数据增强
在训练数据拆分上评估数据增强,以增加高质量训练样本的数量。
Intuition
通常希望通过数据扩充来增加训练数据的规模和多样性。它涉及使用现有样本生成合成但真实的示例。
-
拆分数据集。想首先拆分数据集,因为如果允许将生成的样本放置在不同的数据拆分中,许多增强技术会导致某种形式的数据泄漏。
例如,一些增强涉及为句子中的某些关键标记生成同义词。如果允许来自相同来源句子的生成句子进入不同的拆分,可能会在不同的拆分中泄漏具有几乎相同的嵌入表示的样本。
-
增加训练拆分。只想在训练集上应用数据增强,因为验证和测试拆分应该用于提供对实际数据点的准确估计。
-
检查和验证。如果扩充数据样本不是模型在生产中可能遇到的输入,那么仅仅为了增加训练样本大小而扩充是没有用的。
数据扩充的确切方法在很大程度上取决于数据类型和应用程序。以下是可以增强不同数据模式的几种方法:
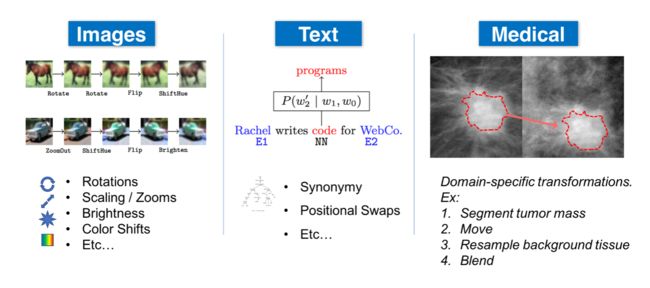 数据扩充类型
数据扩充类型
使用 Snorkel 进行数据扩充
- 一般:归一化、平滑、随机噪声、合成过采样( SMOTE)等。
- 自然语言处理(NLP):替换(同义词、tfidf、嵌入、屏蔽模型)、随机噪声、拼写错误等。
- 计算机视觉(CV):裁剪、翻转、旋转、填充、饱和、增加亮度等。
warning
虽然某些数据模式(例如图像)的转换很容易检查和验证,但其他模式可能会引入无提示错误。例如,改变文本中标记的顺序可以显着改变含义(“这真的很酷”→“这真的很酷吗”)。因此,重要的是要衡量增强策略将引入的噪声,并对发生的转换进行精细控制。
library
根据特征类型和任务,有许多数据增强库允许扩展训练数据。
自然语言处理 (NLP)
- NLPAug:NLP 的数据增强。
- TextAttack:用于 NLP 中的对抗性攻击、数据增强和模型训练的框架。
- TextAugment:文本增强库。
计算机视觉(简历)
- Imgaug:用于机器学习实验的图像增强。
- Albumentations:快速图像增强库。
- Augmentor:用于机器学习的 Python 图像增强库。
- Kornia.augmentation:在 GPU 中执行数据增强的模块。
- SOLT:用于深度学习的数据增强库,支持图像、分割掩码、标签和关键点。
其他
- Snorkel:在弱监督下生成训练数据的系统。
- DeltaPy:表格数据扩充和特征工程。
- Audiomentations:一个用于音频数据增强的 Python 库。
- Tsaug:一个用于时间序列增强的 Python 包。
应用
让使用nlpaug库来扩充数据集并评估生成样本的质量。
pip install nlpaug==1.1.0 transformers==3.0.2 -q
pip install snorkel==0.9.8 -q
import nlpaug.augmenter.word as naw
# Load tokenizers and transformers
substitution = naw.ContextualWordEmbsAug(model_path="distilbert-base-uncased", action="substitute")
insertion = naw.ContextualWordEmbsAug(model_path="distilbert-base-uncased", action="insert")
text = "Conditional image generation using Variational Autoencoders and GANs."
# Substitutions
substitution.augment(text)
替换对来说似乎不是一个好主意,因为某些关键字为标签提供了强烈的信号,所以不想改变它们。另外请注意,这些增强不是确定性的,每次运行它们时都会有所不同。让尝试插入...
