人工智能实验-动物识别系统
**
实验一:产生式系统实验
**
一、实验目的:
熟悉一阶谓词逻辑和产生式表示法,掌握产生式系统的运行机制,以及基于规则推理的基本方法。
二、实验内容:
设计并编程实现一个小型产生式系统(如分类、诊断等类型)
三、实验要求:
1.具体应用领域自选,具体系统名称自定。
2.用一阶谓词逻辑和产生式规则作为知识表示,利用产生式系统实验程序,建立知识库,分别运行正、反推理。
四、实验算法:
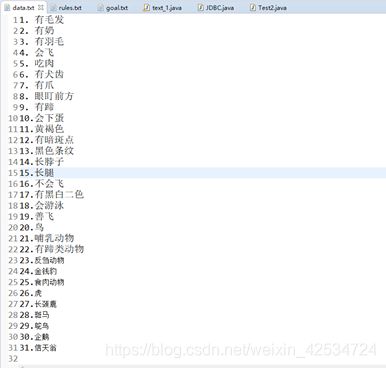
本次实验我实现了动物识别系统的产生式系统,在实验开始前首先应建立该系统的综合数据库,规则库,和目标库。
初学者,不喜勿喷
实验准备:
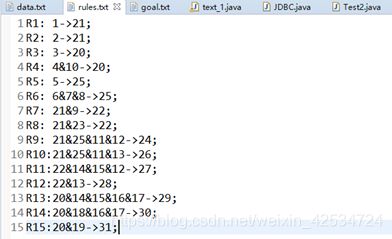
规则库:rules.txt
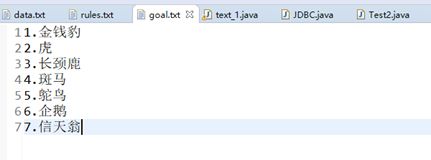
目标库:goal.txt
综合数据库:data.txt
实验代码:
package AI.Text;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.io.*;
public class text_1 {
public static String Data[]=new String[50]; //综合数据库
public static int Data_count=0; //记录综合数据库中数据的个数
public static int Rules_Cond[][]=new int [100][100]; //记录规则库中的规则条件
public static int Rules_Cond_count[]=new int[100]; //记录每条规则条件的个数
public static int Rules_Resl[]=new int [100]; //记录规则库中的规则结果
public static int Rules_count=0; //规则数
public static String Goal[]=new String[50]; //目标数组
public static int Goal_count=0; //目标的数量
public static String Jug[]=new String[50]; //存放输入的条件
public static int Jug_int[]=new int[50]; //存放输入的条件的编号 其中Jug_int[i]+1=data里面的编号
public static int Jug_count=0; //记录输入的条件数
public static int etc[]=new int[100];
//初始化函数
public static void Init() {
for(int i=0;i<Rules_count;i++) {
etc[i]=0;
}
for(int i=0;i<Jug_count;i++) {
Jug[i]=null;
Jug_int[i]=0;
}
Jug_count=0;
}
//读取特征
public static void ReadData() throws IOException {
BufferedReader filereade = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("data.txt"));
String Temp;
//计算数据的个数
while ((Temp = filereade.readLine()) != null) {
Data_count++;
}
BufferedReader filereader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("data.txt"));
int i=0;
while ((Temp = filereader.readLine()) != null) {
Data[i++]=Temp.substring(3);
}
}
//读取规则
public static void ReadRules() throws IOException {
BufferedReader filereade = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("rules.txt"));
String Temp;
//计算数据的个数
while ((Temp = filereade.readLine()) != null) {
Rules_count++;
}
BufferedReader filereader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("rules.txt"));
int i=0;
while ((Temp = filereader.readLine()) != null) {
Temp=Temp.substring(4);
int m=0;
int n=0;
int len=Temp.length();
for(int j=0;j<len;j++) {
if(Temp.charAt(j)=='&') {
String str=Temp.substring(m,j);
Rules_Cond[i][n++]=Integer.valueOf(str).intValue();
m=j+1;
}
else if(Temp.charAt(j)=='-') {
String str=Temp.substring(m,j);
Rules_Cond[i][n++]=Integer.valueOf(str).intValue();
m=j+2;
}
else if(Temp.charAt(j)==';') {
String str=Temp.substring(m,j);
Rules_Resl[i]=Integer.valueOf(str).intValue();
break;
}
}//for
Rules_Cond_count[i++]=n;
}//while
Init();
}
//读取目标文件
public static void ReadGoal() throws IOException{
BufferedReader filereade = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("goal.txt"));
String Temp;
//计算数据的个数
while ((Temp = filereade.readLine()) != null) {
Goal_count++;
}
BufferedReader filereader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("goal.txt"));
int i=0;
while ((Temp = filereader.readLine()) != null) {
Goal[i++]=Temp.substring(2);
}
}
//将输入的条件转换为编号
public static void Trans() {
