【微服务】springboot + dubbo 整合Sentinel限流
一、前言
限流对一个生产环境的系统来说,具有重要的意义,限流的目的是为了保护系统中的某些核心业务资源不被瞬间的大并发流量冲垮而采取的一种措施,因此一个成熟的架构设计方案,限流也需要纳入到架构设计和规划中。
二、常用的限流解决方案
微服务经过多年的发展和沉淀,对于限流来说,也有了一些通用的解决方案,列举常用的供参考
- sentinel,springcloud-alibaba技术栈下的一个组件,提供了不仅限流,dashboard等在内的灵活的功能;
- guava,google提供的一款限流SDK,简单易用;
- 网关限流,nginx,可在nginx中配置一定的限流规则对请求进行限流;
- 利用限流算法思想的指导,如令牌桶、漏桶算法等自定义限流组件;
可参考之前一篇对于限流方案的总结:常用限流方案总结
三、dubbo中的限流
dubbo作为一款优秀的服务治理框架,在各大中小互联网公司都有使用,在微服务治理中,服务发布者使用dubbo可以发布服务出去,给平台中其他应用调用,使用起来很方便;
可以说所有的应用服务,一旦业务量上去了,应用服务要抗的压力也必然增加,对于服务提供方来说,高频大并发的调用,对于服务治理来说绝对是一项挑战,因此在这个问题上,dubbo官方在dubbo出厂的时候就根据可能遇到的情况提供了一系列配套的服务限流、降级、熔断等策略,可以参考官方的说明,小编这里之前也做了一些总结:dubbo服务限流与降级总结
dubbo官方限流方案的问题
官方提供的限流方案,个人认为其中一个比较大的问题在于运用起来不够灵活,举例来说,看如下的一种限流策略,即线程池限流的配置
在实际操作的时候,会发现这个 executes的参数值设置多大合适呢?其实很难断定,因为具体到某个服务接口来说,这个跟大环境下接口被调用的频率,接口响应的速度,服务器配置等诸多因素有关,况且来说,默认情况下,dubbo的线程池数量为200个,加上这个前提,对某个服务接口来说,设置这个参数就更难了;
于是,我们思考,从使用的灵活性上面来说,是否有更好的解决办法呢?
四、实验前置准备
为了更好的模拟出实验效果,先预先搭建一个基于springboot整合dubbo的聚合模块工程demo
1、项目结构如下
2、各个模块pom依赖
根pom模块依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.3.7.RELEASE
UTF-8
UTF-8
1.8
api模块依赖
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.18.6
provider/consumer模块依赖
com.alibaba.csp
sentinel-core
1.8.0
com.congge
api-common
1.0-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.apache.dubbo
dubbo
2.7.1
org.apache.curator
curator-recipes
2.13.0
org.apache.curator
curator-framework
2.13.0
3、api模块主要业务
实体类
@Data
public class User implements Serializable {
private String id;
private String userName;
private String address;
}服务接口
public interface UserService {
User getById(String userId);
}4、provider模块主要业务
provider模块主要提供一个实现api模块服务接口的实现类
import com.congge.entity.User;
import com.congge.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public User getById(String userId) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(userId);
user.setAddress("杭州");
user.setUserName("zhangsan");
return user;
}
}提供dubbo相关的一个xml配置文件
启动类
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource;
@ImportResource("classpath:spring/providers.xml")
@SpringBootApplication
public class ProviderApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ProviderApp.class,args);
}
}5、consumer 模块主要业务
提供一个web接口,然后调用provider中的dubbo服务接口进行调用
import com.congge.entity.User;
import com.congge.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/get")
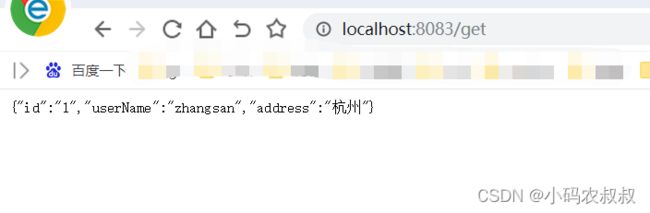
public User getUser(){
return userService.getById("1");
}
}提供dubbo相关的一个xml配置文件
启动类
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource;
@ImportResource("classpath:spring/consumers.xml")
@SpringBootApplication
public class ConsumerApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConsumerApp.class,args);
}
}6、整合测试
启动本地zookeeper服务,再分别启动provider和consumer的服务,通过浏览器调用一下,看到下面的结果后,说明demo搭建完成;
五、通用限流方案之 —— guava
guava是谷歌提供的一款限流SDK组件,使用起来简单灵活,既可以用作web接口的限流,也可以用作dubbo接口的限流,本文以dubbo接口限流为例进行说明,在provider模块新增如下依赖:
com.google.guava
guava
31.0.1-jre
使用guava对dubbo接口进行限流思路
这里提供两种思路供给参考,前提是基于自定义注解
思路1:
- 自定义限流注解;
- 在需要进行限流的dubbo实现类的方法级别上添加自定义注解(对provider来说的);
