【C++进阶】map和set——下篇(红黑树的学习以及封装map和set)
C++学习历程:入门
- 博客主页:一起去看日落吗
- 持续分享博主的C++学习历程
博主的能力有限,出现错误希望大家不吝赐教- 分享给大家一句我很喜欢的话: 也许你现在做的事情,暂时看不到成果,但不要忘记,树成长之前也要扎根,也要在漫长的时光中沉淀养分。静下来想一想,哪有这么多的天赋异禀,那些让你羡慕的优秀的人也都曾默默地翻山越岭。
目录
- 1. 红黑树
-
- 1.1 红黑树的概念
- 1.2 红黑树的性质
- 1.3 红黑树节点的定义
- 1.4 红黑树结构
- 1.5 红黑树的插入操作
- 1.6 红黑树的验证
- 1.7 红黑树与AVL树的比较
- 1.8 红黑树的模拟实现
- 2. 红黑树模拟实现STL中的map与set
-
- 2.1 改造红黑树
- 2.2 map的模拟实现
- 2.3 set的模拟实现
- 2.4 测试
1. 红黑树
1.1 红黑树的概念
红黑树,是一种二叉搜索树,但在每个结点上增加一个存储位表示结点的颜色,可以是Red或
Black。 通过对任何一条从根到叶子的路径上各个结点着色方式的限制,红黑树确保没有一条路
径会比其他路径长出俩倍,因而是接近平衡的。
1.2 红黑树的性质
- 每个结点不是红色就是黑色
- 根节点是黑色的
- 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的两个孩子结点是黑色的
- 对于每个结点,从该结点到其所有后代叶结点的简单路径上,均 包含相同数目的黑色结点
- 每个叶子结点都是黑色的(此处的叶子结点指的是空结点)
思考:为什么满足上面的性质,红黑树就能保证:其最长路径中节点个数不会超过最短路径节点
个数的两倍?
答:假设黑色节点数量有N个,最短路径为:logN,最长路径为:2*logN,因此最长路径中节点个数不会超过最短路径中节点个数的两倍,所以如果用红黑树来完成查找效率也是非常高的。
1.3 红黑树节点的定义
//节点不是黑就是红,因此可以直接用枚举
enum Colour
{
RED,
BLACK
};//节点的颜色
template<class K, class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;//节点左孩子
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;//节点右孩子
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;//节点的父亲
pair<K, V> _kv;//节点中存放的键值对
Colour _col;//节点的颜色
RBTreeNode(const pair<K,V> kv)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_kv(kv)
,_col(RED)
{}
};
思考:在节点的定义中,为什么要将节点的默认颜色给成红色的?
答:在上面的性质中第三条和第四条是最重要的两点性质。假设我们默认颜色给黑色,那么必然会破环性质4(每条路径上包含相同数目的黑节点),如果破坏性质4代价会非常大,这是一种全局的破坏,其他每条路径的节点会因该路径增加了一个黑节点而不满足红黑树性质,调整起来非常麻烦;那么如果我们默认颜色给红色呢,必然会破坏性质3(没有连续的红节点),但是破坏这条性质只会影响当前路径,并不会对其他路径造成影响,影响面小。所以综上所述我们不难发现,默认给成红色是更好的。
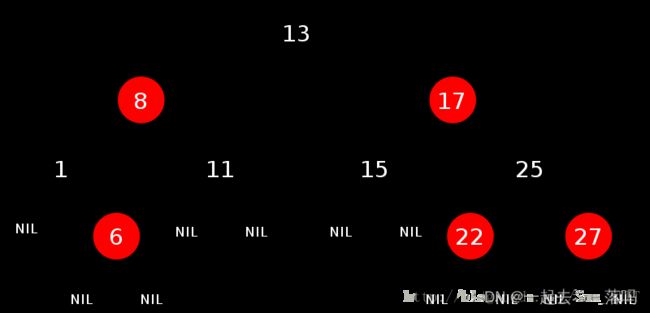
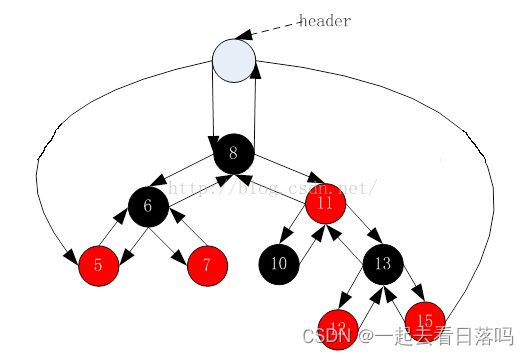
1.4 红黑树结构
在STL中,红黑树的实现中增加一个头结点,因为跟节点必须为黑色,为了与根节点进行区分,将头结点给成黑色,并且让头结点的 pParent 域指向红黑树的根节点,pLeft域指向红黑树中最小的节点,_pRight域指向红黑树中最大的节点,如下:
注意: 在下面的实现中,我们采用不带头节点的方式来模拟实现红黑树
1.5 红黑树的插入操作
红黑树是在二叉搜索树的基础上加上其平衡限制条件,因此红黑树的插入可分为两步:
-
按照二叉搜索树规则插入新节点
-
检测新节点插入后,红黑树的性质是否造到破坏
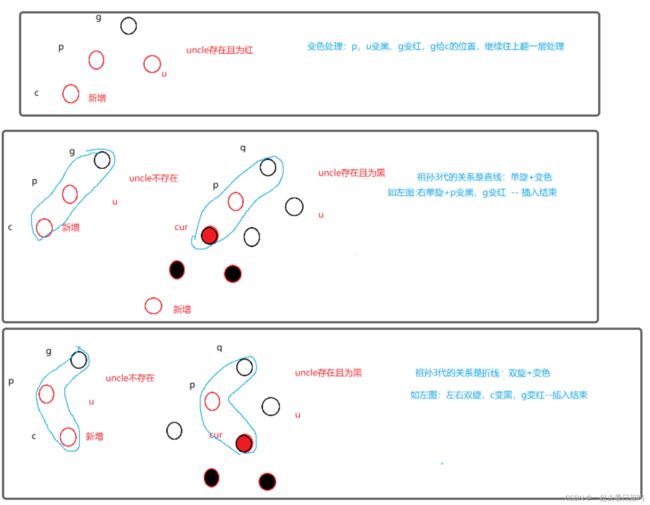
因为新节点的默认颜色是红色,因此:如果其父节点的颜色是黑色,没有违反红黑树任何性质,则不需要调整;但当新插入节点的父节点颜色为红色时,就违反了性质三不能有连在一起的红色节点,此时需要对红黑树分情况来讨论:
在分情况讨论之前记住一句话:关键看叔叔的脸色!
- 情况一: cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u存在且为红
- 情况二: cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u为黑
- 情况三: cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u为黑