for(int i=0;i<Jug_count;i++) {
String str=Jug[i];
for(int j=0;j<Data_count;j++) {
if(str.equals(Data[j])) {
Jug_int[i]=j;
break;
}
}
}
}
public static void Add() {
for(int i=0;i<Rules_count;i++) {
int flag=0;
int resl=Rules_Resl[i];
for(int j=0;j<Goal_count;j++) {
if(Data[resl-1].equals(Goal[j])) {
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag==1) { //判断目标是不是goal里面的
continue;
}else {
int sd=1;
for(int k=0;k<Rules_Cond_count[i];k++) {
int npc=Rules_Cond[i][k];
int q=0;
for(int p=0;p<Jug_count;p++) {
if(npc-1==Jug_int[p]) {
q=1; //找到了
break;
}
}//p
if(q==0) { //没找到
sd=0;
break;
}
}//k
if(sd==1) {
Jug[Jug_count++]=Data[Rules_Resl[i]-1];
Trans();
}
}//else
}//i
}
//逆向搜索主程序
public static void Find_1() {
JFrame tf = new JFrame("推理过程及推理结果:");
tf.setSize(500, 300);
tf.setLocation(300, 200);
tf.setVisible(true);
tf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.HIDE_ON_CLOSE);
JTextArea showarea = new JTextArea(12, 34);
JScrollPane scrollpane = new JScrollPane(showarea);
showarea.setEditable(false);
tf.add(scrollpane);
showarea.setText("");
Add();
String str = null;
for(int i=0;i<Goal_count;i++) {
int npc=1;
showarea.append("判断该动物是不是"+Goal[i]+"\n");
int tr = 0; //记录目标
int pc=0;
for(int j=0;j<Data_count;j++) {
if(Goal[i].equals(Data[j])) {
tr=j;
break;
}
}
for(int j=0;j<Rules_count;j++) {
if(tr+1==Rules_Resl[j]) {//tr+1
pc=j;
break;
}
}
for(int j=0;j<Rules_Cond_count[pc];j++) {
int flag=0;
int we=Rules_Cond[pc][j];
showarea.append("它是"+Data[we-1]+"吗?\t");
for(int k=0;k<Jug_count;k++) {
if(we-1==Jug_int[k]) {
showarea.append("是"+"\n");
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag==0) {
showarea.append("否"+"\n");
npc=0;
break;
}
}
if(npc==0) {
showarea.append("它不是"+Goal[i]+"\n\n");
}else {
str=Goal[i];
showarea.append("它是"+Goal[i]+"\n\n");
}
}
if(str!=null)
showarea.append("\n推理结果:它是"+str);
else
showarea.append("\n条件不足,推理不出!!");
}
//正向搜索主程序
public static void Find() {
JFrame tf = new JFrame("推理过程及推理结果:");
tf.setSize(500, 300);
tf.setLocation(300, 200);
tf.setVisible(true);
tf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.HIDE_ON_CLOSE);
JTextArea showarea = new JTextArea(12, 34);
JScrollPane scrollpane = new JScrollPane(showarea);
showarea.setEditable(false);
tf.add(scrollpane);
showarea.setText("");
while(true) {
int flag = 0;
String ob = null;
int npc=0;
for(int i=0;i<Rules_count;i++) {
if(etc[i]==1) {
continue;
}
int num=Rules_Cond_count[i];
for(int j=0;j<num;j++) {
flag=0;
for(int k=0;k<Jug_count;k++) {
if(Rules_Cond[i][j]-1==Jug_int[k]) {
ob=Data[Rules_Resl[i]-1];
flag=1;
break;
}
}
if(flag==0)
break;
}
if(flag==1) {
int w=i+1;
showarea.append("使用规则"+w+":");
for(int r=0;r<num;r++) {
if(r<num-1)
showarea.append(Data[Rules_Cond[i][r]-1]+" & ");
else
showarea.append(Data[Rules_Cond[i][r]-1]+"");
}
showarea.append("---->"+Data[Rules_Resl[i]-1]+"\n\n");
Jug_int[Jug_count++]=Rules_Resl[i]-1;
etc[i]=1;
for(int q=0;q<Goal_count;q++) {
if(ob.equals(Goal[q])) {
npc=1;
showarea.append("推理结果为:"+ob);
break;
}
}
break;
}
}
if(flag==0) {
showarea.append("条件不足!");
return;
}
if(npc!=0)
break;
}
}
//制作界面
private static void createAndShowGUI() {
