pytorch中的NLLLoss和CrossEntropyLoss
NLLLoss
NLLLoss就是负对数似然(negative log likelihood loss)
计算公式:
n l l l o s s = − ∑ n = 1 N y n log p r o b ( x n ) nllloss=-\sum_{n=1}^{N}y_n\log prob(x_n) nllloss=−n=1∑Nynlogprob(xn)
举个例子就是:
x=[0.1,0.2,-0.7]
y=[0,1,0]
计算过程就是:对x进行softmax转换成概率,然后对每一个值取log,再乘以标签
-log(softmax(x))*y
我们详细看代码:
定义变量
import torch
batch_size=5
num_classes=6
outputs=torch.randn(batch_size,num_classes)#outputs表示模型的最后输出,还未经过归一化
targets=[2,0,5,1,2]#标签
targets=torch.LongTensor(targets)
不使用库函数
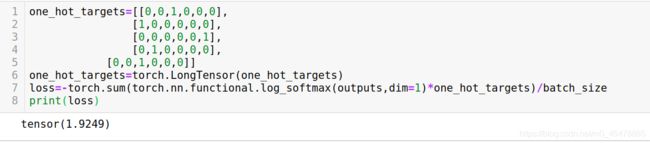
one_hot_targets=[[0,0,1,0,0,0],
[1,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,1],
[0,1,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,1,0,0,0]]
one_hot_targets=torch.LongTensor(one_hot_targets)
loss=-torch.sum(torch.nn.functional.log_softmax(outputs,dim=1)*one_hot_targets)/batch_size
print(loss)
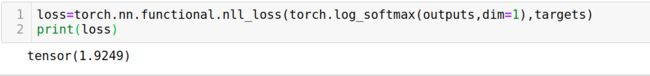
使用torch.nn.functional.nll_loss
loss=torch.nn.functional.nll_loss(torch.log_softmax(outputs,dim=1),targets)
print(loss)
- 将targets转成one_hot形式
- 将inputs和one_hot targets点乘
- 点乘后将所有值相加,然后除以batch_size
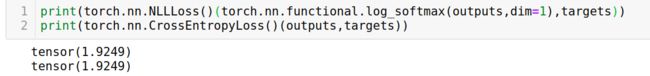
就是这么简单,functioanl.nll_loss和torch.nn.NLLLoss是一样的
使用torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss和torch.nn.NLLLoss
总结
归根到底,就是这一行代码:
loss=-torch.sum(torch.nn.functional.log_softmax(outputs,dim=1)*one_hot_targets)/batch_size
没什么难点的。
需要注意的是,上式千万不要用torch,mean代替torch.sum()/batch_size
因为torch.mean()是将所有的值相加之后除以的是batch_size*num_classes