pair<Node*, bool> Insert(const pair<K, V> kv)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = BLACK;//根节点给黑色
return make_pair(_root, true);
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)//循环去找空位
{
if (kv.first > cur->_kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if(kv.first < cur->_kv.first)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return make_pair(cur, false);
}
}
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
newnode->_col = RED;//链接上新节点
if (kv.first > parent->_kv.first)
{
parent->_right = newnode;
newnode->_parent = parent;
}
else
{
parent->_left = newnode;
newnode->_parent = parent;
}
cur = newnode;
//父节点存在且父节点为红色时需要继续处理
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
//关键看叔叔的脸色
if (parent == grandfather->_left)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//具体变色的情况需要画图分析:
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
//注意需要继续向上处理,容易忘记
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(grandfather);//右单旋
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
RotateL(parent);//先以父节点为旋转点左旋
RotateR(grandfather);//再以g为旋转点右旋
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;//旋转+变色过后一定是满足所有性质的直接退出循环
}
}
else
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else // 情况2:+ 情况3:
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else // cur == parent->_left
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(newnode, true);
}
1.6 红黑树的验证
红黑树的检测分为两步:
- 检测其是否满足二叉搜索树(中序遍历是否为有序序列)
- 检测其是否满足红黑树的性质
bool _CheckBlance(Node* root, int blackNum, int count)//balckNum相当于一个标尺,count就是用来记录每条路径的黑节点数目
{
if (root == nullptr)//如果root走到空节点
{
if (count != blackNum)//count不等于最左路径的黑色节点数
{
cout << "黑色节点的数量不相等" << endl;
return false;//返回假
}
return true;//否则返回真
}
if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED)
{
cout << "存在连续的红色节点" << endl;
return false;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
{
count++;
}
return _CheckBlance(root->_left, blackNum, count)
&& _CheckBlance(root->_right, blackNum, count);//再递归到各子树的子问题
}
bool CheckBlance()
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
return true;
}
if (_root->_col == RED)
{
cout << "根节点是红色的" << endl;
return false;
}
// 找最左路径做黑色节点数量参考值
