Python:使用灰色预测对数据进行预测
灰色预测代码
# condig:utf-8
import torch as th
import numpy as np
class GM():
def __init__(self):
# 判断是否可用 gpu 编程 , 大量级计算使用GPU
self._is_gpu = False # th.cuda.is_available()
def fit(self,dt:list or np.ndarray):
self._df :th.Tensor = th.from_numpy(np.array(dt,dtype=np.float32))
if self._is_gpu:
self._df.cuda()
self._n:int = len(self._df)
self._x,self._max_value = self._sigmod(self._df)
z:th.Tensor = self._next_to_mean(th.cumsum(self._x,dim=0))
self.coef:th.Tensor = self._coefficient(self._x, z)
del z
self._x0:th.Tensor = self._x[0]
self._pre:th.Tensor = self._pred()
# 归一化
def _sigmod(self,x:th.Tensor):
_maxv:th.Tensor = th.max(x)
return th.div(x,_maxv),_maxv
# 计算紧邻均值数列
def _next_to_mean(self, x_1:th.Tensor):
z:th.Tensor = th.zeros(self._n-1)
if self._is_gpu:
z.cuda()
for i in range(1,self._n): # 下标从0开始,取不到最大值
z[i - 1] = 0.5 * x_1[i] + 0.5 * x_1[i - 1]
return z
# 计算系数 a,b
def _coefficient(self,x:th.Tensor,z:th.Tensor):
B:th.Tensor = th.stack((-1*z, th.ones(self._n-1)),dim=1)
Y:th.Tensor = th.tensor(x[1:],dtype=th.float32).reshape((-1,1))
if self._is_gpu:
B.cuda()
Y.cuda()
# 返回的是a和b的向量转置,第一个是a 第二个是b;
return th.matmul(th.matmul(th.inverse(th.matmul(B.t(), B)), B.t()),Y)
def _pred(self,start:int=1,end:int=0):
les:int = self._n+end
resut:th.Tensor = th.zeros(les)
if self._is_gpu:
resut.cuda()
resut[0] = self._x0
for i in range(start,les):
resut[i] = (self._x0 - (self.coef[1] / self.coef[0])) * \
(1 - th.exp(self.coef[0])) * th.exp(-1 * self.coef[0] * (i))
del les
return resut
# 计算绝对误差
def confidence(self):
return round((th.sum(th.abs(th.div((self._x-self._pre),self._x)))/self._n).item(),4)
# 预测个数,默认个数大于等于0,
def predict(self,m:int=1,decimals:int=4):
y_pred:th.Tensor = th.mul(self._pre,self._max_value)
y_pred_ = th.zeros(1)
if m<0:
return "预测个数需大于等于0"
elif m>0:
y_pred_:th.Tensor = self._pred(self._n,m)[-m:].mul(self._max_value)
else:
if self._is_gpu:
return list(map(lambda _: round(_, decimals), y_pred.cpu().numpy().tolist()))
else:
return list(map(lambda _:round(_,decimals),y_pred.numpy().tolist()))
# cat 拼接 0 x水平拼接,1y垂直拼接
result:th.Tensor = th.cat((y_pred,y_pred_),dim=0)
del y_pred,y_pred_
if self._is_gpu:
return list(map(lambda _: round(_, decimals), result.cpu().numpy().tolist()))
return list(map(lambda _:round(_,decimals),result.numpy().tolist()))
if __name__=="__main__":
ls = np.arange(91,100,2)
print(type(ls))
# ls = list(range(91, 100, 2))
gm = GM()
gm.fit(ls)
print(gm.confidence())
print(ls)
print(gm.predict(m=2))
经调试,建议代码中
“Y:th.Tensor = th.tensor(x[1:],dtype=th.float32).reshape((-1,1))”
改为
“Y: th.Tensor = th.as_tensor(x[1:], dtype=th.float32).reshape((-1, 1))”
例子
我们有以下两个数据(2017年全年数据):
data1.csv
data2.csv
按机器ID分类,将其中商品为饮料和商品为非饮料的按月份提取出来,然后分别预测其在2018年1月的交易额。
代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import torch as th
def everyone(word1):
data1 = pd.read_csv("../data/task1-1{}.csv".format(word1), encoding="gbk")
data2 = pd.read_csv("../data/data2.csv", encoding="gbk")
data2 = np.array(data2)
data1['date'] = pd.DatetimeIndex(data1['支付时间'])
def everymonth(word2):
newData = data1[data1['date'].dt.month == word2]
select = []
for i1 in newData['商品']:
for i2 in data2:
if (i1 == i2[0]):
select.append(i2[1])
newData = pd.DataFrame(newData)
