PyTorch中torch.gather()函数
一. torch.gather()函数
官方文档:torch.gather函数,定义:从原tensor中获取指定dim和指定index的数据。
看到这个核心定义,我们很容易想到gather()的基本想法其实就类似从完整数据中按索引取值般简单,比如下面从列表中按索引取值:
lst = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
value = lst[2] # value = 3
value = lst[2:4] # value = [3, 4]
上面的取值例子是取单个值或具有逻辑顺序序列的例子,而对于深度学习常用的批量tensor数据来说,我们的需求可能是选取其中多个且乱序的值,此时gather()就是一个很好的tool,它可以帮助我们从批量tensor中取出指定乱序索引下的数据,因此其用途如下:
用途:方便从批量tensor中获取指定索引下的数据,该索引是高度自定义化的,可乱序的。
二. 举例
找个3x3的二维矩阵做个实验:
import torch
tensor_0 = torch.arange(3, 12).view(3, 3)
print(tensor_0)
输出结果:
tensor([[ 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11]])
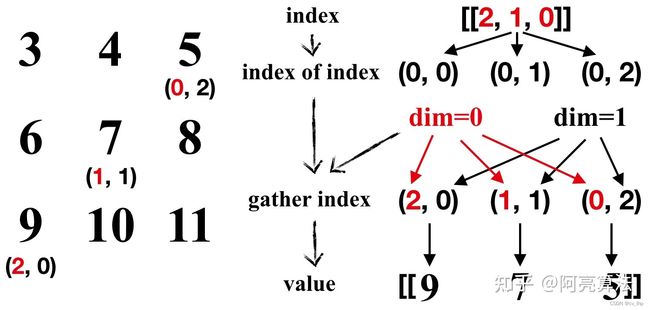
2.1 输入行向量index,并替换行索引(dim=0)
index = torch.tensor([[2, 1, 0]])
tensor_1 = tensor_0.gather(0, index)
print(tensor_1)
输出结果如下:
tensor([[9, 7, 5]])
2.2 输入行向量index,并替换列索引(dim=1)
index = torch.tensor([[2, 1, 0]])
tensor_1 = tensor_0.gather(1, index)
print(tensor_1)
输出结果
tensor([[5, 4, 3]])
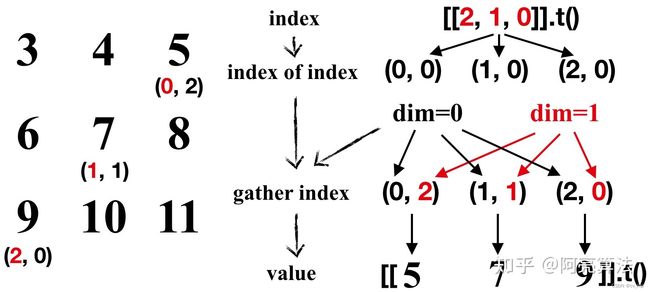
2.3 输入列向量index,并替换列索引(dim=1)
index = torch.tensor([[2, 1, 0]]).t()
tensor_1 = tensor_0.gather(1, index)
print(tensor_1)
输出结果如下:
tensor([[5],
[7],
[9]])
2.4 输入二维矩阵index,并替换列索引(dim=1)
index = torch.tensor([[0, 2],
[1, 2]])
tensor_1 = tensor_0.gather(1, index)
print(tensor_1)
输出结果:
tensor([[3, 5],
[7, 8]])
过程如上
三. 总结
从上面例子,可以归纳出torch.gather()的使用要点:
- 输入index的shape等于输出value的shape
- 输入index的索引值仅替换该index中对应dim的index值
- 最终输出为替换index后在原tensor中的值
四. 一句话简单理解
torch.gather的理解:
index=[ [x1,x2,x2],
[y1,y2,y2],
[z1,z2,z3] ]
如果dim=0
填入方式
[ [(x1,0),(x2,1),(x3,2)]
[(y1,0),(y2,1),(y3,2)]
[(z1,0),(z2,1),(z3,2)] ]
如果dim=1
[ [(0,x1),(0,x2),(0,x3)]
[(1,y1),(1,y2),(1,y3)]
[(2,z1),(2,z2),(2,z3)] ]
五. 参考链接
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/352877584