Pygame 使用Djkstra广度搜索寻找迷宫(相对)最短路径
基于之前写的迷宫生成器实现了Djkstra算法搜索路径。
https://blog.csdn.net/ChillingKangaroo/article/details/122800431
Djkstra基于广度优先算法,与简单搜索不同的是Djkstra在访问每一个节点的时候会计算到该节点的最短路径以及上一个节点,如果有新的路径比之前的路径更短,储存的上一个路径点则会被替换掉。在完成计算之后只需要取终点的数据然后就可以沿记录找到已搜索范围中最短的路径。
因为我之前迷宫基于深度优先生成,另外因为路径没有权重(走一格的距离都是相同的)所以其实Djkstra不太能发挥出来,实现中没有使用优先级序列,不过算法还是有效的。
实现用了python的链表,动态添加很方便,在没有找到终点的时候循环,每次循环查找列表中节点的四个方向,如果没有访问过则添加到新列表中,循环结尾再把新列表值给查找列表,在查找到终点时就停止。
实现效果如下,绿色表示djkstra查找范围,蓝色表示最短路径,使用40x40矩阵测试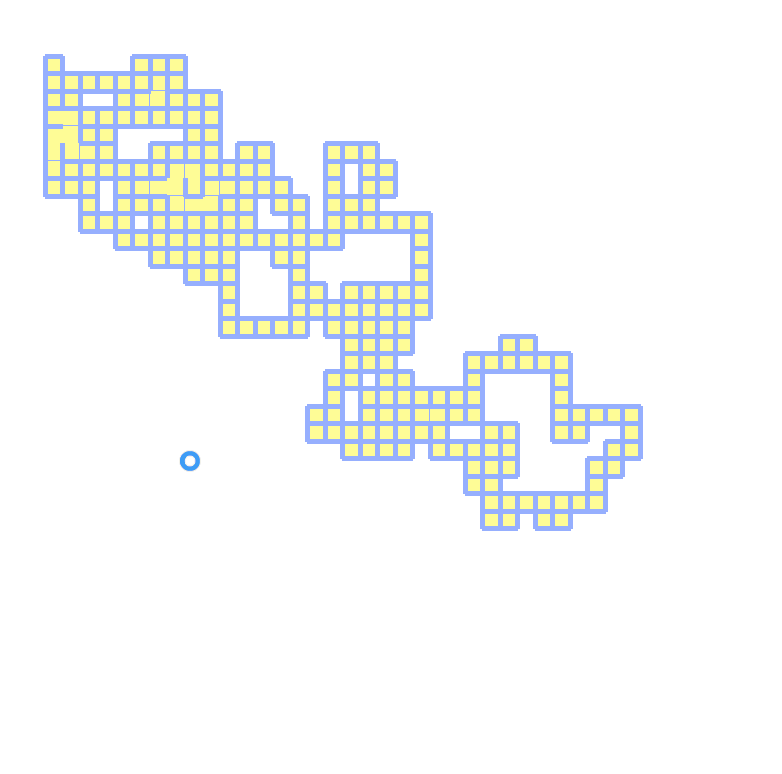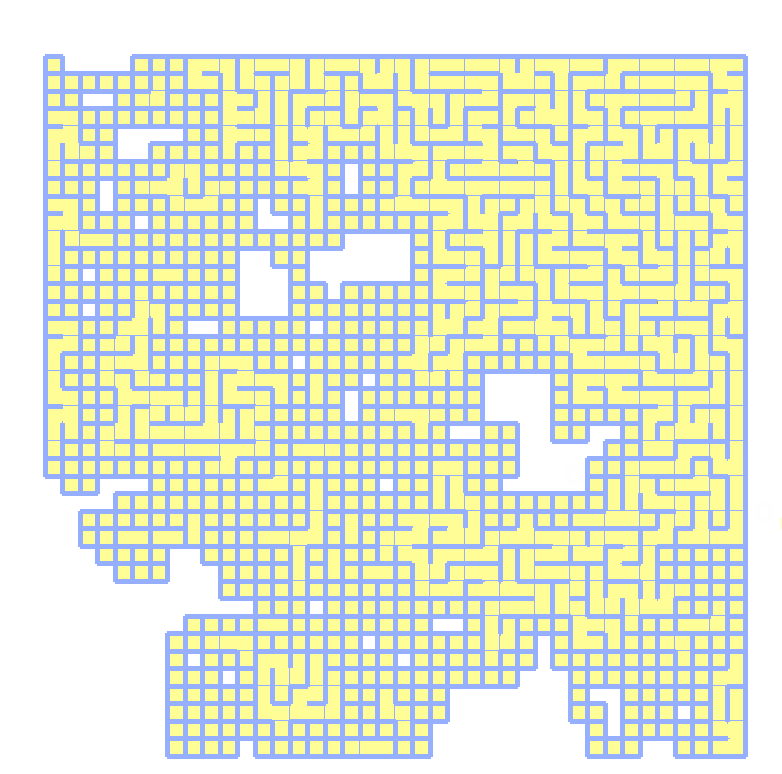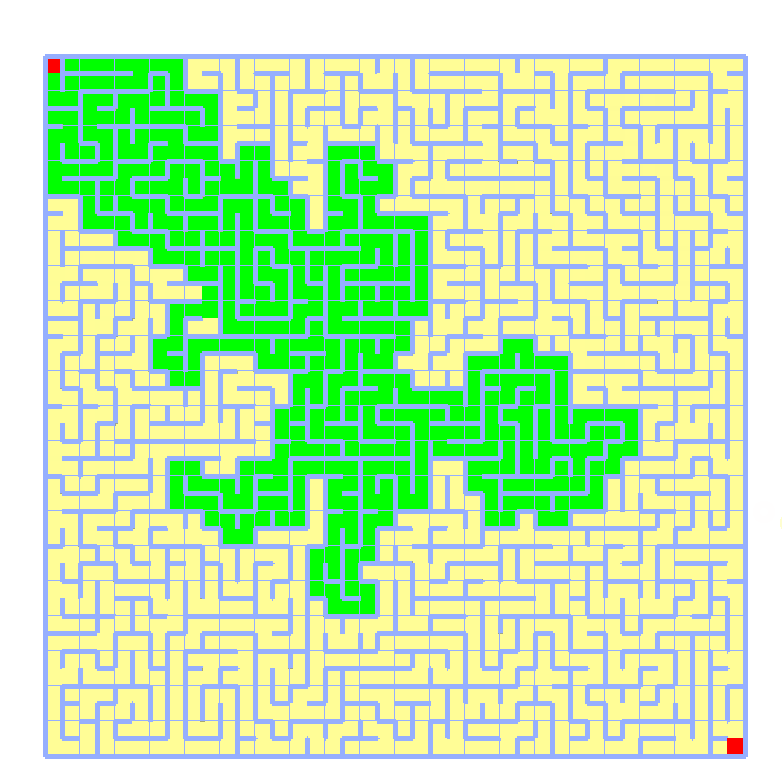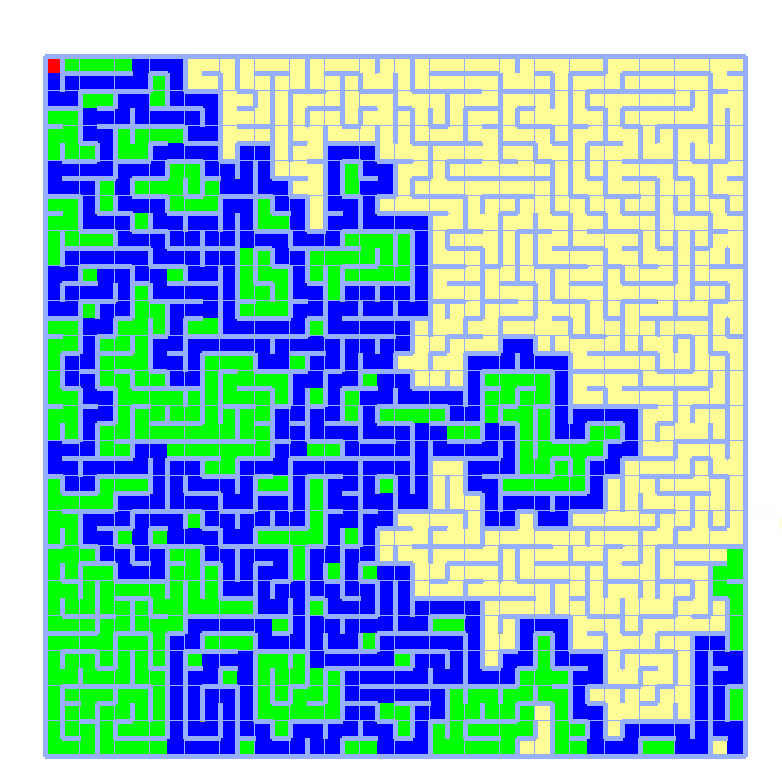
import pygame as pg
import time
import random
class Tile(): #Tile is for generating maze
def __init__(self,grid_size,screen_size,x,y):
self.x,self.y = x,y
self.connected = [0,0,0,0] # up,right,down,left 0 for not connected
self.grid_size = grid_size
self.tile_size = [(screen_size[0]-100)/grid_size[0],(screen_size[1]-100)/grid_size[1]]
self.rectangle = (self.x*self.tile_size[0]+50,self.y*self.tile_size[1]+50,self.tile_size[0],self.tile_size[1])
self.points = [ [self.x*self.tile_size[0]+50,self.y*self.tile_size[1]+50], #uppper left
[self.x*self.tile_size[0]+50+self.tile_size[0],self.y*self.tile_size[1]+50], #upper right
[self.x*self.tile_size[0]+50+self.tile_size[0],self.y*self.tile_size[1]+50+self.tile_size[1]], #lower right
[self.x*self.tile_size[0]+50,self.y*self.tile_size[1]+50+self.tile_size[1]], #lower left
]
self.visited = False
self.color = (255,253,150)
