【数据挖掘】决策树C4.5算法Python实现
目录
- 前言
- 注意
-
- C4.5算法
- 导入库
- 分析样本数据
- 计算各个属性对应的信息增益率
- 构建决策树
- 计算决策树的正确率
- 决策树的可视化
- 写在最后
前言
文章内容为对数据挖掘实验作业的记录,如果您是为了作业而来看的这篇文章,还请不要无脑拷贝,本人编程能力较弱,代码写的并不优雅,注释尽可能写的详细了。
和上一篇文章ID3算法实现的过程基本一致,不同之处在于C4.5使用信息增益率作为选择标准,为了区别于上一种方式,这里对连续值的处理使用遍历来查找一个使信息增益率最优的值。
注意
程序可能要跑20-30分钟
C4.5算法
导入库
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from math import log
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
分析样本数据
# 从本地读取样本数据集,这里选择前两种癌症数据进行分析
BLCA = pd.read_csv(r'数据集/BLCA/rna.csv')
KIRC = pd.read_csv(r'数据集/KIRC/rna.csv')
print(BLCA.shape)
print(KIRC.shape)
(3217, 400)
(3217, 489)
# 对数据进行转置,之后每行对应一个样本数据,每列对应一个属性
BLCASet = BLCA.T
BLCASet = BLCASet.iloc[1:,:].astype('float32')
KIRCSet = KIRC.T
KIRCSet = KIRCSet.iloc[1:,:].astype('float32')
# 插入一列数据用来标识不同的类别
BLCASet.insert(loc=3217, column=3217, value='BLCA')
KIRCSet.insert(loc=3217, column=3217, value='KIRC')
# 转为numpy类型方便处理
BLCASet = np.array(BLCASet)
KIRCSet = np.array(KIRCSet)
# 将两种癌症样本数据进行合并
DataSet = np.vstack((BLCASet,KIRCSet))
计算各个属性对应的信息增益率
def I(s1, s2):
'''
计算信息熵
'''
t = s1+s2
if t==0:
return 0
p1 = float(s1/t)
p2 = float(s2/t)
if p1==1 or p2==1:
return 1
if p1*p2!=0:
return -p1*log(p1,2)-p2*log(p2,2)
else:
if p1==0:
return -p2*log(p2,2)
else:
return -p1*log(p1,2)
# 计算总熵
I_t = I(BLCASet.shape[0],KIRCSet.shape[0])
# 接下来为计算每种属性可能的最优信息增益率
row = DataSet.shape[0] # 获取数据集行数
col = DataSet.shape[1] # 获取数据集列数
divList = [] # 存储获得最大信息增益率的划分点
Gain = [] # 存储信息增益
Gain_Ratio = [] # 存储信息增益率
Sel = [] # 存储节点决策:0表示大于等于能确定、1表示小于能够确定
Dec = [] # 存储当前决策下能够确定的类别
S11 = []
S12 = []
S21 = []
S22 = []
for i in range(col-1):
data = DataSet[:,i]
divdata = set(data) # 去重
divdata = list(divdata)
for j in range(len(divdata)): # 遍历所有属性值,以每个属性取值为划分点进行划分
div = divdata[j]
s11 = 0
s12 = 0
s21 = 0
s22 = 0
for k in range(row): # 对每个所有数据进行统计
if data[k]>=div:
if DataSet[k][-1] == 'BLCA': #s11存储所有大于等于划分点且属于BLCA的样本
s11 = s11+1
if DataSet[k][-1] == 'KIRC': #s12存储所有大于等于划分点且属于KIRC的样本
s12 = s12+1
else:
if DataSet[k][-1] == 'BLCA': #s21存储所有小于划分点且属于BLCA的样本
s21 = s21+1
if DataSet[k][-1] == 'KIRC': #s22存储所有小于划分点且属于BLCA的样本
s22 = s22+1
I1 = I(s11, s12) # I(s11,s12)
I2 = I(s21, s22) # I(s21,s22)
Ii = I(s11+s12, s21+s22) # 计算该属性的信息熵
gain = I_t-((s11+s12)/len(data)*I1+(s21+s22)/len(data)*I2) # 该属性的信息增益
gain_ratio = gain/Ii # 该属性在该划分下的信息增益率
# 接下来为更新信息增益率,保存该属性所有属性值之下的最大信息增益率所对应的一些信息
if j==0:
divList.append(div)
Gain.append(gain)
Gain_Ratio.append(gain_ratio)
if I1<I2:
Sel.append(0)
if s11>s12:
Dec.append('BLCA')
else:
Dec.append('KIRC')
else:
Sel.append(1)
if s21>s22:
Dec.append('BLCA')
else:
Dec.append('KIRC')
S11.append(s11)
S12.append(s12)
S21.append(s21)
S22.append(s22)
elif gain_ratio>Gain_Ratio[i]: # 当前信息增益率更优
Gain_Ratio.pop()
Gain_Ratio.append(gain_ratio)
Gain.pop()
Gain.append(gain)
S11.pop()
S11.append(s11)
S12.pop()
S12.append(s12)
S21.pop()
S21.append(s21)
S22.pop()
S22.append(s22)
divList.pop()
divList.append(div)
if I1<I2:
Sel.pop()
Sel.append(0)
if s11>s12:
Dec.pop()
Dec.append('BLCA')
else:
Dec.pop()
Dec.append('KIRC')
else:
Sel.pop()
Sel.append(1)
if s21>s22:
Dec.pop()
Dec.append('BLCA')
else:
Dec.pop()
Dec.append('KIRC')
# 按照Gain中值的降序,对其下标进行排序
indexList = np.argsort(Gain_Ratio)[::-1]
构建决策树
# 这里对data中的数据进行决策,判断其所属
def decisionTree(data, i):
if i==len(data)-1:
# print(f"第{i}层可以做决策")
if Sel[indexList[i-1]]==0:
if S11[indexList[i-1]]>=S12[indexList[i-1]]:
return 'KIRC'
else:
return 'BLCA'
else:
if S21[indexList[i-1]]>=S22[indexList[i-1]]:
return 'KIRC'
else:
return 'BLCA'
elif Sel[indexList[i]]==0 and data[i]>=divList[indexList[i]]: # 大于等于可以决策
# print(f"第{i}层可以做决策")
return Dec[indexList[i]]
elif Sel[indexList[i]]==1 and data[i]<divList[indexList[i]]: # 小于可以决策