- 通过一个aop的类,配置切点表达式为自定义注解,在环绕通知(around)中进行限流;
思路2:
- 自定义限流注解;
- 在需要进行限流的dubbo实现类的方法级别上添加自定义注解(对provider来说的);
- 通过前置aop通知或者工程启动加载的时读取自定义限流注解的方法(资源),并配置到容器;
- 通过dubbo的Filter逻辑中匹配特定的服务接口进行限流;
思路1和思路2都可以落地实现,看个人的需求,本文以思路2为例做一下代码层面的实现
1、自定义限流注解
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface LxRateLimit {
//资源名称
String name() default "默认资源";
//限制每秒访问次数,默认为3次
double perSecond() default 1;
/**
* 限流Key类型
* 自定义根据业务唯一码来限制需要在请求参数中添加 String limitKeyValue
*/
LimitKeyTypeEnum limitKeyType() default LimitKeyTypeEnum.IPADDR;
}2、限流工具类
该类用于提供一个全局使用的限流工具类,即被限流的资源使用到的工具类;
public class LxRateLimitUtil {
private static int PER_SECOND_COUNT = 2;
public static LoadingCache caches = CacheBuilder.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000)
.expireAfterWrite(1, TimeUnit.DAYS)
.build(new CacheLoader() {
@Override
public RateLimiter load(String key) throws Exception {
// 新的IP初始化 (限流每秒两个令牌响应)
return RateLimiter.create(PER_SECOND_COUNT);
}
});
} 3、自定义加载自定义限流注解的类
在实际开发中,扫描的包路径可以根据自己的实际情况指定;
import org.reflections.Reflections;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
@Component
public class InitTargetRatelimitClassMethods {
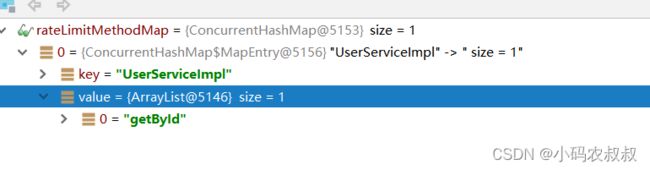
public static final Map> rateLimitMethodMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static final String SCAN_PACKAGES = "com.congge.service.impl";
@PostConstruct
public void initLoadConfig(){
handleInitRateLimitAnnoation();
}
public void handleInitRateLimitAnnoation() {
Reflections reflections = new Reflections(SCAN_PACKAGES);
Set> restController = reflections.getTypesAnnotatedWith(Service.class);
restController.forEach(aClass -> {
String className = aClass.getName();
List fullNames = Arrays.asList(className.split("\\."));
String mapKey = fullNames.get(fullNames.size()-1);
Method[] methods = aClass.getDeclaredMethods();
List targetMethodNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++){
if(methods[i].isAnnotationPresent(LxRateLimit.class)){
targetMethodNames.add(methods[i].getName());
}
}
if(!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(targetMethodNames)){
rateLimitMethodMap.put(mapKey,targetMethodNames);
}
});
}
} 集合中的数据结构如下:
4、自定义dubbofilter,在自定义filter中进行限流
import com.congge.ratelimit.InitTargetRatelimitClassMethods;
import com.congge.ratelimit.LxRateLimitUtil;
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.RateLimiter;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
@Slf4j
public class DubboAccessFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Class anInterface = invoker.getInterface();
String methodName = invocation.getMethodName();
String remoteAddress = RpcContext.getContext().getRemoteAddressString();
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
doApiAccessLimit(anInterface, methodName, remoteAddress);
return result;
}
private void doApiAccessLimit(Class anInterface, String methodName, String remoteAddress) {
String simpleClassName = anInterface.getName();
List fullNames = Arrays.asList(simpleClassName.split("\\."));
String mapKey = fullNames.get(fullNames.size() - 1) + "Impl";
