SfM两视图三维点云重建--【VS2015+OpenCV3.4+PCL1.8】
概述
视觉三维重建,是指使用相机采集的图片、根据相关知识推导目标物体三维信息的过程。这里借鉴《视觉SLAM14讲》中的分类方法,将视觉三维重建分为基于特征点和非提取特征点的重建。本文旨在使用基于特征点的重建方法完成相邻两张图片间的三维重建。
步骤
基于特征点的视觉三维重建方法主要包括如下流程:
- 提取单张图片特征点;
- 多张图片间特征点的匹配;
- 利用对极几何约束,使用SfM恢复两相机间的三维变换关系;
- 使用三角量测法(或称三角化法),重构二维图像对应点的三维点信息。
按照我的理解,上述流程可以概括为如下两部分:求解相机内外参、三维重建。
- 求解相机内外参:
提取特征点并进行匹配只是为了组成匹配对,以方便计算基本矩阵F/本质矩阵E(对极几何约束),而计算出矩阵E或F后,即可进行SVD分解得到两相机间的三维变换关系(旋转矩阵R、平移矩阵t)。至此,是为求解相机内外参的过程。当然,也可以使用相机标定的方式获取相机内外参数,但多张重建会比较繁琐。 - 三维重建
在已知两图片间变换矩阵的情况下,就可以使用三角化进行三维重建了。重建后的三维点是以第一张图片对应的相机坐标系为世界坐标系。
这里只是进行简单的介绍,并不涉及复杂的原理,有兴趣的可参考14讲中的内容,网上也有许多优秀博文可供参考。
代码
环境:Win10+VS2015+OpenCV3.4+PCL1.8
#include 结果
使用的原图:
重建结果:
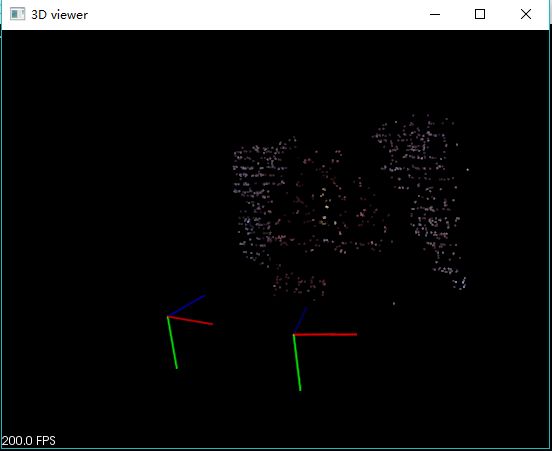
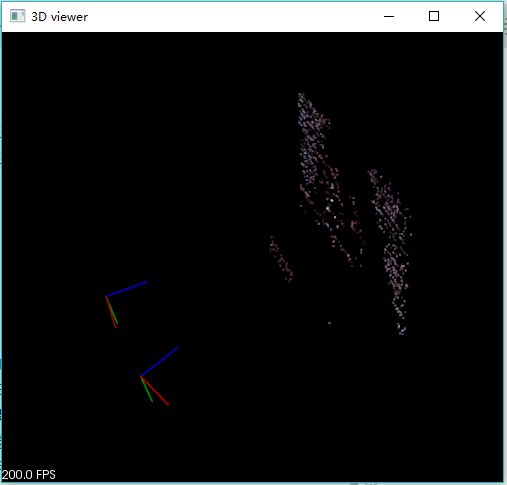
注意事项
- 使用任意两张相邻图片进行重建时,内参数K略有不同,但不影响重建效果。但要尽量选择相邻的图片,否则可能会因为匹配的特征点较少而重建失败。
- 本文代码在分解本质矩阵E时,使用的是recoverPose(),当然也可以使用SVD分解本质矩阵。但是使用SVD分解会得到4个可能的解,只有选择正确的R、T才能完成重建,否则归一化的坐标之后无法正常显示;而使用recoverPose则能直接得到正确的R、t。
// 使用SVD分解本质矩阵E,
// 但要确认使用4个解中的哪个正确:把任意一点代入四种解中,检测该点在两个相机下的深度,当两相机下深度值均为正时的解,即为正确的解--《视觉SLAM14讲P148》
SVD svd(E, SVD::MODIFY_A);
Matx33d W(0, -1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1); // equation $9.13 page 258(MVG)
Matx33d Wt(0, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1); // W的转置矩阵
// SVD分解的4个解
Mat_<double> R1 = svd.u * Mat(W) * svd.vt; // equation $9.14 page 258,SVD分解:R=UW(Vt)或R=U(Wt)(Vt)
Mat_<double> R2 = svd.u * Mat(Wt) * svd.vt;
Mat_<double> t1 = svd.u.col(2); // t = U(0, 0, 1).transpose() = u3 page 259
Mat_<double> t2 = -svd.u.col(2);
- 在使用triangulatePoints()进行三维重建时,有两种归一化方式,即归一化变换矩阵和归一化点坐标,具体操作方法见代码。这两种方式本质是相同的,只不过是归一化的先后顺序而已。
参考
- OpenCV实现SfM(二):双目三维重建
- 对极几何-本质矩阵-基本矩阵 --推导本质矩阵时,在左叉乘T之后,左点乘的应该是P’的转置,而不是P’。
- 完整工程下载:SfM稀疏三维点云重建【VS2015+OpenCV3.4+PLC1.8】–完整工程文件