# Insertions
insertion.augment(text)
使用多个变分自动编码器和甘斯的自动条件逆图像生成算法。
好一点但仍然很脆弱,现在它可能会插入可能影响误报标签出现的关键词。也许不是替换或插入新标记,而是让尝试简单地用它们的别名交换机器学习相关的关键字。将使用 Snorkel 的转换函数来轻松实现这一点。
# Replace dashes from tags & aliases
def replace_dash(x):
return x.replace("-", " ")
# Aliases
aliases_by_tag = {
"computer-vision": ["cv", "vision"],
"mlops": ["production"],
"natural-language-processing": ["nlp", "nlproc"]
}
# Flatten dict
flattened_aliases = {}
for tag, aliases in aliases_by_tag.items():
tag = replace_dash(x=tag)
if len(aliases):
flattened_aliases[tag] = aliases
for alias in aliases:
_aliases = aliases + [tag]
_aliases.remove(alias)
flattened_aliases[alias] = _aliases
print (flattened_aliases["natural language processing"])
print (flattened_aliases["nlp"])
['nlp', 'nlproc'] ['nlproc', 'natural language processing']
现在将按原样使用标签和别名,但可以使用inflect
aliases_by_tag包来解释多个标签,或者在替换别名之前应用词干提取等。
# We want to match with the whole word only
print ("gan" in "This is a gan.")
print ("gan" in "This is gandalf.")
# \b matches spaces
def find_word(word, text):
word = word.replace("+", "\+")
pattern = re.compile(fr"\b({word})\b", flags=re.IGNORECASE)
return pattern.search(text)
# Correct behavior (single instance)
print (find_word("gan", "This is a gan."))
print (find_word("gan", "This is gandalf."))
现在让使用 snorkeltransformation_function系统地将此转换应用于数据。
from snorkel.augmentation import transformation_function
@transformation_function()
def swap_aliases(x):
"""Swap ML keywords with their aliases."""
# Find all matches
matches = []
for i, tag in enumerate(flattened_aliases):
match = find_word(tag, x.text)
if match:
matches.append(match)
# Swap a random match with a random alias
if len(matches):
match = random.choice(matches)
tag = x.text[match.start():match.end()]
x.text = f"{x.text[:match.start()]}{random.choice(flattened_aliases[tag])}{x.text[match.end():]}"
return x
# Swap
for i in range(3):
sample_df = pd.DataFrame([{"text": "a survey of reinforcement learning for nlp tasks."}])
sample_df.text = sample_df.text.apply(preprocess, lower=True, stem=False)
print (swap_aliases(sample_df.iloc[0]).text)
# Undesired behavior (needs contextual insight)
for i in range(3):
sample_df = pd.DataFrame([{"text": "Autogenerate your CV to apply for jobs using NLP."}])
sample_df.text = sample_df.text.apply(preprocess, lower=True, stem=False)
print (swap_aliases(sample_df.iloc[0]).text)
autogenerate vision apply jobs using nlp autogenerate cv apply jobs using natural language processing autogenerate cv apply jobs using nlproc
使用 nlp 自动生成视觉应用作业 使用自然语言处理自动生成简历申请职位 使用 nlproc 自动生成简历申请工作
现在将定义一个增强策略来应用转换函数与某些规则(生成多少样本,是否保留原始数据点等)
from snorkel.augmentation import ApplyOnePolicy, PandasTFApplier
# Transformation function (TF) policy
policy = ApplyOnePolicy(n_per_original=5, keep_original=True)
tf_applier = PandasTFApplier([swap_aliases], policy)
train_df_augmented = tf_applier.apply(train_df)
train_df_augmented.drop_duplicates(subset=["text"], inplace=True)
train_df_augmented.head()
len(train_df), len(train_df_augmented)
(668, 913)
现在,将跳过数据扩充,因为它变化无常,而且根据经验,它不会显着提高性能。但是,一旦可以控制要扩充的词汇类型以及扩充的确切内容,就会看到这会非常有效。
warning
无论使用什么方法,重要的是要验证不仅仅是为了扩充而扩充。可以通过执行任何现有的数据验证测试甚至创建特定的测试来应用于增强数据来做到这一点。
本文主体源自以下链接:
@article{madewithml,
author = {Goku Mohandas},
title = { Made With ML },
howpublished = {\url{https://madewithml.com/}},
year = {2022}
}
本文由 mdnice 多平台发布