Map> rateLimitMethodMap = InitTargetRatelimitClassMethods.rateLimitMethodMap;
if (rateLimitMethodMap.containsKey(mapKey) && rateLimitMethodMap.get(mapKey).contains(methodName)) {
String cacheKey = remoteAddress + ":" + simpleClassName + ":" + methodName;
RateLimiter rateLimiter = null;
try {
rateLimiter = LxRateLimitUtil.caches.get(cacheKey);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (!rateLimiter.tryAcquire()) {
throw new RuntimeException("【被限流了】您调用的速度太快了,请慢点操作");
}
}
}
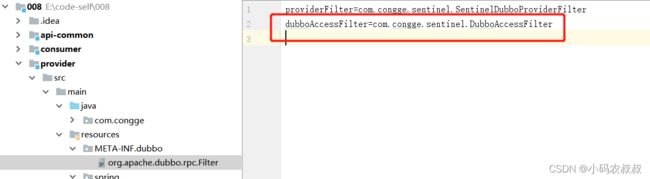
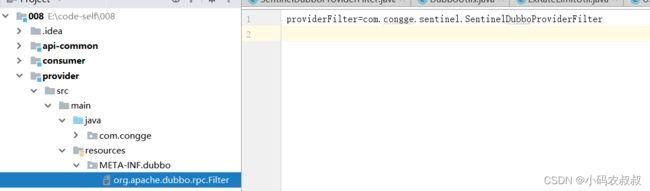
} 然后分别在配置文件中将上述的自定义filter添加到dubbo的spi配置文件中
最好将该filter配置到xml文件中
5、限流业务测试
provider端的工作准备完毕,为了模拟出效果,我们可以手动将QPS的值调到1个,再对消费端的接口做如下改造
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/get")
public User getUser(){
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
userService.getById("1");
}
return userService.getById("1");
}
}再次启动provider和consumer端的服务,浏览器做如下的调用,观察控制台输出效果
当然在实际运用中,消费端可以捕获异常,然后以更友好的方式将结果展现给客户端,对这种实现方式可以优化改进的地方如下:
- 扫描的包路径可以写到配置文件,或者用其他的方式定义;
- 每秒限制的访问次数的值设定可以从配置文件读取,或者用其他方式定义;
六、通用限流方案之 —— Sentinel
sentinel 简介
Sentinel 是面向分布式服务架构的流量控制组件,主要以流量为切入点,从限流、流量整形、熔断降级、系统负载保护、热点防护等多个维度来帮助开发者保障微服务的稳定性。
sentinel属于springcloud-alibaba微服务体系下的一款用于限流,熔断,降级等一体的组件,还提供了dashboard用于对接口资源使用的精准控制,功能强大,简单已用,既可以在整个springcloud-alibaba微服务架构中使用,也可以单独拿来使用,关于单独限流使用时可以参考:java使用sentinel
dubbo整合sentinel限流思路
- 自定义全局的dubbo filter,用于拦截dubbo api被调用时的信息;
- 使用sentinel自定义限流规则;
- 在自定义Filter中加载限流规则,并对dubbo api进行规则校验和限流;
1、自定义dubbo filter
在这段代码中,基本上完成了整合思路中的所有步骤,其实用的就是Sentinel的原生的api对资源进行的限流;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.Entry;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.EntryType;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.SphU;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.Tracer;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.context.ContextUtil;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.log.RecordLog;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.BlockException;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.RuleConstant;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRuleManager;
import com.congge.sentinel.fallback.DubboFallbackRegistry;
import org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.Activate;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Activate(group = "provider")
public class SentinelDubboProviderFilter implements Filter {
public SentinelDubboProviderFilter() {
RecordLog.info("Sentinel Apache Dubbo provider filter initialized");
}
public static void initRule(String resourceName) {
List rules = new ArrayList<>();
FlowRule rule = new FlowRule();
rule.setResource(resourceName);
//使用QPS的方式
rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
rule.setCount(1);
rules.add(rule);
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
String resourceName = DubboUtils.getResourceName(invoker, invocation);
String interfaceName = invoker.getInterface().getName();
//加载定义的限流规则
initRule(resourceName);
// Get origin caller.
