index,:].reshape((num_features,1))#785*1
layers_activations[0] = layers_activation
#逐层计算
for layer_index in range(num_layers - 1):
layer_theta = thetas[layer_index] #得到当前权重参数值 25*785 10*26
layer_input = np.dot(layer_theta,layers_activation) #第一次得到25*1 第二次10*1
layers_activation = np.vstack((np.array([[1]]),sigmoid(layer_input)))
layers_inputs[layer_index + 1] = layer_input #后一层计算结果
layers_activations[layer_index + 1] = layers_activation #后一层经过激活函数后的结果
output_layer_activation = layers_activation[1:,:]
delta = {}
#标签处理
bitwise_label = np.zeros((num_label_types,1))
bitwise_label[labels[example_index][0]] = 1
#计算输出层和真实值之间的差异
delta[num_layers - 1] = output_layer_activation - bitwise_label
#遍历循环 L L-1 L-2 ...2
for layer_index in range(num_layers - 2,0,-1):
layer_theta = thetas[layer_index]
next_delta = delta[layer_index+1]
layer_input = layers_inputs[layer_index]
layer_input = np.vstack((np.array((1)),layer_input))
#按照公式进行计算
delta[layer_index] = np.dot(layer_theta.T,next_delta)*sigmoid_gradient(layer_input)
#过滤掉偏置参数
delta[layer_index] = delta[layer_index][1:,:]
for layer_index in range(num_layers-1):
layer_delta = np.dot(delta[layer_index+1],layers_activations[layer_index].T)
deltas[layer_index] = deltas[layer_index] + layer_delta #第一次25*785 第二次10*26
for layer_index in range(num_layers -1):
deltas[layer_index] = deltas[layer_index] * (1/num_examples)
return deltas
#定义损失函数
@staticmethod
def cost_function(data,labels,thetas,layers):
num_layers = len(layers)#层数
num_examples = data.shape[0]#样本个数
num_labels = layers[-1]#label是layers的最后一层
#前向传播走一次
predictions = MultilayerPerceptron.feedforward_propagation(data,thetas,layers)
#制作标签,每一个样本的标签都得是one-hot
bitwise_labels = np.zeros((num_examples,num_labels))
for example_index in range(num_examples):
bitwise_labels[example_index][labels[example_index][0]] = 1
bit_set_cost = np.sum(np.log(predictions[bitwise_labels == 1]))
bit_not_set_cost = np.sum(np.log(1-predictions[bitwise_labels == 0]))
cost = (-1/num_examples) *(bit_set_cost+bit_not_set_cost)
return cost
#定义前向传播函数
@staticmethod
def feedforward_propagation(data,thetas,layers):
num_layers = len(layers)
num_examples = data.shape[0]
in_layer_activation = data#输入数据
# 逐层计算
for layer_index in range(num_layers - 1):
theta = thetas[layer_index]
out_layer_activation = sigmoid(np.dot(in_layer_activation,theta.T))
# 正常计算完之后是num_examples*25,但是要考虑偏置项 变成num_examples*26
out_layer_activation = np.hstack((np.ones((num_examples,1)),out_layer_activation))
in_layer_activation = out_layer_activation
#返回输出层结果,结果中不要偏置项了
return in_layer_activation[:,1:]
#定义矩阵还原函数
@staticmethod
def thetas_roll(unrolled_thetas,layers):
num_layers = len(layers)
thetas = {}#指定一个字典方便索引那一层矩阵
unrolled_shift = 0#指定一个标志位 记录到那一层
for layer_index in range(num_layers - 1):
in_count = layers[layer_index]
out_count = layers[layer_index+1]
thetas_width = in_count + 1
thetas_height = out_count