newData['种类'] = select
data = np.array(newData)
drink = 0
noDrink = 0
for k1 in data:
# print(k1[-1])
if(k1[-1] == "饮料"):
drink = drink + k1[3]
else:
noDrink = noDrink + k1[3]
return drink,noDrink
res = []
for i in range(1,13):
res.append(everymonth(i))
return res
def getMouth(word):
drink = []
noDrink = []
for i in range(0,12):
drink.append(word[i][0])
noDrink.append(word[i][1])
return drink,noDrink
class GM():
def __init__(self):
# 判断是否可用 gpu 编程 , 大量级计算使用GPU
self._is_gpu = False # th.cuda.is_available()
def fit(self, dt: list or np.ndarray):
self._df: th.Tensor = th.from_numpy(np.array(dt, dtype=np.float32))
if self._is_gpu:
self._df.cuda()
self._n: int = len(self._df)
self._x, self._max_value = self._sigmod(self._df)
z: th.Tensor = self._next_to_mean(th.cumsum(self._x, dim=0))
self.coef: th.Tensor = self._coefficient(self._x, z)
del z
self._x0: th.Tensor = self._x[0]
self._pre: th.Tensor = self._pred()
# 归一化
def _sigmod(self, x: th.Tensor):
_maxv: th.Tensor = th.max(x)
return th.div(x, _maxv), _maxv
# 计算紧邻均值数列
def _next_to_mean(self, x_1: th.Tensor):
z: th.Tensor = th.zeros(self._n - 1)
if self._is_gpu:
z.cuda()
for i in range(1, self._n): # 下标从0开始,取不到最大值
z[i - 1] = 0.5 * x_1[i] + 0.5 * x_1[i - 1]
return z
# 计算系数 a,b
def _coefficient(self, x: th.Tensor, z: th.Tensor):
B: th.Tensor = th.stack((-1 * z, th.ones(self._n - 1)), dim=1)
Y: th.Tensor = th.as_tensor(x[1:], dtype=th.float32).reshape((-1, 1))
if self._is_gpu:
B.cuda()
Y.cuda()
# 返回的是a和b的向量转置,第一个是a 第二个是b;
return th.matmul(th.matmul(th.inverse(th.matmul(B.t(), B)), B.t()), Y)
def _pred(self, start: int = 1, end: int = 0):
les: int = self._n + end
resut: th.Tensor = th.zeros(les)
if self._is_gpu:
resut.cuda()
resut[0] = self._x0
for i in range(start, les):
resut[i] = (self._x0 - (self.coef[1] / self.coef[0])) * \
(1 - th.exp(self.coef[0])) * th.exp(-1 * self.coef[0] * (i))
del les
return resut
# 计算绝对误差
def confidence(self):
return round((th.sum(th.abs(th.div((self._x - self._pre), self._x))) / self._n).item(), 4)
# 预测个数,默认个数大于等于0,
def predict(self, m: int = 1, decimals: int = 4):
y_pred: th.Tensor = th.mul(self._pre, self._max_value)
y_pred_ = th.zeros(1)
if m < 0:
return "预测个数需大于等于0"
elif m > 0:
y_pred_: th.Tensor = self._pred(self._n, m)[-m:].mul(self._max_value)
else:
if self._is_gpu:
return list(map(lambda _: round(_, decimals), y_pred.cpu().numpy().tolist()))
else:
return list(map(lambda _: round(_, decimals), y_pred.numpy().tolist()))
# cat 拼接 0 x水平拼接,1y垂直拼接
result: th.Tensor = th.cat((y_pred, y_pred_), dim=0)
del y_pred, y_pred_
if self._is_gpu:
return list(map(lambda _: round(_, decimals), result.cpu().numpy().tolist()))
return list(map(lambda _: round(_, decimals), result.numpy().tolist()))
def fit(word):
ls = word[0]
ls2 = word[1]
gm = GM()
gm.fit(ls)
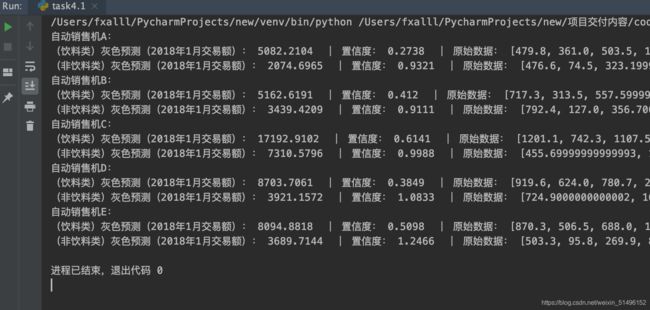
print('(饮料类)灰色预测(2018年1月交易额):',gm.predict(m=1)[len(ls)],' | 置信度:',gm.confidence(),' | 原始数据:',ls)
gm.fit(ls2)
print('(非饮料类)灰色预测(2018年1月交易额):',gm.predict(m=1)[len(ls)],' | 置信度:',gm.confidence(),' | 原始数据:',ls2)
def getRes(word):
res = everyone(word)
print('自动销售机{}:'.format(word))
fit(getMouth(res))
if __name__ == '__main__':
type = ['A','B','C','D','E']
for i in range(0,5):
getRes(type[i])