def draw(self,color = None): #x,y represents the tile coordinates
color = self.color if not color else color
pg.draw.rect(screen,color,self.rectangle)
for i in range(4):
if not self.connected[i]:
pg.draw.line(screen,(150,175,255),(self.points[i]),(self.points[((i+1)%4)]),5)
class Node():
def __init__(self):
self.visited = False
self.last_node = None
self.steps = None
def maze_gen(path):
global tile_covered
x,y = path[-1]
if x < 0 or x >= grid_size[0] or y < 0 or y >= grid_size[1]:
print(f'index out of range at {x,y}')
return
if matrix[y][x].visited:
print(f'node already visited at {x,y}')
return
elif tile_covered <= grid_size[0]*grid_size[1]:
tile_covered += 1
print(x,y)
matrix[y][x].visited = True
path_choice = [0,1,2,3]
random.shuffle(path_choice)
for i in path_choice:
x_,y_ = x+directions[i][0],y+directions[i][1]
path.append([x_,y_])
if maze_gen(path): # tile is not visited
matrix[y][x].connected[i] = 1 #walls of current node
matrix[y_][x_].connected[(i+2)%4] = 1#reverse the vector direction
matrix[y][x].draw()
matrix[y_][x_].draw()
pg.display.update()
path.pop(-1)
return True
else:
print('all node visited')
return
def djkstra():
end_point = (grid_size[0]-1,grid_size[1]-1)
x,y = start_point
matrix[y][x].draw((255,0,0))
matrix[end_point[0]][end_point[1]].draw((255,0,0))
pg.display.update()
border = [[0,0]]
steps = 0
while True:
steps += 1
new_border = []
for x,y in border:
if (x,y) == end_point:
print('exit found')
return end_point
for i in range(4):
if matrix[y][x].connected[i]: #if there is a way