JFrame f = new JFrame("动物识别系统");
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT, 200, 50));
f.setSize(500, 300);
f.setLocation(300, 200);
f.setVisible(true);
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JButton btn0 = new JButton("进入");
JButton btn1 = new JButton("退出");
f.add(btn0);
f.add(btn1);
//进入
btn0.addActionListener(e -> {
JFrame tf = new JFrame("查询");
tf.setSize(700, 500);
tf.setLocation(300, 200);
tf.setVisible(true);
tf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.HIDE_ON_CLOSE);
JTextArea showarea = new JTextArea(20, 50);
JScrollPane scrollpane = new JScrollPane(showarea);
showarea.setEditable(false);
JPanel panel = new JPanel(new GridLayout(0, 2,50, 20));
showarea.setText("");
showarea.append("规则库:\n");
showarea.append("序号\t结论\t\t\t条件\n\n");
int npc=1;
for (int i = 0; i < Rules_count; i++) {
showarea.append("R"+npc+":\t");
showarea.append("animal["+Data[Rules_Resl[i]-1]+"]:----------->\t");
int t=Rules_Cond_count[i];
for(int j=0;j<t;j++) {
if(j<t-1)
showarea.append("is["+Data[Rules_Cond[i][j]-1]+"] & ");
else
showarea.append("is["+Data[Rules_Cond[i][j]-1]+"]\n");
}
showarea.append("\n");
npc++;
}
JTextField Rule = new JTextField(1000);
JLabel label_Rule = new JLabel(" 输入综合数据库中存放的实事(以;间隔;结束):");
JButton btn = new JButton("正向推理");
JButton btn_1 = new JButton("逆向推理");
//逆向推理btn_1
btn_1.addActionListener(o -> {
Init();
String rule = Rule.getText();
if (rule != null && !rule.trim().equals("")) {
int m=0;
for(int i=0;i<rule.length();i++) {
if(rule.charAt(i)==';') {
Jug[Jug_count++]=rule.substring(m, i);
m=i+1;
}
}
Trans();
Find_1();
}else {
JDialog dialog = new JDialog(tf, "提示", true);
dialog.setSize(200, 100);
dialog.setLocation(500, 300);
JLabel label = new JLabel(" 推理规则不能为空!");
dialog.add(label);
dialog.setVisible(true);
dialog.setDefaultCloseOperation(JDialog.HIDE_ON_CLOSE);
}
});
//正向推理btn
btn.addActionListener(o -> {
Init();
String rule = Rule.getText();
if (rule != null && !rule.trim().equals("")) {
int m=0;
for(int i=0;i<rule.length();i++) {
if(rule.charAt(i)==';') {
Jug[Jug_count++]=rule.substring(m, i);
m=i+1;
}
}
Trans();
Find();
}else {
JDialog dialog = new JDialog(tf, "提示", true);
dialog.setSize(200, 100);
dialog.setLocation(500, 300);
JLabel label = new JLabel(" 推理规则不能为空!");
dialog.add(label);
dialog.setVisible(true);
dialog.setDefaultCloseOperation(JDialog.HIDE_ON_CLOSE);
}
});
panel.add(label_Rule);
panel.add(Rule);
panel.add(btn);
panel.add(btn_1);
tf.add(scrollpane);
tf.add(panel, BorderLayout.PAGE_END);
});
//退出
btn1.addActionListener(e -> System.exit(0));
}
public static void Run() throws IOException {
ReadData();
ReadRules();
ReadGoal();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
Run();
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(text_1::createAndShowGUI);
}
}
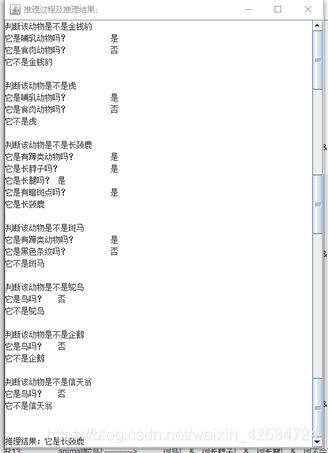
点击【进入】后:进入查询界面;这个界面上面是一个文本域,在文本域里面有显示规则库,中间部分是输入框,输入想查询的事实。注:每个事实之间以英文的分号分隔开,并且需要以英文分号结束。下面是两个按钮,分别是【正向推理】和【反向推理】,可以选择自己想要的推理方式。

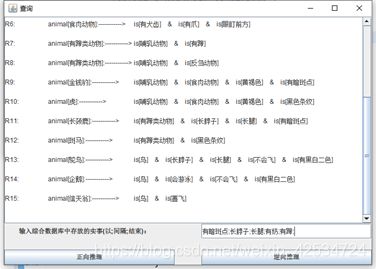
上面输入的事实是书上给出的例子,看下会不会得到同样的结果。
输入的事实为书上的例子:有暗斑点;长脖子;长腿;有奶;有蹄;
逆向推理:下面是截长图的效果。可以清晰看到推理结果正确,因此,逆向推理正确!