int blackNum = 0;
Node* left = _root;
while (left)
{
if (left->_col == BLACK)
{
blackNum++;
}
left = left->_left;
}
int count = 0;
return _CheckBlance(_root, blackNum, count);
}
1.7 红黑树与AVL树的比较
红黑树和AVL树都是高效的平衡二叉树,增删改查的时间复杂度都是O( l o g 2 N log_2 N log2N),红黑树不追
求绝对平衡,其只需保证最长路径不超过最短路径的2倍,相对而言,降低了插入和旋转的次数,
所以在经常进行增删的结构中性能比AVL树更优,而且红黑树实现比较简单,所以实际运用中红
黑树更多。
1.8 红黑树的模拟实现
RBTree.h
//
// RBTree.hpp
// RedBlackTree
//
// Created by 卜绎皓 on 2022/11/17.
//
#pragma once
#include2. 红黑树模拟实现STL中的map与set
对map和set进行封装,虽然要传不同的参数类型,但是我们只需传个模版,根据不同的需要取不同的参数类型
2.1 改造红黑树
因为关联式容器中存储的是<key, value>的键值对,因此
k为key的类型,
ValueType: 如果是map,则为pair<K, V>; 如果是set,则为k
KeyOfValue: 通过value来获取key的一个仿函数类
迭代器的好处是可以方便遍历,是数据结构的底层实现与用户透明
#pragma once
#include2.2 map的模拟实现
#pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"
namespace Bernard
{
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT//定义map的仿函数内部类
{
//map的V类型为pair键值对
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;//返回pair中的第一个值
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
}
2.3 set的模拟实现
#pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"
namespace Bernard
{
template<class K>
class set
{
//set里面定义内部类重载operator()
//set的V类型为K
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;//直接返回key
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& k)
{
return _t.Insert(k);
}
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
}
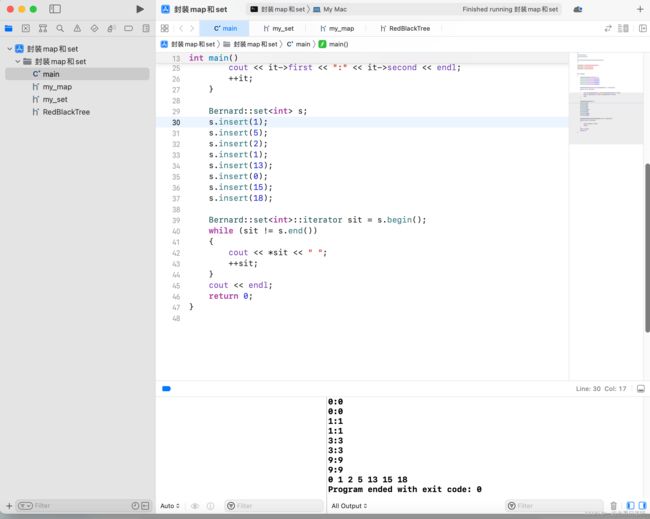
2.4 测试
//
// main.cpp
// 封装map和set
//
// Created by 卜绎皓 on 2022/11/17.
//
#include "RedBlackTree.hpp"
#include "my_map.hpp"
#include "my_set.hpp"
int main()
{
Bernard::map<int, int> m;
m.insert(make_pair(1, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(3, 3));
m.insert(make_pair(0, 0));
m.insert(make_pair(9, 9));
Bernard::map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end())
{
cout << (*it).first << ":" << (*it).second << endl;
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
Bernard::set<int> s;
s.insert(1);
s.insert(5);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(13);
s.insert(0);
s.insert(15);
s.insert(18);
Bernard::set<int>::iterator sit = s.begin();
while (sit != s.end())
{
cout << *sit << " ";
++sit;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}