# print(f"第{i}层可以做决策")
return Dec[indexList[i]]
else:
return decisionTree(data, i+1)
# deep指定决策树的深度
deep = 5
data = np.array(DataSet[:,indexList[:deep]])
data = np.hstack((data,DataSet[:,-1].reshape(data.shape[0],1)))
计算决策树的正确率
total = data.shape[0]
corr = 0
mis = 0
for i in range(0, total):
global corr, mis
res = decisionTree(data[i], 0)
# print(res)
if res == data[i][-1]:
# print('正确')
corr = corr + 1
else:
# print('错误')
mis = mis + 1
print(f"{corr}/{total}")
print(f"深度为{deep}的决策树的正确率为{corr/total}")
876/887
深度为5的决策树的正确率为0.9875986471251409
决策树的可视化
# 接下来为绘图的代码,唯独这里不是这一块不是原创,不过好像网上用的好像都一样?
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else:
numLeafs += 1
return numLeafs
def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key])
else:
thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > maxDepth : maxDepth = thisDepth
return maxDepth
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle = "sawtooth",fc="0.8")
leafNode = dict(boxstyle = "round4",fc="0.8")
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-")
def plotNode(nodeTxt,centerPt,parentPt,nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt,xy=parentPt,\
xycoords='axes fraction',xytext=centerPt,textcoords='axes fraction',\
va="center",ha="center",bbox=nodeType,arrowprops=arrow_args)
def plotMidText(cntrPt,parentPt,txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid,yMid,txtString)
def plotTree(myTree,parentPt,nodeTxt):
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree)
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
cntrPt = (plotTree.xoff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW,\
plotTree.yoff)
plotMidText(cntrPt,parentPt,nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr,cntrPt,parentPt,decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yoff = plotTree.yoff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key))
else:
plotTree.xoff = plotTree.xoff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key],(plotTree.xoff,plotTree.yoff),\
cntrPt,leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xoff,plotTree.yoff),cntrPt,str(key))
plotTree.yoff = plotTree.yoff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalD
def createPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1,facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks=[],yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111,frameon=False,**axprops)
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
plotTree.xoff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW
plotTree.yoff = 1.0
plotTree(inTree,(0.5,1.0),'')
plt.show()
# 分析绘制树的代码可以知道,我们首先需要提供用“字典”表示的树
# 编写一个递归构建树的函数
def genInTree(deep,i):
if i==deep:
if Sel[indexList[i]]==0:
if S11[indexList[i-1]]>=S12[indexList[i-1]]:
return {divList[indexList[i]]:{">=":"BLCA","<":"KIRC"}}
else:
return {divList[indexList[i]]:{">=":"KIRC","<":"BLCA"}}
else:
if S21[indexList[i-1]]>=S22[indexList[i-1]]:
return {divList[indexList[i]]:{">=":"KIRC","<":"BLCA"}}
else:
return {divList[indexList[i]]:{">=":"BLCA","<":"KIRC"}}
else:
if Sel[indexList[i]]==0:
return {divList[indexList[i]]:{">=":Dec[i],"<":genInTree(deep,i+1)}}
else:
return {divList[indexList[i]]:{">=":genInTree(deep,i+1),"<":Dec[i]}}
# 上述函数的输出大概是这个样子
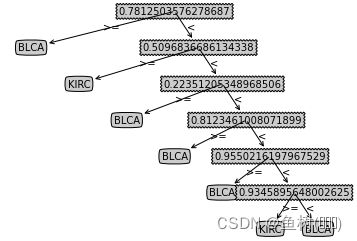
genInTree(6,0)
{0.7812503576278687: {'>=': 'BLCA',
'<': {0.5096836686134338: {'>=': 'KIRC',
'<': {0.22351205348968506: {'>=': 'BLCA',
'<': {0.8123461008071899: {'>=': 'BLCA',
'<': {0.9550216197967529: {'>=': 'BLCA',
'<': {0.9345895648002625: {'>=': 'BLCA',
'<': {-0.5671966075897217: {'>=': 'KIRC', '<': 'BLCA'}}}}}}}}}}}}}}
# 其中deep为深度,也可以手动填
createPlot(genInTree(deep,0))
写在最后
这学期真是挺忙的 >_<,可以说算是百忙之中抽出时间来写这个选修课作业了ಥ_ಥ