thetas_volume = thetas_width * thetas_height
start_index = unrolled_shift
end_index = unrolled_shift + thetas_volume
layer_theta_unrolled = unrolled_thetas[start_index:end_index]
thetas[layer_index] = layer_theta_unrolled.reshape((thetas_height,thetas_width))
unrolled_shift = unrolled_shift+thetas_volume
return thetas
数据集训练:
minist.py:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mping
import math
from multilayer_perceptron import MultilayerPerceptron
data = pd.read_csv('../neural_network/data/mnist-demo.csv')
numbers_to_display = 25#要展示图像的数量
num_cells = math.ceil(math.sqrt(numbers_to_display))
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
for plot_index in range(numbers_to_display):
digit = data[plot_index:plot_index+1].values
digit_label = digit[0][0]
digit_pixels = digit[0][1:]
image_size = int(math.sqrt(digit_pixels.shape[0]))
frame = digit_pixels.reshape((image_size,image_size))
plt.subplot(num_cells,num_cells,plot_index+1)
plt.imshow(frame,cmap='Purples')
plt.title(digit_label)
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.5,hspace=0.5)
plt.show()
train_data = data.sample(frac = 0.8)
test_data = data.drop(train_data.index)
train_data = train_data.values
test_data = test_data.values
num_training_examples = 5000
x_train = train_data[:num_training_examples,1:]
y_train = train_data[:num_training_examples,[0]]
x_test = test_data[:,1:]
y_test = test_data[:,[0]]
layers=[784,25,10]
normalize_data = True
max_iterations = 500
alpha = 0.1
multilayer_perceptron = MultilayerPerceptron(x_train,y_train,layers,normalize_data)
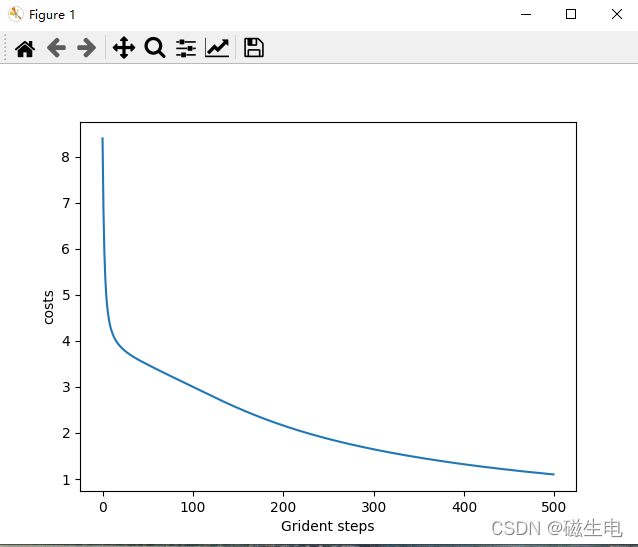
(thetas,costs) = multilayer_perceptron.train(max_iterations,alpha)
plt.plot(range(len(costs)),costs)
plt.xlabel('Grident steps')
plt.ylabel('costs')
plt.show()
y_train_predictions = multilayer_perceptron.predict(x_train)
y_test_predictions = multilayer_perceptron.predict(x_test)
train_p = np.sum(y_train_predictions == y_train)/y_train.shape[0] * 100
test_p = np.sum(y_test_predictions == y_test)/y_test.shape[0] * 100
print ('训练集准确率:',train_p)
print ('测试集准确率:',test_p)
numbers_to_display = 64
num_cells = math.ceil(math.sqrt(numbers_to_display))
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 15))
for plot_index in range(numbers_to_display):
digit_label = y_test[plot_index, 0]
digit_pixels = x_test[plot_index, :]
predicted_label = y_test_predictions[plot_index][0]
image_size = int(math.sqrt(digit_pixels.shape[0]))
frame = digit_pixels.reshape((image_size, image_size))
color_map = 'Greens' if predicted_label == digit_label else 'Reds'
plt.subplot(num_cells, num_cells, plot_index + 1)
plt.imshow(frame, cmap=color_map)
plt.title(predicted_label)
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='both', bottom=False, left=False, labelbottom=False, labelleft=False)
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5, wspace=0.5)
plt.show()