String application = DubboUtils.getApplication(invocation, "");
Entry interfaceEntry = null;
Entry methodEntry = null;
try {
ContextUtil.enter(resourceName, application);
interfaceEntry = SphU.entry(interfaceName, EntryType.IN);
methodEntry = SphU.entry(resourceName, EntryType.IN, 1, invocation.getArguments());
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
if (result.hasException()) {
Throwable e = result.getException();
// Record common exception.
Tracer.traceEntry(e, interfaceEntry);
Tracer.traceEntry(e, methodEntry);
}
return result;
} catch (BlockException e) {
return DubboFallbackRegistry.getProviderFallback().handle(invoker, invocation, e);
} catch (RpcException e) {
Tracer.traceEntry(e, interfaceEntry);
Tracer.traceEntry(e, methodEntry);
throw e;
} finally {
if (methodEntry != null) {
methodEntry.exit(1, invocation.getArguments());
}
if (interfaceEntry != null) {
interfaceEntry.exit();
}
ContextUtil.exit();
}
}
} DubboUtils
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invocation;
import org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker;
public class DubboUtils {
public static final String SENTINEL_DUBBO_APPLICATION_KEY = "dubboApplication";
public static String getApplication(Invocation invocation, String defaultValue) {
if (invocation == null || invocation.getAttachments() == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bad invocation instance");
}
return invocation.getAttachment(SENTINEL_DUBBO_APPLICATION_KEY, defaultValue);
}
public static String getResourceName(Invoker invoker, Invocation invocation) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(64);
buf.append(invoker.getInterface().getName())
.append(":")
.append(invocation.getMethodName())
.append("(");
boolean isFirst = true;
for (Class clazz : invocation.getParameterTypes()) {
if (!isFirst) {
buf.append(",");
}
buf.append(clazz.getName());
isFirst = false;
}
buf.append(")");
return buf.toString();
}
private DubboUtils() {}
}
2、将自定义的filter配置到spi以及xml文件
3、整合测试
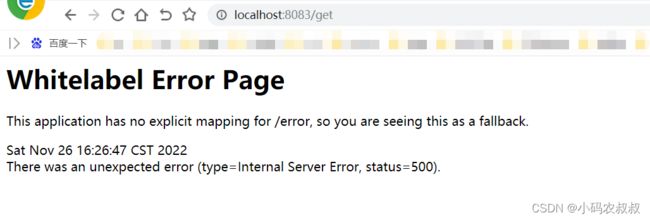
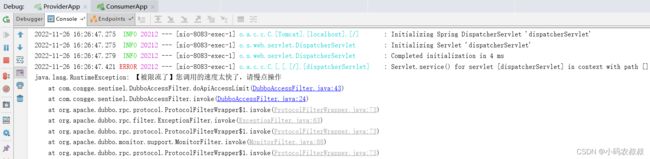
为了模拟出效果,将规则方法在的QPS调整为1,然后分别启动provider和consumer服务,浏览器做如下调用,观察到下面的效果,说明接口被限流了;
关于该实现方案的优化改进
尽管也能实现限流,但发现这个限流是针对所有的dubbo api,显然这个范围有点大了,可以在filter 中,对限流的接口来源做一下缩小,仍然可以利用第一个思路中,针对特定的那些添加了限流注解的api接口进行限流即可,有兴趣的同学可自行研究下,限于篇幅,这里就不再过多赘述了。