next_x,next_y = directions[i][0]+x,directions[i][1]+y
if found_path[next_y][next_x].visited == False:
new_border.append([next_x,next_y])
matrix[next_y][next_x].draw((0,255,0))
pg.display.update()
if found_path[next_y][next_x].last_node == None:
found_path[next_y][next_x].last_node = (x,y)
elif steps < found_path[next_y][next_x].steps:
found_path[next_y][next_x].last_node = (x,y)
print(f'setting {x,y} to visited')
found_path[y][x].visited = True
border = new_border
if new_border == []:
print('No exit point found')
return
def draw_path(end_point):
if not end_point:
return
else:
x,y = end_point
while [x,y] != start_point:
print(f'going though node {x,y}')
matrix[y][x].draw((0,0,255))
print(f'{(x,y)} == {start_point}:')
print((x,y) == start_point)
x,y = found_path[y][x].last_node
pg.display.update()
screen_size = [800,800]
grid_size = [40,40]
tile_covered = 0
run = True
screen = pg.display.set_mode(screen_size)
matrix = []
directions = [[0,-1],[1,0],[0,1],[-1,0]] # up,right,down,left 0 for not connected
found_path = [[Node() for x in range(grid_size[0])] for y in range(grid_size[1])]
for y in range(grid_size[1]):
temp = []
for x in range(grid_size[0]):
tile = Tile(grid_size,screen_size,x,y)
temp.append(tile)
matrix.append(temp)
pg.init()
path = [[0,0]]
start_point = [0,0]
screen.fill((255,255,255))
maze_gen(path)
pg.display.update()
print('======== Generation Finished ========')
end_point = djkstra()
draw_path(end_point)
while run:
for event in pg.event.get():
if event.type == pg.QUIT:
run = False
pg.quit()